ChlorpropamideCAS# 94-20-2 |
- Etomoxir
Catalog No.:BCC1564
CAS No.:124083-20-1
- Verteporfin
Catalog No.:BCC3690
CAS No.:129497-78-5
- Elacridar
Catalog No.:BCC1546
CAS No.:143664-11-3
- Etofenamate
Catalog No.:BCC1563
CAS No.:30544-47-9
- Etifoxine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1561
CAS No.:56776-32-0
- Etimizol
Catalog No.:BCC1562
CAS No.:64-99-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 94-20-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2727 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H13ClN2O3S | M.Wt | 276.74 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (361.35 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl-3-propylurea | ||
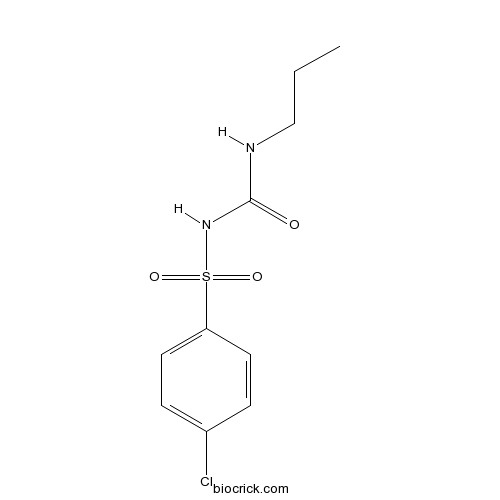
| SMILES | CCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RKWGIWYCVPQPMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H13ClN2O3S/c1-2-7-12-10(14)13-17(15,16)9-5-3-8(11)4-6-9/h3-6H,2,7H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Chlorpropamide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Target: Chlorpropamide belongs to the sulfonylurea class of insulin secretagogues, which act by stimulating β cells of the pancreas to release insulin.Chlorpropamide is not recommended for the treatment of NIDDM as it increases blood pressure and the risk of retinopathy. Up to 80% of the single oral dose of chlorpropramide is metabolized, likely in the liver; 80-90% of the dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug and metabolites. | |||||

Chlorpropamide Dilution Calculator

Chlorpropamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6135 mL | 18.0675 mL | 36.135 mL | 72.27 mL | 90.3375 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7227 mL | 3.6135 mL | 7.227 mL | 14.454 mL | 18.0675 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3614 mL | 1.8068 mL | 3.6135 mL | 7.227 mL | 9.0338 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0723 mL | 0.3614 mL | 0.7227 mL | 1.4454 mL | 1.8068 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0361 mL | 0.1807 mL | 0.3614 mL | 0.7227 mL | 0.9034 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Chlorpropamide is a sulfonylurea class drug for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Benzyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8869
CAS No.:94-18-8
- Sodium 4-amiropparaty Hyalrate
Catalog No.:BCC3855
CAS No.:94-16-6
- Propylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN8416
CAS No.:94-13-3
- Benzocaine
Catalog No.:BCC4636
CAS No.:94-09-7
- Synephrine
Catalog No.:BCN6308
CAS No.:94-07-5
- p53 and MDM2 proteins-interaction-inhibitor racemic
Catalog No.:BCC1831
CAS No.:939983-14-9
- RG7112
Catalog No.:BCC1894
CAS No.:939981-39-2
- p53 and MDM2 proteins-interaction-inhibitor chiral
Catalog No.:BCC1830
CAS No.:939981-37-0
- BI 6015
Catalog No.:BCC6249
CAS No.:93987-29-2
- ACTB-1003
Catalog No.:BCC5587
CAS No.:939805-30-8
- PF-00562271
Catalog No.:BCC3684
CAS No.:939791-38-5
- [Ac-Tyr1,D-Phe2]GRF 1-29, amide (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5719
CAS No.:93965-89-0
- Tetracaine
Catalog No.:BCC9175
CAS No.:94-24-6
- Butylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN8418
CAS No.:94-26-8
- Benzyl nicotinate
Catalog No.:BCC8874
CAS No.:94-44-0
- 2-Amino-6-ethoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8541
CAS No.:94-45-1
- Piperine
Catalog No.:BCN1018
CAS No.:94-62-2
- N,N'-Bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine
Catalog No.:BCC9064
CAS No.:94-93-9
- NVP-BHG712
Catalog No.:BCC3963
CAS No.:940310-85-0
- Suplatast Tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC4961
CAS No.:94055-76-2
- Poliumoside
Catalog No.:BCN1204
CAS No.:94079-81-9
- R-7128
Catalog No.:BCC1880
CAS No.:940908-79-2
- SB743921
Catalog No.:BCC4559
CAS No.:940929-33-9
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
Crystallization and polymorphic transitions of chlorpropamide in aqueous 2-hydroxybutyl-beta-cyclodextrin solution.[Pubmed:20036739]
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010 Feb 19;39(4):248-55.
Effects of cyclodextrins on crystallization of Chlorpropamide and the polymorphic transition mechanism of the drug in aqueous solution were investigated. In the presence of 2-hydroxybutyl-beta-cyclodextrin, Chlorpropamide was exclusively crystallized to metastable Form II and III polymorphs, whereas it was crystallized to stable Form A in the absence of the beta-cyclodextrin at 4 degrees C. The crystallization to metastable Form II or III polymorph was dependent upon 2-hydroxybutyl-beta-cyclodextrin concentrations employed, i.e. crystallization to Form III at a lower concentration (0.5 mM), whereas to Form II in a higher concentration (5 mM). At an intermediate concentration (2 mM), the least stable Form II crystal was initially precipitated, but it was transformed to Form III crystal. At higher temperature, Form III crystal was converted to stable Form A crystal. In aqueous solution, Chlorpropamide crystallized to stable Form A crystal consecutively through metastable Forms II and III, according to "Ostwald's Rule of Stages". 2-Hydroxybutyl-beta-cyclodextrin inhibits the transition of Form II to Form III at higher concentrations and that of Form III to Form A at lower concentrations. The results suggest that 2-hydroxybutyl-beta-cyclodextrin is useful for selective preparation of metastable Chlorpropamide polymorphs occurring during crystallization according to the Ostwald's rule.
The polymorphic phase transformations in the chlorpropamide under pressure.[Pubmed:25393056]
J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan;104(1):81-6.
The crystal structure and vibrational spectra of the Chlorpropamide have been studied by means of the X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy at pressures up to 24.6 and 4.4 GPa, respectively. Two polymorphic phase transitions, between initial orthorhombic form-A and a monoclinic form-AI at P approximately 1.2 GPa and, in additional, to another monoclinic form-AII at P approximately 3.0 GPa, were observed. At pressures above 9.6 GPa, a transformation to the amorphous phase of Chlorpropamide was revealed. The lattice parameters, unit cell volumes, and vibration modes as functions of pressure were obtained for the different polymorphic modifications of Chlorpropamide.
A high-pressure polymorph of chlorpropamide formed on hydrostatic compression of the alpha-form in saturated ethanol solution.[Pubmed:23364463]
Acta Crystallogr B. 2013 Feb;69(Pt 1):77-85.
The crystal structure of the high-pressure polymorph (alpha') of an antidiabetic drug, Chlorpropamide [4-chloro-N-(propylaminocarbonyl)benzenesulfonamide, C(10)H(13)ClN(2)O(3)S], which is formed at ~2.8 GPa from the alpha-polymorph (P2(1)2(1)2(1)) on hydrostatic compression in saturated ethanol solution, has been determined. As a result of the phase transition, the a, c and alpha parameters change jumpwise, whereas the changes in b parameter are continuous through the phase transition point. The high-pressure form is monoclinic (P2(1)11) and has Z' equal to 2, the two independent molecules differing in their conformations. The hydrogen bonds expand slightly in the high-pressure polymorph after the transition, and this expansion is interrelated with the changes in molecular conformations enabling a denser packing. The transition is reversible, but the crystal quality deteriorates as a result of multiple compression-decompression cycles, and a pseudomerohedral twinning accompanies the transformation.
Solid-state transformations in the beta-form of chlorpropamide on cooling to 100 K.[Pubmed:21422615]
Acta Crystallogr B. 2011 Apr;67(Pt 2):163-76.
A single-crystal X-ray diffraction study of the effect of cooling down to 100 K on the beta-form of Chlorpropamide, 4-chloro-N-(propylaminocarbonyl)benzenesulfonamide, has revealed reversible phase transitions at approximately 257 K and between 150 and 125 K: beta (Pbcn, Z' = 1) <--> beta(II) (P2/c, Z' = 2) <--> beta(III) (P2/n, a' = 2a, Z' = 4); the sequence corresponds to cooling. Despite changes in the space group and number of symmetry-independent molecules, the volume per molecule changes continuously in the temperature range 100-300 K. The phase transition at approximately 257 K is accompanied by non-merohedral twinning, which is preserved on further cooling and through the second phase transition, but the original single crystal does not crack. DSC (differential scanning calorimetry) and X-ray powder diffraction investigations confirm the phase transitions. Twinning disappears on heating as the reverse transformations take place. The second phase transition is related to a change in conformation of the alkyl tail from trans to gauche in 1/4 of the molecules, regularly distributed in the space. Possible reasons for the increase in Z' upon cooling are discussed in comparison to other reported examples of processes (crystallization, phase transitions) in which organic crystals with Z' > 1 have been formed. Implications for pharmaceutical applications are discussed.


