CromakalimKir6 (KATP) channel opener CAS# 94470-67-4 |
- LDN193189 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1695
CAS No.:1062368-62-0
- ASP3026
Catalog No.:BCC1372
CAS No.:1097917-15-1
- PHA-665752
Catalog No.:BCC1181
CAS No.:477575-56-7
- ALK inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1339
CAS No.:761436-81-1
- ALK inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1340
CAS No.:761438-38-4
- Golvatinib (E7050)
Catalog No.:BCC4423
CAS No.:928037-13-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 94470-67-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 443423 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H18N2O3 | M.Wt | 286.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | BRL 34915 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in DMSO | ||
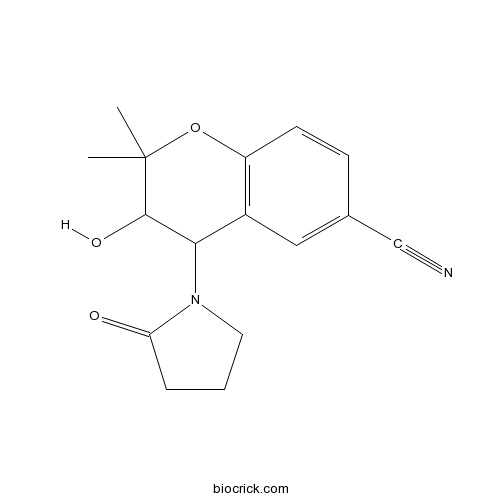
| Chemical Name | 3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydrochromene-6-carbonitrile | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C(C(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=C2)C#N)N3CCCC3=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TVZCRIROJQEVOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H18N2O3/c1-16(2)15(20)14(18-7-3-4-13(18)19)11-8-10(9-17)5-6-12(11)21-16/h5-6,8,14-15,20H,3-4,7H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Prototypical Kir6 (KATP) channel opener. Relaxes rabbit isolated portal vein with an IC50 value of 21 nM. Potent, orally active and hypotensive in vivo. |

Cromakalim Dilution Calculator

Cromakalim Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4925 mL | 17.4624 mL | 34.9247 mL | 69.8495 mL | 87.3118 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6985 mL | 3.4925 mL | 6.9849 mL | 13.9699 mL | 17.4624 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3492 mL | 1.7462 mL | 3.4925 mL | 6.9849 mL | 8.7312 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0698 mL | 0.3492 mL | 0.6985 mL | 1.397 mL | 1.7462 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1746 mL | 0.3492 mL | 0.6985 mL | 0.8731 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Syzalterin
Catalog No.:BCN3969
CAS No.:94451-48-6
- Bacopaside X
Catalog No.:BCC8126
CAS No.:94443-88-6
- BKM120
Catalog No.:BCC1279
CAS No.:944396-07-0
- JNJ 28871063 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7662
CAS No.:944342-90-9
- QS 11
Catalog No.:BCC7648
CAS No.:944328-88-5
- A-803467
Catalog No.:BCC5075
CAS No.:944261-79-4
- MJ 15
Catalog No.:BCC7852
CAS No.:944154-76-1
- Peficitinb (ASP015K, JNJ-54781532)
Catalog No.:BCC6503
CAS No.:944118-01-8
- PG 106
Catalog No.:BCC6330
CAS No.:944111-22-2
- Isomartynoside
Catalog No.:BCN4497
CAS No.:94410-22-7
- Tetrachlorohydroquinone dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN1301
CAS No.:944-78-5
- Dimethylmatairesinol
Catalog No.:BCN4496
CAS No.:943989-68-2
- Lck inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1690
CAS No.:944795-06-6
- Rhuscholide A
Catalog No.:BCN4498
CAS No.:944804-58-4
- Isodaphnoretin B
Catalog No.:BCN6913
CAS No.:944824-29-7
- Decernotinib(VX-509)
Catalog No.:BCC6456
CAS No.:944842-54-0
- Angelic anhydride
Catalog No.:BCN3411
CAS No.:94487-74-8
- 2'-Acetylacteoside
Catalog No.:BCN3409
CAS No.:94492-24-7
- Tamibarotene
Catalog No.:BCC1983
CAS No.:94497-51-5
- CYM 5541
Catalog No.:BCC6321
CAS No.:945128-26-7
- 7-Prenyljacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN7353
CAS No.:94513-60-7
- 4-Hydroxy-2-methoxyphenol 1-O-(6-O-syringoyl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1300
CAS No.:945259-61-0
- 3,4-Dihydro-6,7-(methylenedioxy)-2(1H)-quinolinone
Catalog No.:BCN1299
CAS No.:94527-34-1
- 20-Deoxocarnosol
Catalog No.:BCN3152
CAS No.:94529-97-2
4-Phenylureido/thioureido-substituted 2,2-dimethylchroman analogs of cromakalim bearing a bulky 'carbamate' moiety at the 6-position as potent inhibitors of glucose-sensitive insulin secretion.[Pubmed:27267004]
Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Oct 4;121:338-351.
The synthesis of 2,2-dimethylchromans bearing a 3/4-chloro/cyano-substituted phenylureido or phenylthioureido moiety at the 4-position and an alkoxycarbonylamino ('carbamate') group at the 6-position is described. These new analogs of the potassium channel opener (+/-)-Cromakalim were further tested on rat pancreatic islets as putative inhibitors of insulin release and on rat aorta rings as putative vasorelaxants. All compounds inhibited insulin secretion and induced a myorelaxant activity. Compound 14o [R/S-N-3-cyanophenyl-N'-(6-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-3,4-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1 -benzopyran-4-yl)urea; BPDZ 711] emerged as the most potent inhibitor of the glucose-sensitive insulin releasing process (IC50 = 0.24 muM) and displayed selectivity towards the pancreatic endocrine tissue. Radioisotopic, fluorimetric and pharmacological investigations were performed on rat pancreatic islet and rat vascular smooth muscle cells in order to decipher its mechanism of action. Our findings suggest that the mechanism of action of 14o is rather unspecific. The compound behaves as a KATP channel opener, a Ca(2+) entry blocker, and promotes an intracellular calcium translocation.
Ocular Hypotensive Effects of the ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel Opener Cromakalim in Human and Murine Experimental Model Systems.[Pubmed:26535899]
PLoS One. 2015 Nov 4;10(11):e0141783.
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is the most prevalent and only treatable risk factor for glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Unfortunately, all current therapeutics used to treat elevated IOP and glaucoma have significant and sometimes irreversible side effects necessitating the development of novel compounds. We evaluated the IOP lowering ability of the broad spectrum KATP channel opener Cromakalim. Cultured human anterior segments when treated with 2 muM Cromakalim showed a decrease in pressure (19.33 +/- 2.78 mmHg at 0 hours to 13.22 +/- 2.64 mmHg at 24 hours; p<0.001) when compared to vehicle treated controls (15.89 +/- 5.33 mmHg at 0 h to 15.56 +/- 4.88 mmHg at 24 hours; p = 0.89). In wild-type C57BL/6 mice, Cromakalim reduced IOP by 18.75 +/- 2.22% compared to vehicle treated contralateral eyes (17.01 +/- 0.32 mmHg at 0 hours to 13.82 +/- 0.37 mmHg at 24 hours; n = 10, p = 0.002). Cromakalim demonstrated an additive effect when used in conjunction with latanoprost free acid, a common ocular hypotensive drug prescribed to patients with elevated IOP. To examine KATP channel subunit specificity, Kir6.2(-/-) mice were treated with Cromakalim, but unlike wild-type animals, no change in IOP was noted. Histologic analysis of treated and control eyes in cultured human anterior segments and in mice showed similar cell numbers and extracellular matrix integrity within the trabecular meshwork, with no disruptions in the inner and outer walls of Schlemm's canal. Together, these studies suggest that Cromakalim is a potent ocular hypotensive agent that lowers IOP via activation of Kir6.2 containing KATP channels, its effect is additive when used in combination with the commonly used glaucoma drug latanoprost, and is not toxic to cells and tissues of the aqueous humor outflow pathway, making it a candidate for future therapeutic development.
Analogs of the ATP-Sensitive Potassium (KATP) Channel Opener Cromakalim with in Vivo Ocular Hypotensive Activity.[Pubmed:27367033]
J Med Chem. 2016 Jul 14;59(13):6221-31.
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel openers have emerged as potential therapeutics for the treatment of glaucoma, lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) in animal models and cultured human anterior segments. We have prepared water-soluble phosphate and dipeptide derivatives of the KATP channel opener Cromakalim and evaluated their IOP lowering capabilities in vivo. In general, the phosphate derivatives proved to be more chemically robust and efficacious at lowering IOP with once daily dosing in a normotensive mouse model. Two of these phosphate derivatives were further evaluated in a normotensive rabbit model, with a significant difference in activity observed. No toxic effects on cell structure or alterations in morphology of the aqueous humor outflow pathway were observed after treatment with the most efficacious compound, (3S,4R)-2, suggesting that it is a strong candidate for development as an ocular hypotensive agent.
The potassium channel opener cromakalim (BRL 34915) activates ATP-dependent K+ channels in isolated cardiac myocytes.[Pubmed:2456760]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):620-5.
In cardiac myocytes, Cromakalim (BRL 34915), a potassium channel opener, activates a time-independent K+ current exhibiting poor voltage-sensitivity. This effect of Cromakalim is antagonized by low concentrations of glibenclamide, a specific blocker of ATP-dependent K+ channels in cardiac cells. Direct recording of the activity of K+ channels in inside-out membrane patches, confirmed that Cromakalim is a potent activator of ATP-dependent K+ channels in cardiac myocytes.
Cromakalim, a potassium channel activator: a comparison of its cardiovascular haemodynamic profile and tissue specificity with those of pinacidil and nicorandil.[Pubmed:2468052]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12(5):535-42.
Studies have been performed to compare the cardiovascular haemodynamic profiles of the potassium channel activator, Cromakalim (BRL 34915), with those of pinacidil and nicorandil. In conscious renal hypertensive cats, Cromakalim was 10 times more potent than pinacidil as an antihypertensive agent while nicorandil was 10 times less potent than pinacidil. Cromakalim and pinacidil had a similar duration of action while nicorandil was short acting. In anaesthetised cats, hypotension evoked by intravenous infusions of Cromakalim, pinacidil, or nicorandil was associated with a decrease in mesenteric vascular resistance but only Cromakalim produced a marked reduction in renal vascular resistance. Cromakalim, pinacidil, and nicorandil were highly specific as inhibitors of tension in vascular (rabbit portal vein) (IC50 = 2.1 x 10(-8), 4.6 x 10(-8), and 1.3 x 10(-6)M, respectively,) rather than cardiac (rabbit papillary muscle), tissue. In view of its antihypertensive efficacy, specificity for vascular tissue, and beneficial effect upon renal haemodynamics, the potassium channel activator, Cromakalim, has advantages in its profile of activity compared to pinacidil and nicorandil.
Comparative effects of K+ channel blockade on the vasorelaxant activity of cromakalim, pinacidil and nicorandil.[Pubmed:2851450]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 2;152(3):331-9.
Three agents with K+ channel blocking activity, procaine, 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and tetraethylammonium (TEA), were tested for inhibition of vasorelaxation and 86Rb+ efflux induced by Cromakalim (BRL 34915), pinacidil and nicorandil in rabbit isolated mesenteric artery. The potency order for inhibition of vasorelaxation was procaine greater than 4-AP greater than TEA and for inhibition of efflux was procaine = 4-AP greater than TEA. The K+ channel blockers did not discriminate between Cromakalim, pinacidil or nicorandil on efflux but demonstrated preferential inhibition of vasorelaxation to Cromakalim greater than pinacidil greater than nicorandil. In addition, the maximum response to Cromakalim was depressed but that to pinacidil and nicorandil was not. The results confirm the role of K+ channel activation in vasorelaxation to Cromakalim, pinacidil and nicorandil, but suggest that additional mechanisms may be involved for pinacidil and, in particular, for nicorandil.


