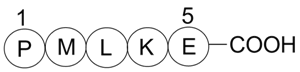
Bax inhibitor peptide P5Bax inhibitor CAS# 579492-83-4 |
- Bavisant dihydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1404
CAS No.:1103522-80-0
- Lidocaine
Catalog No.:BCC1084
CAS No.:137-58-6
- Mianserin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1114
CAS No.:21535-47-7
- Loratadine
Catalog No.:BCC1262
CAS No.:79794-75-5
- Bavisant dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1403
CAS No.:929622-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 579492-83-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10218792 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H48N6O8S | M.Wt | 616.77 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >61.7mg/mL in DMSO or water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-4-methyl-2-[[(2S)-4-methylsulfanyl-2-[[(2S)-pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]pentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C1CCCN1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GAQGZEPUTWPXOG-SXYSDOLCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H48N6O8S/c1-16(2)15-21(33-25(38)19(11-14-42-3)31-23(36)17-8-6-13-29-17)26(39)30-18(7-4-5-12-28)24(37)32-20(27(40)41)9-10-22(34)35/h16-21,29H,4-15,28H2,1-3H3,(H,30,39)(H,31,36)(H,32,37)(H,33,38)(H,34,35)(H,40,41)/t17-,18-,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Originally reported to be a cell-permeable synthetic peptide inhibitor of Bax that blocks apoptosis. Also available: Bax inhibitor peptide V5 and Negative control . |

Bax inhibitor peptide P5 Dilution Calculator

Bax inhibitor peptide P5 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bax inhibitor peptide P5 (BIP P5) is a peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria [1].
Bax is a pro-apoptotic member of Bcl-2 family proteins and plays an important role in mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Bax stays in the cytosol and transfers into mitochondria after apoptotic stimuli [1].
BIP P5 is a membrane-permeable peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria. In HeLa cells, BIP P5 protected cells from UVC- and STS-induced apoptosis. In U87-MG glioma cells, MCF-7 breast cancer cells and LNCaP prostate cancer cells, BIP P5 also inhibited apoptosis induced by anti-cancer drugs cisplatin, etoposide and doxorubicin. While BIP P5 did not suppress UVC- or STS-induced apoptosis in Bax-deficient cells (DU145), which suggested BIP P5 only suppressed Bax-mediated apoptosis. The caspase activation and the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria triggered by apoptotic stimuli were also significantly inhibited by BIP P5. BIP P5 inhibited the interaction of Ku70 and endogenous Bax in a dose-dependent way [1].
Reference:
[1]. Sawada M, Hayes P, Matsuyama S. Cytoprotective membrane-permeable peptides designed from the Bax-binding domain of Ku70. Nat Cell Biol, 2003, 5(4): 352-357.
- Bax inhibitor peptide V5
Catalog No.:BCC2394
CAS No.:579492-81-2
- Officinalisinin I
Catalog No.:BCN2825
CAS No.:57944-18-0
- L(+)-Asparagine Monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8332
CAS No.:5794-13-8
- Z-Cys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2784
CAS No.:57912-35-3
- Corynoxidine
Catalog No.:BCN6798
CAS No.:57906-85-1
- 19-Nor-4-hydroxyabieta-8,11,13-trien-7-one
Catalog No.:BCN1411
CAS No.:57906-31-7
- o-Anisic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9108
CAS No.:579-75-9
- Lobelanine
Catalog No.:BCN2156
CAS No.:579-21-5
- Oligomycin A
Catalog No.:BCC2530
CAS No.:579-13-5
- Myrianthic acid 3,23-acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN7517
CAS No.:578710-52-8
- Clozapine
Catalog No.:BCC5037
CAS No.:5786-21-0
- Idarubicin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1194
CAS No.:57852-57-0
- Caffeine
Catalog No.:BCN5807
CAS No.:58-08-2
- Pyrimethamine
Catalog No.:BCC2307
CAS No.:58-14-0
- Aminophenazone
Catalog No.:BCC8815
CAS No.:58-15-1
- Methyltestosterone
Catalog No.:BCC9045
CAS No.:58-18-4
- Testosterone cypionate
Catalog No.:BCC9167
CAS No.:58-20-8
- Testosterone
Catalog No.:BCN2193
CAS No.:58-22-0
- Menadione
Catalog No.:BCN8351
CAS No.:58-27-5
- Desipramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7553
CAS No.:58-28-6
- Promethazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5480
CAS No.:58-33-3
- Prochlorperazine
Catalog No.:BCC3846
CAS No.:58-38-8
- Tetrabenazine
Catalog No.:BCC5277
CAS No.:58-46-8
- Theophylline
Catalog No.:BCN1258
CAS No.:58-55-9
Mitochondrial regulation of insect cell apoptosis: evidence for permeability transition pore-independent cytochrome-c release in the Lepidopteran Sf9 cells.[Pubmed:19146980]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;41(6):1430-40.
Role of cytochrome-c in insect cell apoptosis is highly controversial, with many earlier reports suggesting lack of involvement of mitochondrial factors in Drosophila while more recent studies have indicated otherwise, thus warranting more in-depth studies of insect cell apoptosis. In the present study, we investigated mitochondrial involvement during actinomycin-D induced apoptosis in Sf9 Lepidopteran cells. Cytochrome-c was released from mitochondria very early during apoptosis, and was preceded quickly by ROS generation and cardiolipin peroxidation. Albeit cytochrome-c release and apoptosis induction were inhibited by bongkrkicacid (BKA) it appears that the release is independent of permeability transition pore (PTP) as it preceded mitochondrial Ca(2+) buildup and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) loss. Further, the release was found to be unaffected by PTP inhibitor cyclosporin-A. Bax inhibitory peptide BiP-P5 could effectively block both cytochrome-c release and apoptosis induction indicating dependence on Bax-channel formation. Inhibition of apoptosis by FSBA, a nucleotide analog that inhibits apoptosome formation through Apaf1 binding, suggested activity of apoptosome similar to mammalian cells. Mitochondria isolated from treated cells activated caspases in the cytosolic fraction of untreated cells while mitochondrial lysates of treated or untreated cells had similar effect. Sequestering cytochrome-c in mitochondrial lysates inhibited DEVDase activity, and addition of purified cytochrome-c and dATP to Sf9 cytosolic fraction induced DEVDase activity, suggesting that cytochrome-c may be exclusively required for Lepidopteran apoptosis. This is the first detailed study demonstrating mitochondrial regulation of Lepidopteran insect cell apoptosis, and reiterates its homology with mammalian cell apoptosis while showing distinctive differences from earlier reports in Drosophila.


