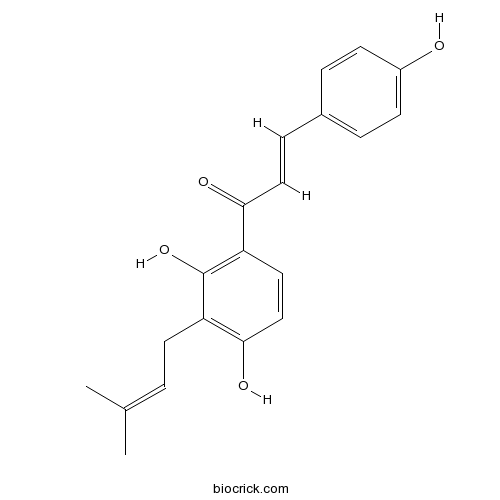
IsobavachalconeDiverse biological activity compound CAS# 20784-50-3 |
- GDC-0068 (RG7440)
Catalog No.:BCC1271
CAS No.:1001264-89-6
- MK-2206 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1274
CAS No.:1032350-13-2
- AZD5363
Catalog No.:BCC1073
CAS No.:1143532-39-1
- A-443654
Catalog No.:BCC1321
CAS No.:552325-16-3
- AKT inhibitor VIII
Catalog No.:BCC1334
CAS No.:612847-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20784-50-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281255 | Appearance | Yellow-orange powder |
| Formula | C20H20O4 | M.Wt | 324.37 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Corylifolinin; Isobacachalcone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 11 mg/mL (33.91 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-1-[2,4-dihydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C=CC(=C1O)C(=O)C=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DUWPGRAKHMEPCM-IZZDOVSWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20O4/c1-13(2)3-9-16-19(23)12-10-17(20(16)24)18(22)11-6-14-4-7-15(21)8-5-14/h3-8,10-12,21,23-24H,9H2,1-2H3/b11-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Isobavachalcone has anti-cancer, anthelmintic, antibacterial, aphrodisiac, anti-inflammatory, astringent and antiplatelet activities, Isobavachalcone can induce apoptotic cell death in neuroblastoma via the mitochondrial pathway; it can significantly inhibit both oligomerization and fibrillization of Aβ42; it can suppress inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression induced by macrophage-activating lipopeptide 2-kDa, polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid, or lipopolysaccharide. |
| Targets | NF-kB | IFN-γ | TLR | Beta Amyloid | NOS | PARP | Caspase | PKC | Akt |
| In vitro | Isobavachalcone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced ICAM-1 expression in brain endothelial cells through blockade of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 25704611]Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 5;754:11-8.Inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various cerebral diseases. Thus, control of brain inflammation is regarded as one of the important therapeutic strategies for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer׳s disease and stroke. Isobavachalcone, a flavonoid from Psoralea corylifolia, is known to possess a wide spectrum of biological activities and is expected to be useful in preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases. However, very little is known regarding its effects on cerebral inflammation.
Autophagy inhibition enhances isobavachalcone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma cells.[Pubmed: 22824846 ]Int J Mol Med. 2012 Oct;30(4):939-44.Despite recent advancements in therapeutic drugs, multiple myeloma remains an incurable disease.
Efflux pumps are involved in the defense of Gram-negative bacteria against the natural products isobavachalcone and diospyrone.[Pubmed: 20160051]Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 May;54(5):1749-52.The activities of two naturally occurring compounds, Isobavachalcone and diospyrone, against documented strains and multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacterial isolates were evaluated.
Abrogation of Akt signaling by Isobavachalcone contributes to its anti-proliferative effects towards human cancer cells.[Pubmed: 20167420 ]Cancer Lett. 2010 Aug 28;294(2):167-77.Akt signaling pathway has attracted much attention as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Herein, we report that Isobavachalcone (IBC), a natural chalcone, potently abrogates Akt signaling and exerts anti-proliferative effects on several human cancer cell lines.
|
| Kinase Assay | Isobavachalcone and bavachinin from Psoraleae Fructus modulate Aβ42 aggregation process through different mechanisms in vitro.[Pubmed: 23907009]FEBS Lett. 2013 Sep 17;587(18):2930-5.Spontaneous aggregation of Aβ is a key factor in the development of Alzheimer's disease. In searching for Aβ aggregation inhibitors from traditional Chinese herbal medicines, we identified two active compounds from Psoraleae Fructus, namely Isobavachalcone and bavachinin.
We further demonstrated that the two compounds modulate Aβ42 aggregation process through different mechanisms. |
| Cell Research | Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei, induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma.[Pubmed: 17917255]Inhibitory effects of bakuchiol, bavachin, and isobavachalcone isolated from Piper longum on melanin production in B16 mouse melanoma cells.[Pubmed: 20622433 ]Isobavachalcone suppresses expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase induced by Toll-like receptor agonists.[Pubmed: 23164691]Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Jan;15(1):38-41.Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play an important role by recognizing many pathogen-associated molecular patterns and inducing innate immunity. Dysregulated activation of TLR signaling pathways induces the activation of various transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κB, leading to the induction of pro-inflammatory gene products such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS).
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(7):1504-6.An EtOH extract of fruits of Piper longum was found to exhibit a potent inhibitory effect against alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)-induced melanin production in B16 mouse melanoma cells.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Oct;30(10):1878-83.Six chalcones from Angelica keiskei KOIDZUMI (Ashitaba in Japanese) and two chalcones from Humulus lupulus L. (hop) were examined for their cytotoxicity in two human neuroblastoma cell lines (IMR-32 and NB-39) and normal cells (primary culture of rat cerebellar granule cells) by [3-(4,5)-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay.
|

Isobavachalcone Dilution Calculator

Isobavachalcone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0829 mL | 15.4145 mL | 30.829 mL | 61.658 mL | 77.0725 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6166 mL | 3.0829 mL | 6.1658 mL | 12.3316 mL | 15.4145 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3083 mL | 1.5414 mL | 3.0829 mL | 6.1658 mL | 7.7072 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0617 mL | 0.3083 mL | 0.6166 mL | 1.2332 mL | 1.5414 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0308 mL | 0.1541 mL | 0.3083 mL | 0.6166 mL | 0.7707 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Neuroblastoma, the most common solid extracranial neoplasm in children, originates from embryonic neural crest cells that usually form the sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla. Isobavachalcone may be applicable as an efficacious and safe drug for the treatment of neuroblastoma.
In vitro: Six chalcones from Angelica keiskei and two chalcones from Humulus lupulus L. (hop) were examined for their cytotoxicity in two human neuroblastoma cell lines (IMR-32 and NB-39) and normal cells (primary culture of rat cerebellar granule cells) by MTT assay. All chalcones exhibited cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma cells, and two of them (isobavachalcone and xanthoangelol H) had no effect on normal cells even at high concentration (10-4M) exposure. Western blot analysis showed that isobavachalcone significantly reduced pro-caspase-3 and pro-caspase-9, and subsequently increased the level of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in both neuroblastoma cell lines. Moreover, Bax was markedly induced by isobavachalcone application [1].
In vivo: After oral administration of IBC (80 mg/kg) to 6 rats, plasma con-centrations of IBC were determined by the described LC–MS/MSmethod. The mean plasma concentration–time profiles (n = 6) are deternimned. The area under the plasma concentration–timecurve (AUC) 1583.1 ng/mL h, average dwell time (MRT) 5.78 h, half-life (t1/2) 6.15 h, peak time (Tmax) 2.25 h, plasma clearance (CL/F) 9.86 L/h , apparent volume of distribution(V/F) 90.34 L, and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) 351.2 ng/mL [2].
Clinical trial: Currently no clinical data are available.
References:
[1] Nishimura R, Tabata K, Arakawa M, Ito Y, Kimura Y, Akihisa T, Nagai H, Sakuma A, Kohno H, Suzuki T. Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei, induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(10):1878-83.
[2] Ma T, Nie LJ, Li HM, Huo Q, Zhang YX, Wu CZ. Determination of isobavachalcone in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;107:50-5.
- Propofol
Catalog No.:BCC9130
CAS No.:2078-54-8
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-heptadien-5-one
Catalog No.:BCN6470
CAS No.:207792-17-4
- 5-hydroxymethyl Tolterodine (PNU 200577, 5-HMT, 5-HM)
Catalog No.:BCC4583
CAS No.:207679-81-0
- HS 014
Catalog No.:BCC5819
CAS No.:207678-81-7
- TPT-260 Dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5172
CAS No.:2076-91-7
- H-Phe(4-NO2)-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3273
CAS No.:207591-86-4
- SB 203186 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5673
CAS No.:207572-69-8
- iso-PPADS tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6749
CAS No.:207572-67-6
- Pirlindole mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC6764
CAS No.:207572-66-5
- (±)-1-(1,2-Diphenylethyl)piperidine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6619
CAS No.:207461-99-2
- BTCP maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6753
CAS No.:207455-25-2
- L-693,403 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC5657
CAS No.:207455-21-8
- 4'-O-Methylbroussochalcone B
Catalog No.:BCN4908
CAS No.:20784-60-5
- Hemokinin 1 (mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC5774
CAS No.:208041-90-1
- Z-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2742
CAS No.:20806-43-3
- Strictosidine
Catalog No.:BCN2641
CAS No.:20824-29-7
- Nocistatin (bovine)
Catalog No.:BCC5703
CAS No.:208253-85-4
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Zooxanthellabetaine A
Catalog No.:BCN1771
CAS No.:208256-89-7
- ZM336372
Catalog No.:BCC3875
CAS No.:208260-29-1
- Digoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5359
CAS No.:20830-75-5
- Daunorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC4115
CAS No.:20830-81-3
- Gentiopicroside
Catalog No.:BCN4909
CAS No.:20831-76-9
- Ethyl 4-(rhamnosyloxy)benzylcarbamate
Catalog No.:BCN7635
CAS No.:208346-80-9
Efflux pumps are involved in the defense of Gram-negative bacteria against the natural products isobavachalcone and diospyrone.[Pubmed:20160051]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 May;54(5):1749-52.
The activities of two naturally occurring compounds, Isobavachalcone and diospyrone, against documented strains and multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacterial isolates were evaluated. The results indicated that the two compounds exhibited intrinsic antibacterial activity against several Gram-negative bacteria, and their activities were significantly improved in the presence of an efflux pump inhibitor (MIC values decreased to below 10 microg/ml). In addition, the activities of Isobavachalcone and diospyrone against various strains exhibiting deletions of the major efflux pump components (AcrAB, TolC) were significantly increased. The overall results indicate that Isobavachalcone and diospyrone could be candidates for the development of new drugs against MDR strains and that their use in combination with efflux pump inhibitors reinforces their activity.
Isobavachalcone suppresses expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase induced by Toll-like receptor agonists.[Pubmed:23164691]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Jan;15(1):38-41.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play an important role by recognizing many pathogen-associated molecular patterns and inducing innate immunity. Dysregulated activation of TLR signaling pathways induces the activation of various transcription factors such as nuclear factor-kappaB, leading to the induction of pro-inflammatory gene products such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). The present study investigated the effect of Isobavachalcone (IBC), a natural chalcone component of Angelica keiskei, on inflammation by modulating iNOS expression induced by TLR agonists in murine macrophages. IBC suppressed iNOS expression induced by macrophage-activating lipopeptide 2-kDa, polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid, or lipopolysaccharide. These results indicate the potential of IBC as a potent anti-inflammatory drug.
Inhibitory effects of bakuchiol, bavachin, and isobavachalcone isolated from Piper longum on melanin production in B16 mouse melanoma cells.[Pubmed:20622433]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(7):1504-6.
An EtOH extract of fruits of Piper longum was found to exhibit a potent inhibitory effect against alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)-induced melanin production in B16 mouse melanoma cells. Bioassay-directed fractionation led to the isolation of prenylated phenolic compounds bakuchiol, bavachin, and Isobavachalcone. These compounds and the crude extract of the fruits of P. longum may have suppressive effects against pigmentation by melanin in the skin.
Isobavachalcone and bavachinin from Psoraleae Fructus modulate Abeta42 aggregation process through different mechanisms in vitro.[Pubmed:23907009]
FEBS Lett. 2013 Sep 17;587(18):2930-5.
Spontaneous aggregation of Abeta is a key factor in the development of Alzheimer's disease. In searching for Abeta aggregation inhibitors from traditional Chinese herbal medicines, we identified two active compounds from Psoraleae Fructus, namely Isobavachalcone and bavachinin. We further demonstrated that the two compounds modulate Abeta42 aggregation process through different mechanisms. Isobavachalcone significantly inhibits both oligomerization and fibrillization of Abeta42, whereas bavachinin inhibits fibrillization and leads to off-pathway aggregation. Both of the compounds attenuated Abeta42-induced toxicity in a SH-SY5Y cell model. These findings may provide valuable information for new drug development and Alzheimer's therapy in the future.
Abrogation of Akt signaling by Isobavachalcone contributes to its anti-proliferative effects towards human cancer cells.[Pubmed:20167420]
Cancer Lett. 2010 Aug 28;294(2):167-77.
Akt signaling pathway has attracted much attention as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Herein, we report that Isobavachalcone (IBC), a natural chalcone, potently abrogates Akt signaling and exerts anti-proliferative effects on several human cancer cell lines. Modeling results from the Sybyl/FlexiDock program suggest that IBC potentially binds to the ATP-binding pocket of Akt, which is confirmed by the observations that IBC inhibits Akt1 kinase in vitro. Further studies reveal that IBC significantly abates Akt phosphorylation at Ser-473 and Akt kinase activity in cells, which subsequently leads to inhibition of Akt downstream substrates and evokes significant levels of apoptosis associated with mitochondria pathway.
Isobavachalcone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced ICAM-1 expression in brain endothelial cells through blockade of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathways.[Pubmed:25704611]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 5;754:11-8.
Inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various cerebral diseases. Thus, control of brain inflammation is regarded as one of the important therapeutic strategies for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers disease and stroke. Isobavachalcone, a flavonoid from Psoralea corylifolia, is known to possess a wide spectrum of biological activities and is expected to be useful in preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases. However, very little is known regarding its effects on cerebral inflammation. In this study, we examined the effect of Isobavachalcone on leukocyte adhesion and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression in brain endothelial cells activated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and explored the possible mechanisms involved. Isobavachalcone significantly down-regulated LPS-induced ICAM-1 expression and leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and suppressed NF-kappaB activity which is implicated in the expression of ICAM-1. It attenuated ICAM-1 expression as well as NF-kappaB transcriptional activity induced by macrophage-activating lipopeptide 2-kDa (MALP-2) or polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid (poly[I:C]). Isobavachalcone also down-regulated LPS or poly[I:C]-induced expression of IFN-beta, which can indirectly activate NF-kappaB. These data imply that Isobavachalcone can modulate both MyD88-dependent and TRIF-dependent signaling of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Taken together, our data suggest that Isobavachalcone inhibits LPS-induced ICAM-1 expression and leukocyte adhesion to brain endothelial cell by blocking TLR4 signaling and thus, has the potential to ameliorate neuronal injury in brain diseases associated with inflammation.
Autophagy inhibition enhances isobavachalcone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma cells.[Pubmed:22824846]
Int J Mol Med. 2012 Oct;30(4):939-44.
Despite recent advancements in therapeutic drugs, multiple myeloma remains an incurable disease. Therefore, a more effective treatment is urgently required. In this study, we show that Isobavachalcone (IBC), a natural chalcone compound, induces apoptosis- and autophagy-related cell death in myeloma cells. The inhibition of autophagy by knocking down beclin-1 or by using autophagy inhibitors, such as 3-methyladenine, bafilomycin A and chloroquine significantly enhanced IBC-induced cell death, as demonstrated by the increased number of Annexin V-positive cells. Moreover, we demonstrate that the collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential contributes to chloroquine and IBC-induced cell death, which is accompanied by the activation of caspase-9, and -3, the cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and the proteolytic activation of protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta). Furthermore, the inhibition of the activation of PKCdelta by rottlerin, an inhibitor of PKCdelta, not only suppressed the activation of PKCdelta, but also the apoptosis induced by the co-treatment of chloroquine and IBC, indicating the involvement of PKCdelta in chloroquine plus IBC-induced cell death. Finally, the combination of chloroquine and IBC had little effect on the viability of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells. As both chloroquine and IBC have been shown to be relatively specific for cancer cells, the combination of these two agents at non-toxic or sub-toxic concentrations represents an attractive novel regimen for myeloma treatment and warrants further investigation in preclinical and clinical studies.
Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei, induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:17917255]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Oct;30(10):1878-83.
Six chalcones from Angelica keiskei KOIDZUMI (Ashitaba in Japanese) and two chalcones from Humulus lupulus L. (hop) were examined for their cytotoxicity in two human neuroblastoma cell lines (IMR-32 and NB-39) and normal cells (primary culture of rat cerebellar granule cells) by [3-(4,5)-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. All chalcones exhibited cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma cells, and two of them (Isobavachalcone and xanthoangelol H) had no effect on normal cells even at high concentration (10(-4) M) exposure. Typical morphologic features of apoptosis, including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation and formation of apoptotic bodies, were observed in Isobavachalcone-treated cells by Hoechst 33342 staining. Western blot analysis showed that Isobavachalcone significantly reduced pro-caspase-3 and pro-caspase-9, and subsequently increased the level of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 in both neuroblastoma cell lines. Moreover, Bax was markedly induced by Isobavachalcone application. These results suggest that Isobavachalcone induces apoptotic cell death in neuroblastoma via the mitochondrial pathway and has no cytotoxicity against normal cells. Therefore, Isobavachalcone may be applicable as an efficacious and safe drug for the treatment of neuroblastoma.


