Calvatic acidCAS# 54723-08-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 54723-08-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 99679 | Appearance | Yellowish-brown powder |
| Formula | C8H5N3O3 | M.Wt | 191.1 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Alvatic acid; Calvatinic acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, methanol and aqueous alkaline solution | ||
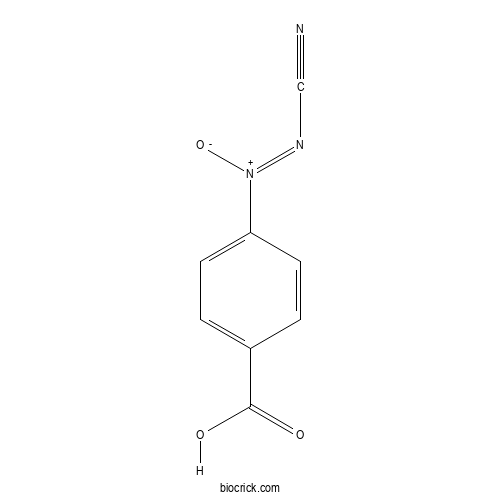
| Chemical Name | (4-carboxyphenyl)-cyanoimino-oxidoazanium | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C(=O)O)[N+](=NC#N)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LDRFVNKBORCKQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H5N3O3/c9-5-10-11(14)7-3-1-6(2-4-7)8(12)13/h1-4H,(H,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Calvatic acid is a new antibiotic with both a carboxylic group and an azoxy function in the benzene ring. It shows antimicrotubular effect. | |||||

Calvatic acid Dilution Calculator

Calvatic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2329 mL | 26.1643 mL | 52.3286 mL | 104.6572 mL | 130.8216 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0466 mL | 5.2329 mL | 10.4657 mL | 20.9314 mL | 26.1643 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5233 mL | 2.6164 mL | 5.2329 mL | 10.4657 mL | 13.0822 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1047 mL | 0.5233 mL | 1.0466 mL | 2.0931 mL | 2.6164 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0523 mL | 0.2616 mL | 0.5233 mL | 1.0466 mL | 1.3082 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3,4-Dimethoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN9777
CAS No.:1131-62-0
- 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9776
CAS No.:4319-02-2
- Nortrachelogenin-5'-C-beta-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9775
CAS No.:858127-39-6
- Glucofrangulin A
Catalog No.:BCN9774
CAS No.:21133-53-9
- DL-Tyrosine
Catalog No.:BCN9773
CAS No.:556-03-6
- 4'-Methoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9772
CAS No.:959-23-9
- (-)-Eburnamonine
Catalog No.:BCN9771
CAS No.:4880-88-0
- Comanthosid A
Catalog No.:BCN9770
CAS No.:70938-59-9
- 2'-Methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9769
CAS No.:19725-47-4
- N-trans-caffeoyloctopamine
Catalog No.:BCN9768
CAS No.:1378868-10-0
- Rebaudioside M
Catalog No.:BCN9767
CAS No.:1220616-44-3
- (S)-(-)-Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN9766
CAS No.:5989-54-8
- alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN9779
CAS No.:101-86-0
- (+/-)-Anabasine
Catalog No.:BCN9780
CAS No.:13078-04-1
- Cannabisin B
Catalog No.:BCN9781
CAS No.:144506-17-2
- Deacylgymnemic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9782
CAS No.:121686-42-8
- Cinobufotenine
Catalog No.:BCN9783
CAS No.:60657-23-0
- Indole
Catalog No.:BCN9784
CAS No.:120-72-9
- 5,6,7-Trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9785
CAS No.:973-67-1
- 3-Methyl-1-butanol
Catalog No.:BCN9786
CAS No.:123-51-3
- Quercetin 3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN9787
CAS No.:143016-74-4
- Ethyl phenylacetate
Catalog No.:BCN9788
CAS No.:101-97-3
- Kaempferol 3-robinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9789
CAS No.:114924-89-9
- Resokaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN9790
CAS No.:2034-65-3
Anti-Helicobacter pylori agents endowed with H2-antagonist properties.[Pubmed:11212121]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Feb 12;11(3):403-6.
New anti-Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) agents endowed with H2-antagonists properties were obtained by combining the lamtidine derived pharmacophoric group with the antibiotic Calvatic acid. All the compounds were tested for their irreversible H2-antagonist properties and for their ability to inhibit 20 H. pylori strains, two of them metronidazole resistant. The most active derivative (compound 4) displayed antimicrobial activity similar to metronidazole.
Inhibition of human placenta glutathione transferase P1-1 by the antibiotic calvatic acid and its diazocyanide analogue--evidence for multiple catalytic intermediates.[Pubmed:9183003]
Eur J Biochem. 1997 May 1;245(3):663-7.
The inhibition mechanism of the dimeric human placenta glutathione transferase (GST) P1-1 by Calvatic acid and the reaction intermediates, i.e. the diazocyanide analogue of Calvatic acid, has been investigated at pH 7.0 and 30.0 degrees C. Experiments performed at different molar ratios of inhibitor/GST P1-1 indicate that 1 mol Calvatic acid inactivates 1 mol GST P1-1, containing two catalytically equivalent active sites. However, 2 mol of the diazocyanide analogue of Calvatic acid inactivate 1 mol GST P1-1. Two disulfide bridges/dimer, probably between Cys47 and Cys101, have been formed during the reaction of GST P1-1 with Calvatic acid and its diazocyanide analogue. The apparent second-order rate constants for GST P1-1 inactivation by Calvatic acid and its diazocyanide analogue are 2.4+/-0.3 M(-1) s(-1) and (8.5+/-0.7) x 10(3) M(-1) s(-1), respectively. The reaction of Calvatic acid with free L-cysteine can be described by a simple process with an apparent second-order rate constant of (5.0+/-0.4) x 10(1) M(-1) s(-1). In contrast, a transient species occurs during the reaction of the diazocyanide analogue of Calvatic acid with free L-cysteine. Kinetics may be described by a second-order process [the rate constant being (8.0+/-0.5) x 10(3) M(-1) s(-1)] followed by a first-order decay [the rate constant corresponding to (1.2+/-0.1) x 10(1) s(-1)]. Calvatic acid represents an enzyme inhibitor acting much slower than its reaction intermediates (i.e. its diazocyanide analogue).
Antimicrotubular effect of calvatic acid and of some related compounds.[Pubmed:10232925]
Cell Biochem Funct. 1995 Dec;13(4):231-8.
A structure-activity relationship has been established between Calvatic acid and some related synthetic compounds, and their ability to inhibit GTP-induced microtubular protein polymerization in vitro. These compounds were effective in a dose- and a time-dependent manner. The most active drug was the p-chloro substituted compound, which showed its inhibitory activity without any preincubation period, which the others needed. Since if cysteine was present, polymerization was no longer affected, an involvement of titratable -SH groups of tubulin could be suggested. In contrast, taxol-induced polymerization was only slightly inhibited by these compounds, and colchicine-binding activity was not generally impaired.
Interactions between calvatic acid and related compounds with rat liver microsomes.[Pubmed:8983928]
Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1995 Oct-Dec;20(4):249-54.
In this study we examined the interactions of liver microsomes with the antibiotic Calvatic acid and with structural analogues, some of which had shown antimicrotubular properties. These drugs decreased cytochrome P-450 content differently according to the substitutions on the azoxy function and the ethoxycarbonyl derivatives were found to be the most effective ones. The decrease in cytochrome P-450 could be prevented by addition of cysteine or GSH, suggesting an involvement of sulphydryl groups. Furthermore, chromatographic analyses showed that ethoxycarbonyl derivatives were completely metabolized, and this would explain the different behaviour of these compounds towards microtubular protein when they were incubated with purified bovine brain protein or with liver or hepatoma extracts.
Inhibition of human placenta glutathione transferase P1-1 by calvatic acid.[Pubmed:8069231]
Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Apr;32(5):819-29.
The inhibition mechanism of the dimeric human placenta glutathione transferase (GST P1-1) by the antibiotic p-carboxyphenylazoxycyanide (Calvatic acid) has been investigated at pH 7.0 and 30.0 degrees C. Experiments performed at different Calvatic acid/GST P1-1 molar ratios indicate that one mole of Calvatic acid inactivates one mole of the homodimeric enzyme molecule, containing two catalytically equivalent active sites. The apparent second order rate constant for GST P1-1 inactivation is 2.4 +/- 0.3 M-1 s-1. The recovery of all the 5,5'-dithio-bis(2-nitro-benzoic acid)-titratable thiol groups as well as the original catalytic activity of GST P1-1 after treatment of the inhibited enzyme with dithiothreitol indicates that two disulfide bridges per dimer, likely between Cys47 and Cys101, have been formed during the reaction with Calvatic acid. To the best of the authors knowledge, Calvatic acid represents a unique case of enzyme inhibitor acting also throughout its reaction product(s).
Effect of calvatic acid and its analogs on ornithine decarboxylase activity in tumour cells.[Pubmed:2277863]
Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;70(2):143-53.
Calvatic acid (p-carboxyphenylazoxycyanide) is an antibiotic containing an azoxycyano group that displays carcinostatic activity. In the present work it has been shown that in AH-130 hepatoma and K562 leukemia cells the antibiotic, at low concentration, decreases ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) levels. The change depends on two summative effects of the drug, impairment of overall protein synthesis and inhibition of enzyme activity. Some analogs of Calvatic acid have been tested in order to gain more insight into the structure-activity relationship. The decarboxylated derivative phenylazoxycyanide proved to be more effective in reducing protein synthesis and ODC activity in the whole tumor cells. The rapidly growing K562 cells displayed high sensitivity to this compound. Calvatic acid analogs devoid of the cyano group were less effective on the same parameters.
Phenylazoxycyanide damages microtubular protein more than its reference antibiotic, calvatic acid.[Pubmed:2706011]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 1;38(7):1121-4.
The effect of phenylazoxycyanide and Calvatic acid, its reference antibiotic, on some functions of tubulin obtained from different sources has been studied. Our purpose was to establish a possible correlation between the antitumour activity of these drugs and their antimicrotubular action. Microtubules are subcellular structures involved in proliferation and maintenance of the cell shape and probably in malignant transformation; indeed most antimitotic drugs influence the stability of microtubules through the interaction with tubulin, their main protein. In this work we found phenylazoxycyanide impairs, more than Calvatic acid, polymerization of purified tubulin from calf brain. It also damages, in a dose-dependent manner, colchicine-binding ability of tubulin derived from rat liver and AH-130 Yoshida ascite hepatoma cells. Compounds displaying an azoxycyano group may represent new antimicrotubular agents and their effect could be modulated by the different polarity and structural characteristic of the molecule.
Some biological effects of calvatic acid and its analog on isolated hepatocytes.[Pubmed:3037657]
Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1987 May;56(2):265-72.
Calvatic acid is a new antibiotic with both a carboxylic group and an azoxy function in the benzene ring. The relationship between structure and biological activity in this substance and one of its analog, phenylazoxyxyanide, was investigated. Isolated hepatocytes were used as an experimental system: the release of lactate dehydrogenase and the colchicine-binding activity of tubulin were first evaluated; effects were dose and time dependent. micromolar concentrations of these drugs determined a significant decrease of the glucose-6-phosphatase activity and a slight inhibition of aminopyrene demethylation. A toxic effect at the microsomal level and an interaction with the microtubular system are thus possible.


