DaunorubicinDNA topoisomerase II inhibitor CAS# 20830-81-3 |
- Cefoselis
Catalog No.:BCC4092
CAS No.:122841-10-5
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Voreloxin
Catalog No.:BCC2044
CAS No.:175414-77-4
- Tigecycline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4228
CAS No.:197654-04-9
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20830-81-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 30323 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H29NO10 | M.Wt | 527.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | RP13057; Daunomycin; Rubidomycin | ||
| Solubility | >83.3mg/mL in DMSO | ||
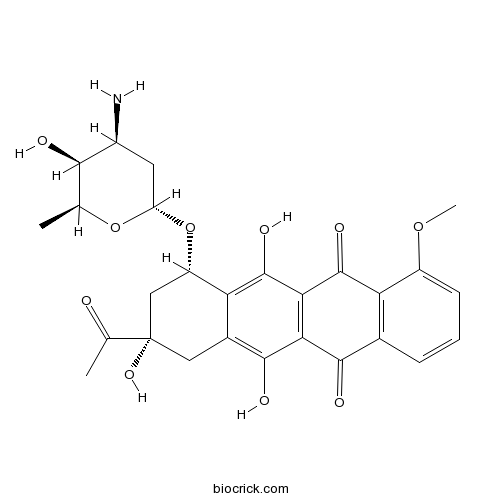
| Chemical Name | (7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2CC(CC3=C(C4=C(C(=C23)O)C(=O)C5=C(C4=O)C=CC=C5OC)O)(C(=O)C)O)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H29NO10/c1-10-22(30)14(28)7-17(37-10)38-16-9-27(35,11(2)29)8-13-19(16)26(34)21-20(24(13)32)23(31)12-5-4-6-15(36-3)18(12)25(21)33/h4-6,10,14,16-17,22,30,32,34-35H,7-9,28H2,1-3H3/t10-,14-,16-,17-,22+,27-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Daunorubicin is a topoisomerase II inhibitor.In Vitro:The mean IC50 value is 0.04 μM for Daunorubicin (Dnr) in Molt-4 cells. Daunorubicin belongs to the anthracyclines, a group of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics. The cytotoxic effects of anthracyclines are caused by DNA intercalation and the ability to interfere with DNA transcription and replication by inhibiting Topoisomerase II as well as by producing reactive oxygen species[2] Daunorubicin inhibits of both DNA and RNA syntheses in HeLa cells over a concentration range of 0.2 through 2 μM. The IC50 value is 0.4 μM for Daunorubicin (Dnr) in human pancreatic cell line L3.6[3].In Vivo:Urinary protein excretion, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level are significantly increased in group Daunorubicin (3 mg/kg, i.v.) compared with those in group Control. Administration of Daunorubicin (DNR) causes a significant increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) level in renal tissue compared with that in the control group[4]. References: | |||||

Daunorubicin Dilution Calculator

Daunorubicin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8957 mL | 9.4783 mL | 18.9566 mL | 37.9133 mL | 47.3916 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3791 mL | 1.8957 mL | 3.7913 mL | 7.5827 mL | 9.4783 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1896 mL | 0.9478 mL | 1.8957 mL | 3.7913 mL | 4.7392 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0379 mL | 0.1896 mL | 0.3791 mL | 0.7583 mL | 0.9478 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.019 mL | 0.0948 mL | 0.1896 mL | 0.3791 mL | 0.4739 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Daunorubicin is an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II [1].
Daunorubicin is an anthracycline antibiotic. It is also used as an effective chemotherapeutic agent against tumors especially acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphocytic leukaemia. Daunorubicin can affect the metabolism and synthesis of DNA and RNA. In the in vitro assay, daunorubicin inhibits the incorporation of thymidine and uridine into L1210 cells. It also inhibits the incorporation of labeled precursors into the isolated DNA and RNA from incubated cells. When treated with leukemic cells isolated from acute lymphocytic leukemia patients, daunorubicin significantly inhibits the biosynthesis of the DNA and RNA macromolecules [2, 3].
References:
[1] Hande K R. Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. European Journal of Cancer, 1998, 34(10): 1514-1521.
[2] Momparler R L, Karon M, Siegel S E, et al. Effect of adriamycin on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in cell-free systems and intact cells. Cancer Research, 1976, 36(8): 2891-2895.
[3] Meriwether W D, Bachur N R. Inhibition of DNA and RNA metabolism by daunorubicin and adriamycin in L1210 mouse leukemia. Cancer research, 1972, 32(6): 1137-1142.
- Digoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5359
CAS No.:20830-75-5
- ZM336372
Catalog No.:BCC3875
CAS No.:208260-29-1
- Zooxanthellabetaine A
Catalog No.:BCN1771
CAS No.:208256-89-7
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Nocistatin (bovine)
Catalog No.:BCC5703
CAS No.:208253-85-4
- Strictosidine
Catalog No.:BCN2641
CAS No.:20824-29-7
- Z-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2742
CAS No.:20806-43-3
- Hemokinin 1 (mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC5774
CAS No.:208041-90-1
- 4'-O-Methylbroussochalcone B
Catalog No.:BCN4908
CAS No.:20784-60-5
- Isobavachalcone
Catalog No.:BCN5415
CAS No.:20784-50-3
- Propofol
Catalog No.:BCC9130
CAS No.:2078-54-8
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-heptadien-5-one
Catalog No.:BCN6470
CAS No.:207792-17-4
- Gentiopicroside
Catalog No.:BCN4909
CAS No.:20831-76-9
- Ethyl 4-(rhamnosyloxy)benzylcarbamate
Catalog No.:BCN7635
CAS No.:208346-80-9
- Stigmastane-3,5,6-triol
Catalog No.:BCN4910
CAS No.:20835-91-0
- Protoaescigenin
Catalog No.:BCC8240
CAS No.:20853-07-0
- Micafungin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC1750
CAS No.:208538-73-2
- H-Tle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2659
CAS No.:20859-02-3
- Primulic Acid 2
Catalog No.:BCC8237
CAS No.:208599-88-6
- Berberine
Catalog No.:BCN4911
CAS No.:2086-83-1
- Boc-His(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3399
CAS No.:20866-46-0
- Ermanin
Catalog No.:BCN4912
CAS No.:20869-95-8
- (1R,1'S,3'R/1R,1'R,3'S)-L-054,264
Catalog No.:BCC7364
CAS No.:208706-12-1
- Saikosaponin D
Catalog No.:BCN1088
CAS No.:20874-52-6
The efficacy of WGA modified daunorubicin anti-resistant liposomes in treatment of drug-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer.[Pubmed:28277825]
J Drug Target. 2017 Jul;25(6):541-553.
BACKGROUND: Breast cancer is the most common malignancy and remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in female. Chemotherapy failure of breast cancer is mainly associated with multidrug resistance of cancer cells. PURPOSE: The WGA modified Daunorubicin anti-resistant liposomes were developed for circumventing the multidrug resistance and eliminating cancer cells. METHODS: WGA was modified on liposomal surface for increasing the intracellular uptake. Tetrandrine was inserted into the phospholipid bilayer for reversing cancer drug-resistance, and Daunorubicin was encapsulated in liposomal aqueous core as an anticancer agent. Evaluations were performed on MCF-7 cells, MCF-7/ADR cells and xenografts of MCF-7/ADR cells. RESULTS: In vitro results showed that WGA modified Daunorubicin anti-resistant liposomes exhibited suitable physicochemical properties, significantly increased intracellular uptake in both MCF-7 cells and MCF-7/ADR cells, and circumvented the multidrug resistance via inhibiting P-gp. In vivo results demonstrated that the targeting liposomes showed a long-circulatory effect in blood system, and could remarkably accumulate at the tumor location. The involved action mechanisms for the enhanced anticancer efficacy were activation of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax and Bok), apoptotic enzymes (caspase 8, caspase 9 and caspase 3). CONCLUSION: The established WGA modified Daunorubicin anti-resistant liposomes could provide a potential strategy for treating resistant MCF-7 breast cancer.
The daunorubicin interplay with mimetic model membranes of cancer cells: A biophysical interpretation.[Pubmed:28153496]
Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017 May;1859(5):941-948.
The present work aimed to study the interactions between the anticancer drug Daunorubicin and lipid membrane mimetic models of cancer cells composed by their most representative classes of phospholipids, with different degrees of complexity. Regarding these anticancer drug-membrane interactions, several biophysical parameters were assessed using liposomes (LUVs) composed of different molar ratios of DMPC, DOPC, DPPS, DOPE and Chol. In this context, Daunorubicin's membrane concentration was determined by calculating its partition coefficient (Kp) between liposomes and water using derivative UV/vis spectrophotometry at 37 degrees C and pH6.3, a typical tumoral microenvironment. Characterization of the zeta potential of such model membranes, in both the absence and presence of the compound, was accomplished through Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS). Fluorescence quenching studies, which determine the location of the drug within the bilayer, were carried out using liposomes labelled with DPH and TMA-DPH, fluorescent probes with known membrane position. Temperature dependent steady-state anisotropy assays were also performed to measure the Daunorubicin effect on the membranes' microviscosity. The overall results support that Daunorubicin permeation depends on the phospholipid membrane composition and causes alterations in the biophysical properties of the bilayers, namely in the membrane fluidity. The interaction of Daunorubicin with the studied phospholipids is mainly driven by electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. These insights demonstrated that not only membranes can affect Daunorubicin accumulation in cells but the compound can alter the properties of membranes. The changes produced by Daunorubicin on the lipid structure may constitute an additional mechanism of action, which might lead to modifications in the location and, consequently, the activity of membrane signaling proteins.
What Is the Best Daunorubicin Dose and Schedule for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Induction?[Pubmed:28154969]
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Jan;18(1):3.
OPINION STATEMENT: Daunorubicin dose intensification for induction in acute myeloid leukemia has been reported as an effective strategy in recent trials to improve patient outcomes without worsening treatment-related toxicity. Based on available evidence, 90 mg/m(2) of Daunorubicin given for three consecutive days (cumulative dose 270 mg/m(2)) as a part of the "7 + 3" induction regimen along with cytarabine is the most effective dose to achieve a complete remission as well as improve survival in patients who can tolerate it. This should be considered strongly in younger patients (less than 65 years of age and especially in those less than 50 years) irrespective of cytogenetic risk (likely more beneficial for favorable and intermediate risk) or molecular mutations (definitely in those with NPM1 or FLT3-ITD mutations). Among older acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (>65 years), using a higher dose of Daunorubicin may not improve survival. It is unclear if Daunorubicin at 60 mg/m(2) for 3 days is as efficacious as the 90 mg/m(2) dose but may be used when there are concerns about tolerability of the higher dose. Although 90 mg/m(2) has no more adverse effects compared to 45 mg/m(2) of Daunorubicin, increasing dosage beyond a cumulative dose of 330 mg/m(2) is detrimental due to increase in early mortality. Idarubicin 12 mg/m(2) for 3 days is an alternative with the possibility of better long-term outcomes. Elderly patients with AML and those with unfavorable cytogenetics, secondary, or treatment-related disease remain challenging to treat. All patients should be treated on clinical trials when available.
Downregulation of myogenic microRNAs in sub-chronic but not in sub-acute model of daunorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.[Pubmed:28303410]
Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Aug;432(1-2):79-89.
Cardiac muscle-related microRNAs play important roles in cardiac development and disease by translational silencing of mRNAs, the dominant mechanism of microRNA action. To test whether they could be involved in Daunorubicin-associated cardiomyopathy (DACM), we determined expression patterns of myomiRs in two distinct models of DACM. We used 10-12 weeks old male Wistar rats. In the sub-acute model, rats were administered with six doses of Daunorubicin (DAU-A, 3 mg/kg, i.p., every 48 h). Rats were sacrificed two days after the last dose. In the sub-chronic model, anaesthetized rats were administered a single dose of Daunorubicin (15 mg/kg, i.v., DAU-C). Age-matched controls (CON) received vehicle. Rats were sacrificed eight weeks later. Left ventricular (LV) functions (LV pressure, rate of pressure development, +dP/dt and decline, -dP/dt) were measured using left ventricular catheterization. Expressions of myomiRs (miR-208a, miR-499, miR-1 and miR-133a), markers of cardiac failure (atrial and brain natriuretic peptides genes; Nppa and Nppb) and myosin heavy chain genes (Myh6, Myh7, Myh7b) in cardiac tissue were determined by RT-PCR. Protein expression of gp91phox NADPH oxidase subunit was detected by immunoblotting. Both DAU groups exhibited a similar depression of LV function, and LV weight reduction, accompanied by an upregulation of natriuretic peptides, and a decrease of Myh6 to total Myh ratio (-18% in DAU-A and - 25% in DAU-C, as compared to controls; both P < 0.05). DAU-C, but not DAU-A rats had a 35% mortality rate and exhibited a significantly increased gp91phox expression (DAU-C: 197 +/- 33 versus CON-C: 100 +/- 11; P < 0.05). Interestingly, myomiRs levels were only reduced in DAU-C compared to CON-C (miR-208: -45%, miR-499: -30%, miR-1: -29%, miR- and miR133a: -25%; all P < 0.05) but were unaltered in DAU-A. The lack of myomiRs expression, particularly in sub-chronic model, suggests the loss of control of myomiRs network on late progression of DACM. We suppose that the poor inhibition of mRNA targets might contribute to chronic DACM.


