PPADS tetrasodium saltP2 purinergic antagonist CAS# 192575-19-2 |
- BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa)
Catalog No.:BCC2139
CAS No.:211914-51-1
- BIBR-1048
Catalog No.:BCC3738
CAS No.:211915-06-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 192575-19-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101086948 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H10N3Na4O12PS2 | M.Wt | 599.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
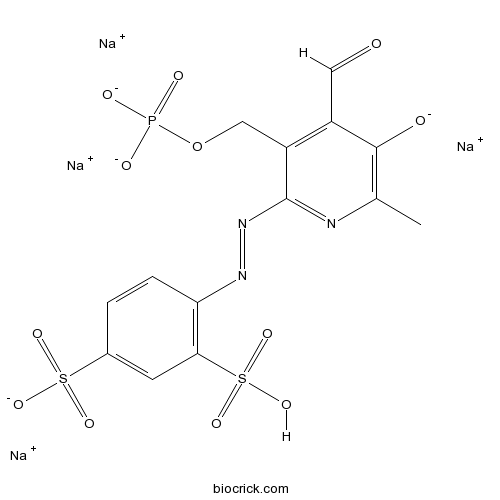
| Chemical Name | tetrasodium;4-[[4-formyl-6-methyl-5-oxido-3-(phosphonatooxymethyl)pyridin-2-yl]diazenyl]-3-sulfobenzenesulfonate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C(C(=N1)N=NC2=C(C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)O)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KURWUCJJNVPCHT-UHFFFAOYSA-J | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14N3O12PS2.4Na/c1-7-13(19)9(5-18)10(6-29-30(20,21)22)14(15-7)17-16-11-3-2-8(31(23,24)25)4-12(11)32(26,27)28;;;;/h2-5,19H,6H2,1H3,(H2,20,21,22)(H,23,24,25)(H,26,27,28);;;;/q;4*+1/p-4 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A non-selective P2 purinergic antagonist. Blocks recombinant P2X1, P2X2, P2X3, P2X5 (IC50 = 1 - 2.6 μM), native P2Y2-like (IC50 ~ 0.9 mM), and recombinant P2Y4 (IC50 ~ 15 mM) receptors. Delays onset of calcium responses to mild hypoosmotic stress in cortical slices. iso-PPADS also available. |

PPADS tetrasodium salt Dilution Calculator

PPADS tetrasodium salt Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6686 mL | 8.3431 mL | 16.6861 mL | 33.3723 mL | 41.7153 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3337 mL | 1.6686 mL | 3.3372 mL | 6.6745 mL | 8.3431 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1669 mL | 0.8343 mL | 1.6686 mL | 3.3372 mL | 4.1715 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0334 mL | 0.1669 mL | 0.3337 mL | 0.6674 mL | 0.8343 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0167 mL | 0.0834 mL | 0.1669 mL | 0.3337 mL | 0.4172 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 11α-Hydroxycanrenone
Catalog No.:BCC8433
CAS No.:192569-17-8
- 9alpha,11,12-Trihydroxydrim-7-en-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN7388
CAS No.:192566-65-7
- Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1183
CAS No.:19254-69-4
- Lomeguatrib
Catalog No.:BCC1133
CAS No.:192441-08-0
- Neuropeptide SF (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5829
CAS No.:192387-39-6
- Neuropeptide AF (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5854
CAS No.:192387-38-5
- Prazosin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2505
CAS No.:19237-84-4
- CGP 71683 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7283
CAS No.:192322-50-2
- SIB 1508Y maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7975
CAS No.:192231-16-6
- Galanganone C
Catalog No.:BCN7486
CAS No.:1922129-46-1
- Galanganone B
Catalog No.:BCN7485
CAS No.:1922129-43-8
- Galanganone A
Catalog No.:BCN7484
CAS No.:1922129-42-7
- 9-Benzoylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8799
CAS No.:19264-68-7
- H-DL-HoSer-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3242
CAS No.:1927-25-9
- PD 161570
Catalog No.:BCC7765
CAS No.:192705-80-9
- C527
Catalog No.:BCC3972
CAS No.:192718-06-2
- Lopinavir
Catalog No.:BCC3621
CAS No.:192725-17-0
- 3-Isomangostin
Catalog No.:BCN1214
CAS No.:19275-46-8
- Cudraflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN8067
CAS No.:19275-49-1
- Cyclomulberrin
Catalog No.:BCN3374
CAS No.:19275-51-5
- ES 936
Catalog No.:BCC6102
CAS No.:192820-78-3
- 2-Amino-2'-nitrodiphenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8522
CAS No.:19284-81-2
- LY310762
Catalog No.:BCC5052
CAS No.:192927-92-7
- Ximelagatran
Catalog No.:BCC6382
CAS No.:192939-46-1
Critical role of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in astrocytic Ca2+ signaling events elicited by cerebral edema.[Pubmed:21187412]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 11;108(2):846-51.
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is a primary influx route for water during brain edema formation. Here, we provide evidence that brain swelling triggers Ca(2+) signaling in astrocytes and that deletion of the Aqp4 gene markedly interferes with these events. Using in vivo two-photon imaging, we show that hypoosmotic stress (20% reduction in osmolarity) initiates astrocytic Ca(2+) spikes and that deletion of Aqp4 reduces these signals. The Ca(2+) signals are partly dependent on activation of P2 purinergic receptors, which was judged from the effects of appropriate antagonists applied to cortical slices. Supporting the involvement of purinergic signaling, osmotic stress was found to induce ATP release from cultured astrocytes in an AQP4-dependent manner. Our results suggest that AQP4 not only serves as an influx route for water but also is critical for initiating downstream signaling events that may affect and potentially exacerbate the pathological outcome in clinical conditions associated with brain edema.
Investigation of the actions of PPADS, a novel P2x-purinoceptor antagonist, in the guinea-pig isolated vas deferens.[Pubmed:8019769]
Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;111(3):913-7.
1. Pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS) was investigated for its ability to act as an antagonist at P2x-purinoceptors which mediate neurogenic excitatory junction potentials (e.j.ps) and contractions in the guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. 2. PPADS (10(-7) M) caused a small potentiation of the phasic, predominantly purinergic component of contractions evoked by symapthetic nerve stimulation, but higher concentrations of PPADS (3 x 10(-6)-3 x 10(-5) M) elicited a substantial and significant concentration-dependent inhibition. In contrast, over the same concentration-range, PPADS had no effect on the tonic, predominantly noradrenergic phase. 3 PPADS (3 x 10(-5) M) also inhibited contractile responses to exogenous alpha,beta-methyleneATP (10(-8)-10(-3)M), a P2x-purinoceptor agonist, without affecting the responses to exogenous noradrenaline (10(-8)-10(-3) M), carbachol (10(-5) M) or histamine (10(-4) M). 4. PPADS (10(-7)-3 x 10(-5) M) produced a concentration-dependent reduction in e.j.p. magnitude and resting membrane potential. The maximum effect was seen at 10(-5) M PPADS, which reduced e.j.p. magnitude from 13.7 +/- 0.6 mV (n = 12) to 1.8 +/- 0.7 mV (n = 12) and membrane potential from -64.8 +/- 0.6 mV (n = 51) to -55.0 +/- 1.8 mV (n = 12). 5. The PPADS-induced depolarization was not inhibited by the P2x-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin (10(-4) M). This indicates that the depolarization was not due to an agonist action of PPADS at P2x-purinoceptors. 6. The results support the proposal that PPADS is a selective antagonist at P2x purinoceptors as opposed to non-P2-purinoceptors in the guinea-pig vas deferens, but its ability to cause membrane depolarization independently of P2x-purinoceptors and also, at a low concentration, to potentiate the phasic component of the neurogenic contraction indicates that it has other actions.
Selective antagonism by PPADS at P2X-purinoceptors in rabbit isolated blood vessels.[Pubmed:8019770]
Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;111(3):923-9.
1. Pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS), a P2-purinoceptor antagonist, was investigated for its ability to antagonize: (1) P2X-purinoceptor-mediated contractions of the rabbit central ear artery and saphenous artery evoked by either alpha,beta-methylene ATP (alpha,beta-MeATP) or electrical field stimulation (EFS); (2) P2Y-purinoceptor-mediated relaxations of the rabbit mesenteric artery; (3) endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent, P2Y-purinoceptor-mediated relaxations of the rabbit aorta. 2. alpha,beta-MeATP (0.1-100 microM) caused concentration-dependent contractions of the rabbit ear and saphenous arteries. The negative log[alpha,beta-MeATP] that produced a contraction equivalent to the EC25 for noradrenaline (ear artery) or histamine (saphenous artery) in the absence of PPADS was 6.60 +/- 0.18 (9) and 6.18 +/- 0.17 (9) in the ear artery and saphenous artery, respectively. These effects of exogenous alpha,beta-MeATP were concentration-dependently inhibited by PPADS (1-30 microM). In the ear artery, the negative log[alpha,beta-MeATP] producing a contractile response equivalent to the EC25 of noradrenaline, in the presence of PPADS at 1, 3 and 10 microM was 6.16 +/- 0.18 (8), 5.90 +/- 0.18 (8) and 4.72 +/- 0.36 (8), respectively (P < 0.01). In the saphenous artery, the negative log[alpha,beta-MeATP] values equivalent to the EC25 for histamine in the presence of PPADS at concentrations of 1, 3, 10 and 30 microM were 5.90 +/- 0.19 (8), 5.73 +/- 0.16 (8), 4.99 +/- 0.14 (8) and 4.51 +/- 0.13 (8), respectively (P < 0.01). 3. PPADS at a concentration of 1 microM had no effect on contractions of the ear artery evoked by EFS (4-64 Hz; 1 microM phentolamine present). At higher concentrations (3-30 MicroM) it caused concentration dependent inhibition of neurogenic contractions. In the saphenous artery, PPADS (1-30 MicroM) concentration-dependently inhibited contractions evoked by EFS at frequencies of 4, 8 and 16 Hz. Contractions evoked by EFS at frequencies of 32 and 64 Hz were significantly inhibited by PPADS only at concentrations of 10 and 30 MicroM.4. PPADS (30 MicroM) had no effect on relaxations to 2-methylthio ATP (3 nM-3 MicroM) in rabbit mesenteric artery and to ATP (1 MicroM-I mM) in rabbit aorta (with endothelium intact or removed). In addition,PPADS (30 MicroM) had no significant influence on the contractile potency of noradrenaline and histamine in rabbit ear and saphenous artery, respectively.5. In conclusion, these results support the evidence that PPADS is a selective antagonist of P2X-purinoceptor-mediated responses.
PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses.[Pubmed:1330591]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):217-9.
We have characterized PPADS (pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid) as a novel antagonist which selectively blocks P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses in rabbit vas deferens at pre- and postjunctional sites. PPADS did not interact with alpha 1-adrenoceptors, muscarinic M2 and M3 receptors, histamine H1 and adenosine A1 receptors. Thus, PPADS is a novel and useful pharmacological tool to study co-transmission in tissues where ATP and co-existing neurotransmitters act in concert.


