CEP 1347JNK inhibitor CAS# 156177-65-0 |
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- Iguratimod
Catalog No.:BCC1641
CAS No.:123663-49-0
- Ibuprofen
Catalog No.:BCC3791
CAS No.:15687-27-1
- Etoricoxib
Catalog No.:BCC1565
CAS No.:202409-33-4
- Ibuprofen Lysine
Catalog No.:BCC2547
CAS No.:57469-77-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 156177-65-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 133005 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C33H33N3O5S2 | M.Wt | 615.76 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in DMSO | ||
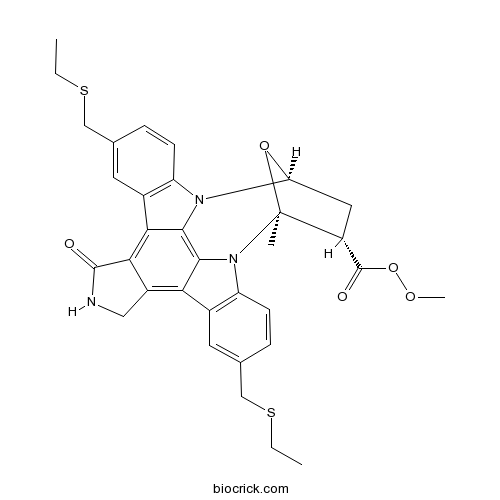
| SMILES | CCSCC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N3C4CC(C(O4)(N5C6=C(C=C(C=C6)CSCC)C7=C8CNC(=O)C8=C2C3=C75)C)C(=O)OOC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WMBUVOLZSWTKMP-KQFGJPIXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C33H33N3O5S2/c1-5-42-15-17-7-9-23-19(11-17)27-28-21(14-34-31(28)37)26-20-12-18(16-43-6-2)8-10-24(20)36-30(26)29(27)35(23)25-13-22(32(38)41-39-4)33(36,3)40-25/h7-12,22,25H,5-6,13-16H2,1-4H3,(H,34,37)/t22-,25+,33+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling. Rescues motor neurons undergoing apoptosis (EC50 = 20 nM). Blocks Aβ-induced cortical neuron apoptosis (EC50 ~51 nM). Does not inhibit ERK1 activity. Neuroprotective. |

CEP 1347 Dilution Calculator

CEP 1347 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.624 mL | 8.12 mL | 16.2401 mL | 32.4802 mL | 40.6002 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3248 mL | 1.624 mL | 3.248 mL | 6.496 mL | 8.12 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1624 mL | 0.812 mL | 1.624 mL | 3.248 mL | 4.06 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0325 mL | 0.1624 mL | 0.3248 mL | 0.6496 mL | 0.812 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0162 mL | 0.0812 mL | 0.1624 mL | 0.3248 mL | 0.406 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CEP-1347, also called KT 7515, is an inhibitor of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway, with an IC50 value for JNK1 activation of 20 ± 2 nM in rat embryonic motoneurons [1].
The JNK pathway, also known as the stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) pathway, is one of the signaling cascades that mediate the apoptotic death in response to a variety of stressful stimuli. JNK activation by phosphorylation is important for neuronal cell death after injury in vivo and after trophic factor withdrawal in vitro [2].
CEP-1347 induced neuronal survival. JNK1 activity in untreated cell cultures increased approximately fourfold within 24 hr after plating. As early as 15 min after the application of CEP-1347 at 500 nM, the activity of JNK1 sharply decreased to ~50% of control levels. For the next 24 hr, the activity of JNK1 continued to decrease. Cultures rich in motoneurons were grown in the presence of CEP-1347 at increasing concentrations, and the IC50 for JNK1 activity at 22 hr was 21 ± 2 nM, whereas the EC50 for cell survival at 5 d was 20 ± 2 nM [1].
CEP-1347 can affect noise-induced hearing loss. Data showed that hearing thresholds 2 d before noise exposure showed no significant difference between the noise-exposed control and treated group. Hearing threshold shifts in all guinea pigs 2 d after the noise exposure. By day 6 after exposure, threshold shifts were significantly less in the CEP-1347 group than in the noise-exposed control group. By 2 weeks after exposure, the difference between the two groups became more pronounced [2].
References:
[1]. Maroney AC, Glicksman MA, Basma AN, et al. Motoneuron apoptosis is blocked by CEP-1347 (KT 7515), a novel inhibitor of the JNK signaling pathway[J]. The Journal of neuroscience, 1998, 18(1): 104-111.
[2]. Pirvola U, Liang XQ, Virkkala J, et al. Rescue of hearing, auditory hair cells, and neurons by CEP-1347/KT7515, an inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2000, 20(1): 43-50.
- Maackiaflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6834
CAS No.:156162-10-6
- BQ-788 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5151
CAS No.:156161-89-6
- Lys-γ3-MSH
Catalog No.:BCC6049
CAS No.:156159-18-1
- SGC 0946
Catalog No.:BCC2216
CAS No.:1561178-17-3
- Alvimopan
Catalog No.:BCC1347
CAS No.:156053-89-3
- Qianhucoumarin E
Catalog No.:BCN3506
CAS No.:156041-02-0
- Angelidiol
Catalog No.:BCN7964
CAS No.:156009-77-7
- H-HoArg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3226
CAS No.:156-86-5
- Sodium butyrate
Catalog No.:BCC4720
CAS No.:156-54-7
- 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4795
CAS No.:156-38-7
- Rabdoternin F
Catalog No.:BCN6399
CAS No.:155977-87-0
- Edultin
Catalog No.:BCC8321
CAS No.:15591-75-0
- Hispidulin 7-O-neohesperidoside
Catalog No.:BCN2952
CAS No.:156186-00-4
- GTS 21 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7948
CAS No.:156223-05-1
- PyAOP
Catalog No.:BCC2819
CAS No.:156311-83-0
- 11-Anhydro-16-oxoalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN7703
CAS No.:156338-93-1
- Ehretioside B
Catalog No.:BCN1703
CAS No.:156368-84-2
- Ailanthoidol
Catalog No.:BCN7705
CAS No.:156398-61-7
- 3,4-Seco-3-oxobisabol-10-ene-4,1-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7550
CAS No.:1564265-85-5
- CWHM-12
Catalog No.:BCC5548
CAS No.:1564286-55-0
- cis-Khellactone
Catalog No.:BCN3703
CAS No.:15645-11-1
- α-Conotoxin ImI
Catalog No.:BCC5974
CAS No.:156467-85-5
- Myricetin 3-O-galactoside
Catalog No.:BCN4703
CAS No.:15648-86-9
- 1-Hydroxytropacocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1919
CAS No.:156497-23-3
Neuroprotective activities of CEP-1347 in models of neuroAIDS.[Pubmed:19966207]
J Immunol. 2010 Jan 15;184(2):746-56.
When the nervous system is infected with HIV-1, it commonly results in neuroinflammation leading to overt neuronal dysfunction and subsequent cognitive and behavioral impairments. The multifaceted disease process, now referred to as HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND), provides a range of molecular targets for adjunctive therapies. One is CEP-1347, an inhibitor of mixed lineage kinases that elicits neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory responses in models of neurodegenerative diseases. Since HAND is associated with inflammatory encephalopathy induced by virus infection and mononuclear phagocytes (perivascular macrophages and microglia) immune activation, we investigated whether CEP-1347 could ameliorate disease in laboratory models of HAND. We now demonstrate that CEP-1347 reduces the levels of secreted proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in HIV-1-infected human macrophages and attenuates dose-dependent neurotoxicity in rodent cortical neurons. CEP-1347-treated mice readily achieve therapeutic drug levels in peripheral blood. HIV-1 encephalitis (HIVE) mice, where human virus-infected monocyte-derived macrophages are stereotactically injected into the basal ganglia of CB17 severe combined immunodeficient mice, received daily intraperitoneal injections of CEP-1347. Here, CEP-1347 treatment of HIVE mice showed a dose-dependent reduction in microgliosis. Dendritic integrity and neuronal loss were sustained and prevented, respectively. These results demonstrate that CEP-1347 elicits anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective responses in an HIVE model of human disease and as such warrants further study as an adjunctive therapy for human disease.
Pharmacokinetic interactions of CEP-1347 and atazanavir in HIV-infected patients.[Pubmed:23737347]
J Neurovirol. 2013 Jun;19(3):254-60.
CEP-1347 is a potent inhibitor of mixed lineage kinase (MLK), which was investigated for ameliorating HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. CEP-1347 and atazanavir pharmacokinetics were determined when CEP-1347 50 mg twice daily was administered to HIV-infected patients (n = 20) receiving combination antiretroviral therapy including atazanavir and ritonavir (ATV/RTV, 300/100 mg) once daily continuously. Co-administration of CEP-1347 and ATV/RTV resulted with significant changes in pharmacokinetics of ATV but not RTV. Specifically, an increase in ATV accumulation ratio of 15 % (p = 0.007) and a prolongation of T((1/2)) from 12.7 to 15.9 h (p = 0.002) were observed. The results suggested that co-administration of CEP-1347 with ATV/RTV in HIV-infected patients might result in limited impact on ATV but not on RTV pharmacokinetics.
CEP-1347/KT-7515, an inhibitor of SAPK/JNK pathway activation, promotes survival and blocks multiple events associated with Abeta-induced cortical neuron apoptosis.[Pubmed:11331414]
J Neurochem. 2001 May;77(3):849-63.
Although the mechanism of neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease (AD) has yet to be elucidated, a putative role for c-jun in this process has emerged. Thus, it was of interest to delineate signal transduction pathway(s) which regulate the transcriptional activity of c-jun, and relate these to alternate gene inductions and biochemical processes associated with beta-amyloid (Abeta) treatment. In this regard, the survival promoting activity of CEP-1347, an inhibitor of the stress-activated/c-jun N-terminal (SAPK/JNK) kinase pathway, was evaluated against Abeta-induced cortical neuron death in vitro. Moreover, CEP-1347 was used as a pharmacologic probe to associate multiple biochemical events with Abeta-induced activation of the SAPK/JNK pathway. CEP-1347 promoted survival and blocked Abeta-induced activation of JNK kinase (MKK4, also known as MEK-4, JNKK and SEK1) as well as other downstream events associated with JNK pathway activation. CEP-1347 also blocked Abeta-induction of cyclin D1 and DP5 genes and blocked Abeta-induced increases in cytoplasmic cytochrome c, caspase 3-like activity and calpain activation. The critical time window for cell death blockade by CEP-1347 resided within the peak of Abeta-induced MKK4 activation, thus defining this point as the most upstream event correlated to its survival-promoting activity. Together, these data link the SAPK/JNK pathway and multiple biochemical events associated with Abeta-induced neuronal death and further delineate the point of CEP-1347 interception within this signal transduction cascade.
Motoneuron apoptosis is blocked by CEP-1347 (KT 7515), a novel inhibitor of the JNK signaling pathway.[Pubmed:9412490]
J Neurosci. 1998 Jan 1;18(1):104-11.
Neurons undergoing apoptosis can be rescued by trophic factors that simultaneously increase the activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and decrease c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38. We identified a molecule, CEP-1347 (KT7515), that rescues motoneurons undergoing apoptosis and investigated its effect on ERK1 and JNK1 activity. Cultured rat embryonic motoneurons, in the absence of trophic factor, began to die 24-48 hr after plating. During the first 24 hr ERK1 activity was unchanged, whereas JNK1 activity increased fourfold. CEP-1347 completely rescued motoneurons for at least 72 hr with an EC50 of 20 +/- 2 nM. CEP-1347 did not alter ERK1 activity but rapidly inhibited JNK1 activation. The IC50 of CEP-1347 for JNK1 activation was the same as the EC50 for motoneuron survival. Inhibition of JNK1 activation by CEP-1347 was not selective to motoneurons. CEP-1347 also inhibited JNK1 activity in Cos7 cells under conditions of ultraviolet irradiation, osmotic shock, and inhibition of glycosylation. Inhibition by CEP-1347 of the JNK1 signaling pathway appeared to be selective, because CEP-1347 did not inhibit p38-regulated mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase-2 (MAPKAP2) activity in Cos7 cells subjected to osmotic shock. The direct molecular target of CEP-1347 was not JNK1, because CEP-1347 did not inhibit JNK1 activity in Cos7 cells cotransfected with MEKK1 and JNK1 cDNA constructs. This is the first demonstration of a small organic molecule that promotes motoneuron survival and that simultaneously inhibits the JNK1 signaling cascade.
Preservation of cholinergic activity and prevention of neuron death by CEP-1347/KT-7515 following excitotoxic injury of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis.[Pubmed:9881861]
Neuroscience. 1998 Sep;86(2):461-72.
We have identified a class of small organic molecules, derived from the indolocarbazole K-252a, that promote the survival of cultured neurons. However, many of these indolocarbazoles inhibit protein kinase C and neurotrophin-activated tyrosine kinase receptors. These kinase inhibitory activities may limit the utility of these compounds for neurological disorders. A bis-ethyl-thiomethyl analogue of K-252a, CEP-1347/KT-7515, has been identified that lacks protein kinase C and tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitory activities, yet retains the ability to promote survival of cultured neurons, including cholinergic neurons derived from the basal forebrain. In the present studies, CEP-1347/KT-7515 was assessed for neurotrophic activity on basal forebrain neurons of in vivo rats following excitotoxic insult. Ibotenate infusion into the nucleus basalis magnocellularis reduced levels of choline acetyltransferase activity in the cortex, as well as reduced numbers of choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive and retrogradely (FluoroGold)-labelled cortically-projecting neurons in the nucleus basalis. Systemically administered CEP-1347/KT-7515 attenuated the loss of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity and the loss of the number of choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive and retrogradely-labelled FluoroGold neurons in the nucleus basalis. Moreover, CEP-1347/KT-7515 ameliorated the loss of cortical choline acetyltransferase if administration was initiated one day, but not seven days post-lesion. Together, these results demonstrate that CEP-1347/KT-7515 protects damaged cortically-projecting basal forebrain neurons from degeneration. Thus, CEP-1347/KT-7515 may have therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, in which basal forebrain cholinergic neurons degenerate.


