Bacitracin ZincCAS# 1405-89-6 |
- CEP-32496
Catalog No.:BCC1079
CAS No.:1188910-76-0
- Sorafenib
Catalog No.:BCN2174
CAS No.:284461-73-0
- Vemurafenib (PLX4032, RG7204)
Catalog No.:BCC1269
CAS No.:918504-65-1
- BRAF inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1436
CAS No.:918505-61-0
- PLX-4720
Catalog No.:BCC1280
CAS No.:918505-84-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1405-89-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3083711 | Appearance | Powder |
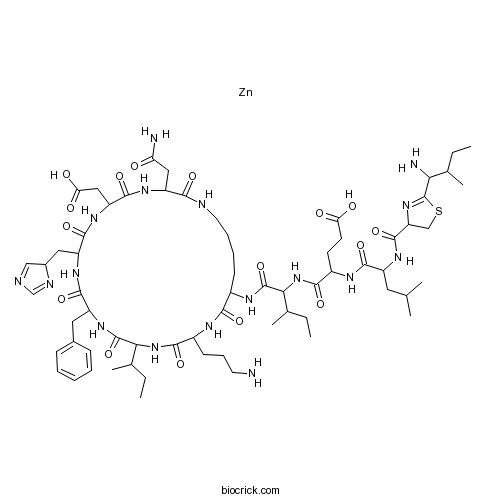
| Formula | C66H103N17O16SZn | M.Wt | 1488.09 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Bacitracin zinc salt; Zinc bacitracin | ||
| Solubility | 1M HCl : 50 mg/mL (33.65 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[[2-[[2-(1-amino-2-methylbutyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-5-[[1-[[3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-18-(3-aminopropyl)-12-benzyl-15-butan-2-yl-6-(carboxymethyl)-9-(4H-imidazol-4-ylmethyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-1,4,7,10,13,16,19-heptazacyclopentacos-21-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid;zinc | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C1C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NCCCCC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N1)CCCN)NC(=O)C(C(C)CC)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C2CSC(=N2)C(C(C)CC)N)CC(=O)N)CC(=O)O)CC3C=NC=N3)CC4=CC=CC=C4.[Zn] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QSNOBVJFKSQBBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C66H103N17O16S.Zn/c1-9-35(6)52(69)66-81-48(32-100-66)63(97)76-43(26-34(4)5)59(93)74-42(22-23-50(85)86)58(92)83-53(36(7)10-2)64(98)75-40-20-15-16-25-71-55(89)46(29-49(68)84)78-62(96)47(30-51(87)88)79-61(95)45(28-39-31-70-33-72-39)77-60(94)44(27-38-18-13-12-14-19-38)80-65(99)54(37(8)11-3)82-57(91)41(21-17-24-67)73-56(40)90;/h12-14,18-19,31,33-37,39-48,52-54H,9-11,15-17,20-30,32,67,69H2,1-8H3,(H2,68,84)(H,71,89)(H,73,90)(H,74,93)(H,75,98)(H,76,97)(H,77,94)(H,78,96)(H,79,95)(H,80,99)(H,82,91)(H,83,92)(H,85,86)(H,87,88); | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bacitracin Zinc is a dephosphorylation of the C55-isoprenyl pyrophosphate interference for inhibition of cleavage of Tyr from Met-enkephalin with IC50 of 10 μM.
Target: Antibacterial
Bacitracin is a mixture of related cyclic polypeptides produced by organisms of the licheniformis group of Bacillus subtilis var Tracy. Its unique name derives from the fact that the bacillus producing it was first isolated in 1943 from a knee scrape from a girl named Margaret Tracy. As a toxic and difficult-to-use antibiotic, bacitracin doesn't work well orally. However, it is very effective topically. Bacitracin is synthesised via the so-called nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), which means that ribosomes are not involved in its synthesis [1, 2]. References: | |||||

Bacitracin Zinc Dilution Calculator

Bacitracin Zinc Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bacitracin Zinc is a dephosphorylation of the C55-isoprenyl pyrophosphate interference for inhibition of cleavage of Tyr from Met-enkephalin with IC50 of 10 μM.A complex of cyclic peptide antibiotics produced by the Tracy-I strain of Bacillus subtilis. The commercial preparation is a mixture of at least nine bacitracins with bacitracin A as the major constituent. It is used topically to treat open infections such as infected eczema and infected dermal ulcers.
- Bacitracin
Catalog No.:BCC4632
CAS No.:1405-87-4
- Glycyrrhizic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5941
CAS No.:1405-86-3
- Tylosin phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC5551
CAS No.:1405-53-4
- Gentamycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1203
CAS No.:1405-41-0
- Capreomycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4644
CAS No.:1405-37-4
- Neomycin sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4682
CAS No.:1405-10-3
- Olopatadine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4545
CAS No.:140462-76-6
- Heteroclitin B
Catalog No.:BCN3745
CAS No.:140461-47-8
- Heteroclitin C
Catalog No.:BCN3632
CAS No.:140460-42-0
- Ergosterol peroxide glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6222
CAS No.:140447-22-9
- 11-Hydroxyjasmonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6221
CAS No.:140447-14-9
- GSK 2830371
Catalog No.:BCC4179
CAS No.:1404456-53-6
- 1,2-Methylenedioxy-3,10,11-trimethoxynoraporphine
Catalog No.:BCN1573
CAS No.:14050-90-9
- Methyl chanofruticosinate
Catalog No.:BCN6223
CAS No.:14050-92-1
- Cassipourine
Catalog No.:BCN2154
CAS No.:14051-10-6
- 4-Ethylsyringol
Catalog No.:BCN3541
CAS No.:14059-92-8
- 12-Hydroxyjasmonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6224
CAS No.:140631-27-2
- Kadsurenin D
Catalog No.:BCN6603
CAS No.:140669-89-2
- Levatin
Catalog No.:BCN2531
CAS No.:140670-84-4
- 1-Deoxydihydroceramide-1-sulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4964
CAS No.:1407-03-0
- 4-Aza-5androstan-1-ene- 3-one-17carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8693
CAS No.:140700-63-6
- Scandine Nb-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN7504
CAS No.:140701-69-5
- PF 06465469
Catalog No.:BCC6268
CAS No.:1407966-77-1
- JNK-IN-7
Catalog No.:BCC1672
CAS No.:1408064-71-0
Effect of zinc bacitracin and phytase on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass and meat traits of broilers.[Pubmed:26608478]
J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2016 Jun;100(3):485-91.
A total of 336 one-day-old Hubbard broiler chickens were randomly distributed among 8 groups, each containing six replicates (7 chickens/replicate). From 1 to 40 days of age, the groups fed the same starter, grower and finisher diets. The control group was unsupplemented; zinc bacitracin (ZnB) group received the antibiotic at 0.5 g/kg; fungal phytase (FP) groups received 250, 500 and 1000 U/kg diet of Aspergillus niger phytase (FP_250, FP_500 and FP_1000 groups), respectively; bacterial phyatse (BP) groups received 250, 500 and 1000 U/kg diet of Escherichia coli phytase (BP_250EP, BP_500EP and BP_1000EP groups) respectively. Considering the whole experimental period, body weight gain was unaffected by ZnB and different concentrations of bacterial and fungal phytase; however, the feed conversion ratio of the group fed a diet supplemented with 500 U of BP was better (p < 0.01) than those fed with a diet supplemented with 500 U of FP. BP_250 group had a higher (p < 0.05) apparent digestibility of ether extract compared to FP_250 group. In conclusion, bacterial phytase at 500 U may enhance performance of broiler chickens fed during days 1-40 of age and yield similar growth performance and economic efficiency to those of eB-supplemented groups.
Multi-year and short-term responses of soil ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes to zinc bacitracin, monensin, and ivermectin, singly or in combination.[Pubmed:25502914]
Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015 Mar;34(3):618-25.
A field experiment was initiated whereby a series of replicated plots received annual applications of ivermectin, monensin, and zinc bacitracin, either singly or in a mixture. Pharmaceuticals were added at concentrations of 0.1 mg/kg soil or 10 mg/kg soil. The authors collected soil samples in 2013, before and after the fourth annual application of pharmaceuticals. In addition, a 30-d laboratory experiment was undertaken with the same soil and same pharmaceuticals, but at concentrations of 100 mg/kg soil. The impact of the pharmaceuticals on nitrification rates, on the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), and on the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) was assessed. None of the pharmaceuticals at 0.1 mg/kg had any effect on nitrification. Referenced to control soil, nitrification was accelerated in soil exposed to 100 mg/kg zinc bacitracin or 10 mg/kg of the pharmaceutical mixture, but none of the treatments inhibited nitrification. Neither AOB abundance nor AOA abundance was affected by the pharmaceuticals at 0.1 mg/kg. At 10 mg/kg, monensin, zinc bacitracin, and a mixture of all 3 pharmaceuticals suppressed the abundance of AOB, and zinc bacitracin and the mixture increased AOA abundance. The decrease in AOB abundance and increase in AOA abundance when exposed to 10 mg/kg soil suggests that AOB are more sensitive to these chemicals and that AOA populations can expand to occupy the partially vacated niche.
Yellow hair following sequential application of bacitracin zinc and selenium sulfide: Report of acquired xanthotrichosis and review of yellow hair discoloration.[Pubmed:27617598]
Dermatol Online J. 2016 Jun 15;22(6).
BackgroundAcquired yellow hair (xanthotrichosis) can result from the deposition of pigmented compounds on the hair shaft or from chemical modification of hair pigment and protein molecules.PurposeA white-haired 77-year-old woman who developed xanthotrichosis of her scalp hair following the sequential application of Bacitracin Zinc ointment and selenium sulfide 2.5% lotion is described and the causes of yellow hair discoloration are reviewed.Materials and methodsThe clinical features of a woman with acquired yellow hair discoloration are presented. Using PubMed and Google Scholar, the following terms were searched and relevant citations were assessed: Bacitracin Zinc, hair discoloration, selenium sulfide, xanthotrichosis, and yellow hair.ResultsYellow hair was observed on the scalp in areas treated with the following regimen: prior to bedtime, several areas of the scalp were treated with a single application of Bacitracin Zinc ointment. The next morning, selenium sulfide 2.5% lotion was applied and then rinsed from the scalp during showering. Yellow hair discoloration was apparent in co-treated areas immediately following rinsing; the discoloration gradually faded over 2-5 days with regular shampooing.ConclusionsAcquired yellow hair shaft discoloration has been reported secondary to multiple etiologies, including environmental and occupational exposures, iatrogenic causes (including topical and systemic drugs) and protein-calorie malnutrition. To this list, we add yellow discoloration of white scalp hair due to application of selenium sulfide following topical use of Bacitracin Zinc in the affected areas as an unexpected adverse effect that may occur in individuals with white hair.
Understanding the mechanisms of zinc bacitracin and avilamycin on animal production: linking gut microbiota and growth performance in chickens.[Pubmed:28243710]
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;101(11):4547-4559.
Unravelling the mechanisms of how antibiotics influence growth performance through changes in gut microbiota can lead to the identification of highly productive microbiota in animal production. Here we investigated the effect of zinc bacitracin and avilamycin on growth performance and caecal microbiota in chickens and analysed associations between individual bacteria and growth performance. Two trials were undertaken; each used 96 individually caged 15-day-old Cobb broilers. Trial 1 had a control group (n = 48) and a zinc bacitracin (50 ppm) treatment group (n = 48). Trial 2 had a control group (n = 48) and an avilamycin (15 ppm) treatment group (n = 48). Chicken growth performance was evaluated over a 10-day period, and caecal microbiota was characterised by sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA gene amplicons. Avilamycin produced no effect on growth performance and exhibited little significant disturbance of the microbiota structure. However, zinc bacitracin reduced the feed conversion ratio (FCR) in treated birds, changed the composition and increased the diversity of their caecal microbiota by reducing dominant species. Avilamycin only produced minor reductions in the abundance of two microbial taxa, whereas zinc bacitracin produced relatively large shifts in a number of taxa, primarily Lactobacillus species. Also, a number of phylotypes closely related to lactobacilli species were positively or negatively correlated with FCR values, suggesting contrasting effects of Lactobacillus spp. on chicken growth performance. By harnessing such bacteria, it may be possible to develop high-productivity strategies in poultry that rely on the use of probiotics and less on in-feed antibiotics.


