Cudraflavone BCAS# 19275-49-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19275-49-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5319925 | Appearance | Powder |
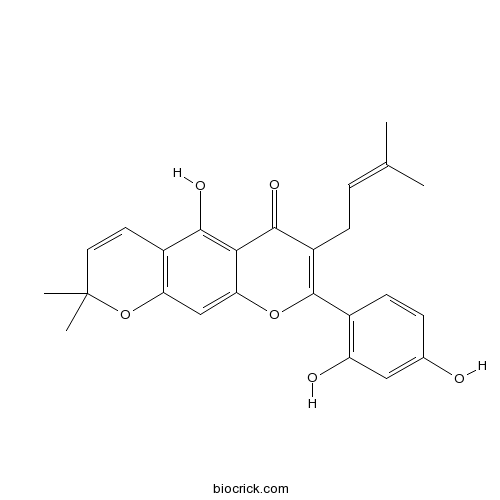
| Formula | C25H24O6 | M.Wt | 420.45 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 8-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-7-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(OC2=CC3=C(C=CC(O3)(C)C)C(=C2C1=O)O)C4=C(C=C(C=C4)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XIWCDUHPYMOFIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H24O6/c1-13(2)5-7-17-23(29)21-20(30-24(17)15-8-6-14(26)11-18(15)27)12-19-16(22(21)28)9-10-25(3,4)31-19/h5-6,8-12,26-28H,7H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Cudraflavone B has anti-proliferative activity, mouse brain monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory effects, apoptotic actions in human gastric carcinoma cells and mouse melanoma cells, and hepatoprotective activity. 2. Cudraflavone B may be a lead for the development of a potential candidate for human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. |
| Targets | MAO | COX | ROS | HO-1 | Nrf2 | PI3K | Akt | IkB | IKK |

Cudraflavone B Dilution Calculator

Cudraflavone B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3784 mL | 11.892 mL | 23.784 mL | 47.5681 mL | 59.4601 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4757 mL | 2.3784 mL | 4.7568 mL | 9.5136 mL | 11.892 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2378 mL | 1.1892 mL | 2.3784 mL | 4.7568 mL | 5.946 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0476 mL | 0.2378 mL | 0.4757 mL | 0.9514 mL | 1.1892 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0238 mL | 0.1189 mL | 0.2378 mL | 0.4757 mL | 0.5946 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-Isomangostin
Catalog No.:BCN1214
CAS No.:19275-46-8
- Lopinavir
Catalog No.:BCC3621
CAS No.:192725-17-0
- C527
Catalog No.:BCC3972
CAS No.:192718-06-2
- PD 161570
Catalog No.:BCC7765
CAS No.:192705-80-9
- H-DL-HoSer-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3242
CAS No.:1927-25-9
- 9-Benzoylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8799
CAS No.:19264-68-7
- PPADS tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6725
CAS No.:192575-19-2
- 11α-Hydroxycanrenone
Catalog No.:BCC8433
CAS No.:192569-17-8
- 9alpha,11,12-Trihydroxydrim-7-en-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN7388
CAS No.:192566-65-7
- Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1183
CAS No.:19254-69-4
- Lomeguatrib
Catalog No.:BCC1133
CAS No.:192441-08-0
- Neuropeptide SF (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5829
CAS No.:192387-39-6
- Cyclomulberrin
Catalog No.:BCN3374
CAS No.:19275-51-5
- ES 936
Catalog No.:BCC6102
CAS No.:192820-78-3
- 2-Amino-2'-nitrodiphenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8522
CAS No.:19284-81-2
- LY310762
Catalog No.:BCC5052
CAS No.:192927-92-7
- Ximelagatran
Catalog No.:BCC6382
CAS No.:192939-46-1
- ZM 323881 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5098
CAS No.:193000-39-4
- ZM323881
Catalog No.:BCC2073
CAS No.:193001-14-8
- CTS-1027
Catalog No.:BCC1502
CAS No.:193022-04-7
- Cardamonin
Catalog No.:BCN1184
CAS No.:19309-14-9
- Otamixaban
Catalog No.:BCC1827
CAS No.:193153-04-7
- cis-Moschamine
Catalog No.:BCN3901
CAS No.:193224-24-7
- 1-O-Acetyl-6alpha-O-(2-methylbutyryl)britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN7747
CAS No.:1932687-71-2
Cudarflavone B provides neuroprotection against glutamate-induced mouse hippocampal HT22 cell damage through the Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed:25061726]
Molecules. 2014 Jul 24;19(8):10818-31.
Oxidative cell damage contributes to neuronal degeneration in many central nervous system (CNS) diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and ischemia. Nrf2 signaling-mediated heme oxygenase (HO)-1 expression acts against oxidants that are thought to play a key role in the pathogenesis of neuronal diseases. Cudraflavone B is a prenylated flavone isolated from C. tricuspidata which has shown anti-proliferative activity, mouse brain monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory effects, apoptotic actions in human gastric carcinoma cells and mouse melanoma cells, and hepatoprotective activity. In this study, Cudraflavone B showed neuroprotective effects and reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibition against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity by inducing the expression of HO-1 in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Furthermore, Cudraflavone B caused the nuclear accumulation of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and increased the promoter activity of antioxidant response elements (ARE) in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. In addition, we found that the Nrf2-midiated HO-1 expression by Cudraflavone B is involved in the cell protective response and ROS reductions, and Cudraflavone B-induced expression of HO-1 was mediated through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway in HT22 cells. Our results demonstrated the potential application of naturally occurring Cudraflavone B as a therapeutic agent from neurodegenerative disease.
Prenylated and geranylated flavonoids increase production of reactive oxygen species in mouse macrophages but inhibit the inflammatory response.[Pubmed:23947936]
J Nat Prod. 2013 Sep 27;76(9):1586-91.
In this study, four prenylated and geranylated flavonoids, Cudraflavone B (1), pomiferin (2), osajin (3), and diplacone (4), were tested for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and to identify any potential relationships between chemical structure and antioxidant or anti-inflammatory properties. The selected flavonoids were examined in cell-free models to prove their ability to scavenge superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and hypochlorous acid. Further, the ability of the flavonoids to influence the formation of reactive oxygen species in the murine macrophage cell line J774.A1 was tested in the presence and absence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The ability of flavonoids to inhibit LPS-induced IkappaB-alpha degradation and COX-2 expression was used as a model for the inflammatory response. The present results indicated that the antioxidant activity was dependent on the chemical structure, where the catechol moiety is especially crucial for this effect. The most potent antioxidant activities in cell-free models were observed for diplacone (4), whereas Cudraflavone B (1) and osajin (3) showed a pro-oxidant effect in J774.A1 cells. All flavonoids tested were able to inhibit IkappaB-alpha degradation, but only diplacone (4) also down-regulated COX-2 expression.


