CWHM-12CAS# 1564286-55-0 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1564286-55-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72949858 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H32BrN5O6 | M.Wt | 590.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 10.5 mg/mL (17.78 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming); | ||
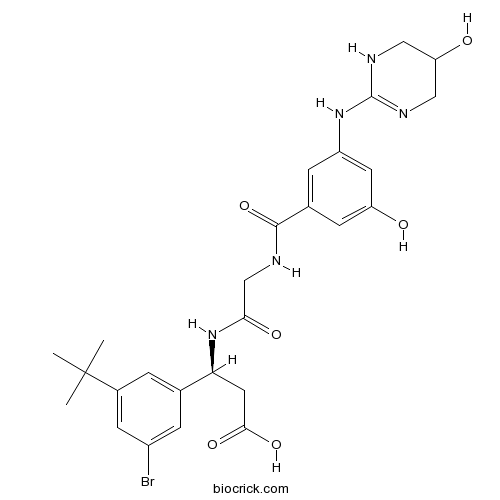
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-(3-bromo-5-tert-butylphenyl)-3-[[2-[[3-hydroxy-5-[(5-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-2-yl)amino]benzoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=CC(=C1)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C2=CC(=CC(=C2)O)NC3=NCC(CN3)O)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YDHAGPCZRFQPOI-NRFANRHFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H32BrN5O6/c1-26(2,3)16-4-14(5-17(27)8-16)21(10-23(36)37)32-22(35)13-28-24(38)15-6-18(9-19(33)7-15)31-25-29-11-20(34)12-30-25/h4-9,20-21,33-34H,10-13H2,1-3H3,(H,28,38)(H,32,35)(H,36,37)(H2,29,30,31)/t21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

CWHM-12 Dilution Calculator

CWHM-12 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6936 mL | 8.4678 mL | 16.9357 mL | 33.8713 mL | 42.3392 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3387 mL | 1.6936 mL | 3.3871 mL | 6.7743 mL | 8.4678 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1694 mL | 0.8468 mL | 1.6936 mL | 3.3871 mL | 4.2339 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0339 mL | 0.1694 mL | 0.3387 mL | 0.6774 mL | 0.8468 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0169 mL | 0.0847 mL | 0.1694 mL | 0.3387 mL | 0.4234 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CWHM-12 is a potent inhibitor of αV integrins with IC50s of 0.2, 0.8, 1.5, and 1.8 nM for αvβ8, αvβ3, αvβ6, and αvβ1.
In Vitro:CWHM-12 (CWHM 12) also less potently inhibits αvβ5 (IC50=61 nM) and αIIbβ3/α2β1/α10β1 (IC50>5000 nM). CWHM-12 demonstrates high potency against all of the five possible β subunit binding partners (αvβ1, αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6 and αvβ8) in in vitro ligand-binding assays, with somewhat less potency against αvβ5 than against the other αv integrins[1].
In Vivo:Mice are treated with CCl4 for 3 weeks to establish fibrotic disease and then treated with CWHM-12 (CWHM 12) or vehicle for the final 3 weeks of CCl4. CWHM-12 significantly reduces liver fibrosis even after fibrotic disease have been established. Digital image quantitation demonstrates significantly reduced p-SMAD3 signaling in the livers of CWHM-12 treated mice compare to controls, demonstrating that the protection from CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis observed in CWHM-12 treated mice is due at least in part to a reduction in TGF-β activation by αv integrins. Besides, administration of CWHM-12 significantly inhibited progression of pulmonary fibrosis[1].
References:
[1]. Henderson NC, et al. Targeting of αv integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med. 2013 Dec;19(12):1617-24.
- 3,4-Seco-3-oxobisabol-10-ene-4,1-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7550
CAS No.:1564265-85-5
- Ailanthoidol
Catalog No.:BCN7705
CAS No.:156398-61-7
- Ehretioside B
Catalog No.:BCN1703
CAS No.:156368-84-2
- 11-Anhydro-16-oxoalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN7703
CAS No.:156338-93-1
- PyAOP
Catalog No.:BCC2819
CAS No.:156311-83-0
- GTS 21 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7948
CAS No.:156223-05-1
- Hispidulin 7-O-neohesperidoside
Catalog No.:BCN2952
CAS No.:156186-00-4
- CEP 1347
Catalog No.:BCC7982
CAS No.:156177-65-0
- Maackiaflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6834
CAS No.:156162-10-6
- BQ-788 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5151
CAS No.:156161-89-6
- Lys-γ3-MSH
Catalog No.:BCC6049
CAS No.:156159-18-1
- SGC 0946
Catalog No.:BCC2216
CAS No.:1561178-17-3
- cis-Khellactone
Catalog No.:BCN3703
CAS No.:15645-11-1
- α-Conotoxin ImI
Catalog No.:BCC5974
CAS No.:156467-85-5
- Myricetin 3-O-galactoside
Catalog No.:BCN4703
CAS No.:15648-86-9
- 1-Hydroxytropacocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1919
CAS No.:156497-23-3
- 7,13-Dideacetyl-9,10-didebenzoyltaxchinin C
Catalog No.:BCN7670
CAS No.:156497-25-5
- Ryanodine
Catalog No.:BCC5742
CAS No.:15662-33-6
- Cisplatin
Catalog No.:BCN1552
CAS No.:14283-03-5
- 1,2,5-Trihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7585
CAS No.:156640-23-2
- Org 20599
Catalog No.:BCC7470
CAS No.:156685-94-8
- Rostafuroxin (PST 2238)
Catalog No.:BCC6431
CAS No.:156722-18-8
- SNC 80
Catalog No.:BCC6785
CAS No.:156727-74-1
- Delphinidin-3-O-rutinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3115
CAS No.:15674-58-5
An Inhibitor of Arginine-Glycine-Aspartate-Binding Integrins Reverses Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.[Pubmed:30766962]
Hepatol Commun. 2018 Dec 27;3(2):246-261.
The presence and stage of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is strongly associated with mortality. Thus, both preventing and reversing fibrosis are critically important approaches to prevent death or the need for liver transplantation from NASH. Recently, fibrosis in several mouse models of organ injury was shown to be prevented and reversed with the potent small molecule, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid tripeptide (RGD)-binding, integrin antagonist (3S)-3-(3-bromo-5-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-3-(2-(3-hydroxy-5-((5-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetra hydropyrimidin-2-yl)amino)benzamido)acetamido)propanoic acid (Center for World Health and Medicine [CWHM]-12). We hypothesized that RGD-binding integrins may play an important role in fibrosis progression in NASH. We assessed the efficacy of CWHM-12 in a choline deficient, amino-acid defined, high-fat diet (CDAHFD) mouse model of NASH. Mice were kept on the CDAHFD or a control diet for 10 weeks, and CWHM-12 was delivered by continuous infusion for the final 4 weeks. The parameters of NASH and liver fibrosis were evaluated before and after drug treatment. Hepatic steatosis, liver injury, and inflammation were significantly induced by the CDAHFD at week 6 and did not change by week 10. Hepatic profibrogenic gene expression was induced by the CDAHFD at week 6, further increased at week 10, and decreased by CWHM-12. Fibrosis measured by analysis of liver collagen was reduced by CWHM-12 to levels significantly less than found at 6 weeks, demonstrating the possibility of reversing already established fibrosis despite ongoing injury. Demonstrated mechanisms of the antifibrotic effect of CWHM-12 included loss of activated hepatic stellate cells through apoptosis and suppression of hepatic profibrotic signal transduction by transforming growth factor beta. Conclusion: RGD-binding integrins may be critical in the development of fibrosis in NASH and may represent potential targets for treating patients with NASH to reverse advanced liver fibrosis.
Neer Award 2018: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha co-expression typifies a subset of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta-positive progenitor cells that contribute to fatty degeneration and fibrosis of the murine rotator cuff.[Pubmed:29653843]
J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018 Jul;27(7):1149-1161.
BACKGROUND AND HYPOTHESIS: After massive tears, rotator cuff muscle often undergoes atrophy, fibrosis, and fatty degeneration. These changes can lead to high surgical failure rates and poor patient outcomes. The identity of the progenitor cells involved in these processes has not been fully elucidated. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRbeta) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRalpha) have previously been recognized as markers of cells involved in muscle fibroadipogenesis. We hypothesized that PDGFRalpha expression identifies a fibroadipogenic subset of PDGFRbeta(+) progenitor cells that contribute to fibroadipogenesis of the rotator cuff. METHODS: We created massive rotator cuff tears in a transgenic strain of mice that allows PDGFRbeta(+) cells to be tracked via green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence. We then harvested rotator cuff muscle tissues at multiple time points postoperatively and analyzed them for the presence and localization of GFP(+) PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells. We cultured, induced, and treated these cells with the molecular inhibitor CWHM-12 to assess fibrosis inhibition. RESULTS: GFP(+) PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells were present in rotator cuff muscle tissue and, after massive tears, localized to fibrotic and adipogenic tissues. The frequency of PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells increased at 5 days after massive cuff tears and decreased to basal levels within 2 weeks. PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells were highly adipogenic and significantly more fibrogenic than PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(-) cells in vitro and localized to adipogenic and fibrotic tissues in vivo. Treatment with CWHM-12 significantly decreased fibrogenesis from PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells. CONCLUSION: PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells directly contribute to fibrosis and fatty degeneration after massive rotator cuff tears in the mouse model. In addition, CWHM-12 treatment inhibits fibrogenesis from PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cells in vitro. Clinically, perioperative PDGFRbeta(+) PDGFRalpha(+) cell inhibition may limit rotator cuff tissue degeneration and, ultimately, improve surgical outcomes for massive rotator cuff tears.
Inhibitors of Arg-Gly-Asp-Binding Integrins Reduce Development of Pancreatic Fibrosis in Mice.[Pubmed:28174730]
Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Mar 16;2(4):499-518.
BACKGROUND & AIMS: Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) regulate the development of chronic pancreatitis (CP) and are activated by the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGFB). Integrins of the alphav family promote TGFB signaling in mice, probably by interacting with the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence of the TGFB latency-associated peptide, which frees TGFB to bind its cellular receptors. However, little is known about the role of integrins in the development of CP. We investigated the effects of small-molecule integrin inhibitors in a mouse model of CP. METHODS: We induced CP in C57BL/6 female mice by repeated cerulein administration. An active RGD peptidomimetic compound (Center for World Health and Medicine [CWHM]-12) was delivered by continuous infusion, starting 3 days before or 5 days after cerulein administration began. Pancreata were collected and parenchymal atrophy, fibrosis, and activation of PSCs were assessed by histologic, gene, and protein expression analyses. We measured CWHM-12 effects on activation of TGFB in co-culture assays in which rat PSC cells (large T immortalized cells [LTC-14]) activate expression of a TGFB-sensitive promoter in reporter cells. RESULTS: Pancreatic tissues of mice expressed messenger RNAs encoding subunits of RGD-binding integrins. Cerulein administration increased expression of these integrins, altered pancreatic cell morphology, and induced fibrosis. The integrin inhibitor CWHM-12 decreased acinar cell atrophy and loss, and substantially reduced fibrosis, activation of PSCs, and expression of genes regulated by TGFB. CWHM-12 also reduced established fibrosis in mice and blocked activation of TGFB in cultured cells. CONCLUSIONS: Based on studies of a mouse model of CP and cultured PSCs, integrins that bind RGD sequences activate PSCs and promote the development of pancreatic fibrogenesis in mice. Small-molecule antagonists of this interaction might be developed for treatment of pancreatic fibrotic diseases.


