Deltorphin IPotent δ agonist CAS# 122752-15-2 |
- Deltarasin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4270
CAS No.:1440898-82-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 122752-15-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 123878 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C37H52N8O10 | M.Wt | 768.87 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 0.40 mg/ml in 50% acetonitrile / water | ||
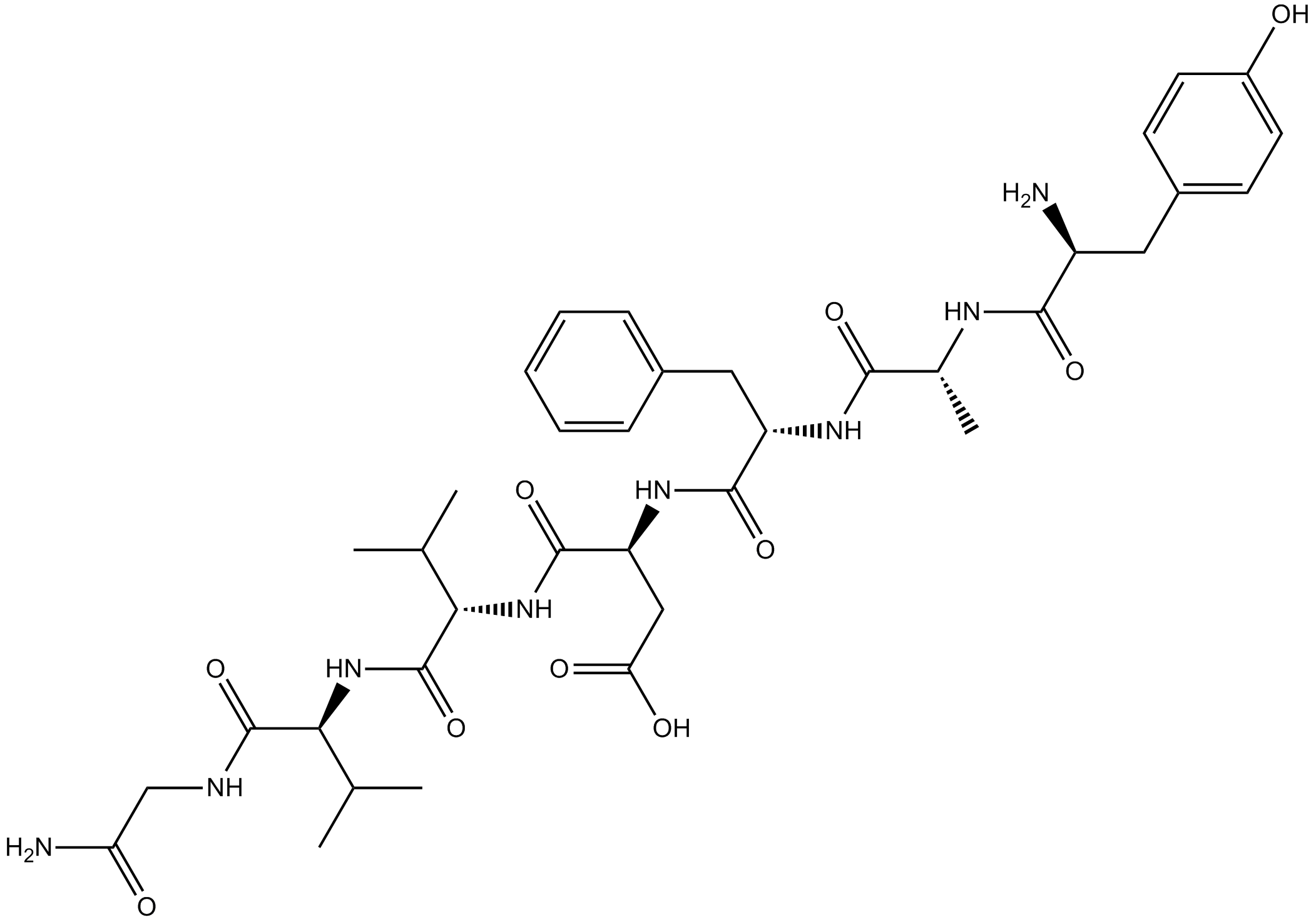
| Sequence | YAFDVVG (Modifications: Ala-2 = D-Ala, Gly-7 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-[[1-[[(2S)-1-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CJAORFIPPWIGPG-OBUNQCGMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C37H52N8O10/c1-19(2)30(36(54)40-18-28(39)47)45-37(55)31(20(3)4)44-35(53)27(17-29(48)49)43-34(52)26(16-22-9-7-6-8-10-22)42-32(50)21(5)41-33(51)25(38)15-23-11-13-24(46)14-12-23/h6-14,19-21,25-27,30-31,46H,15-18,38H2,1-5H3,(H2,39,47)(H,40,54)(H,41,51)(H,42,50)(H,43,52)(H,44,53)(H,45,55)(H,48,49)/t21-,25+,26+,27+,30+,31?/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent δ-opioid receptor agonist (IC50 = 0.5 nM in human granulocytes). Exhibits a high rate of blood-brain barrier penetrance. |

Deltorphin I Dilution Calculator

Deltorphin I Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Bi-linderone
Catalog No.:BCN6116
CAS No.:1227375-09-8
- Philanthotoxin 74
Catalog No.:BCC7478
CAS No.:1227301-51-0
- Liangshanin A
Catalog No.:BCN6115
CAS No.:122717-54-8
- AZD3839
Catalog No.:BCC6471
CAS No.:1227163-84-9
- 4-Fluoro-1-(3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl)-1-(2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl)-1H-isoindol-3-amine
Catalog No.:BCC5113
CAS No.:1227163-56-5
- BAY 87-2243
Catalog No.:BCC4131
CAS No.:1227158-85-1
- SB 277011A dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7887
CAS No.:1226917-67-4
- ATB-346
Catalog No.:BCC5289
CAS No.:1226895-20-0
- FLLL32
Catalog No.:BCC6499
CAS No.:1226895-15-3
- Norpterosin B
Catalog No.:BCN7101
CAS No.:1226892-20-1
- Norpterosin B glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7302
CAS No.:1226785-88-1
- MK3102
Catalog No.:BCC6417
CAS No.:1226781-44-7
- [D-Ala2]-Deltorphin II
Catalog No.:BCC5723
CAS No.:122752-16-3
- StemRegenin 1 (SR1)
Catalog No.:BCC3637
CAS No.:1227633-49-9
- A 943931 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7772
CAS No.:1227675-50-4
- SCH 39166 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7317
CAS No.:1227675-51-5
- MNI-caged-NMDA
Catalog No.:BCC5888
CAS No.:1227675-52-6
- CEP-32496 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1468
CAS No.:1227678-26-3
- ACTH (1-39)
Catalog No.:BCC6028
CAS No.:12279-41-3
- GSK2334470
Catalog No.:BCC4982
CAS No.:1227911-45-6
- Gadodiamide
Catalog No.:BCC4663
CAS No.:122795-43-1
- Marinopyrrole A
Catalog No.:BCC4098
CAS No.:1227962-62-0
- Sabutoclax
Catalog No.:BCC2236
CAS No.:1228108-65-3
- 8-Geranyloxy-5,7-dimethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6117
CAS No.:1228175-65-2
N-terminal guanidinylation of the cyclic 1,4-ureido-deltorphin analogues: the synthesis, receptor binding studies, and resistance to proteolytic digestion.[Pubmed:25755050]
J Pept Sci. 2015 Jun;21(6):467-75.
The synthesis of a series of N-guanidinylated cyclic ureidopeptides, analogues of 1,4-ureido-deltorphin/dermorphine tetrapeptide is described. The delta- and mu-opioid receptor affinity of new guanidinylated analogues and their non-guanidinylated precursors was determined by the displacement radioligand binding experiments. Our results indicate that the guanidinylation of cyclic 1,4-ureidodeltorphin peptide analogues does not exhibit a uniform influence on the opioid receptor binding properties, similarly as reported earlier for some linear peptides. All analogues were also tested for their in vitro resistance to proteolysis during incubation with large excess of chymotrypsin, pepsin, and papain by means of mass spectroscopy. Guanidinylated ureidopeptides 1G-4G showed mixed mu agonist/delta agonist properties and high enzymatic stability indicating their potential as therapeutic agents for treatment of pain.
Effects of Deltorphin II and Its Retroenantio Analog on Cardiac Tolerance to Ischemia and Reperfusion.[Pubmed:28091919]
Bull Exp Biol Med. 2017 Jan;162(3):306-309.
Selective agonist of delta2-opioid receptors Deltorphin II and its retroenantio analog (0.12 mg/kg intravenously) were preventively injected to male Wistar rats 15 min prior to 45-min coronary occlusion or 5 min before 120-min reperfusion. Administration of Deltorphin II before artery occlusion and before reperfusion decreased the infarct size/area at risk ratio. Deltorphin II prevented the appearance of ischemia-provoked ventricular arrhythmias and exerted no effect on HR and BP (systolic and diastolic). The retroenantio analog of Deltorphin II produced no antiarrhythmic or infarct-limiting effects, but reduced HR without affecting BP. Deltorphin II can be viewed as a promising prototype for a medicinal remedy to treat acute myocardial infarction.
Synthesis and pharmacology of halogenated delta-opioid-selective [d-Ala(2)]deltorphin II peptide analogues.[Pubmed:25844930]
ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;6(6):905-10.
Deltorphins are naturally occurring peptides produced by the skin of the giant monkey frog (Phyllomedusa bicolor). They are delta-opioid receptor-selective agonists. Herein, we report the design and synthesis of a peptide, Tyr-d-Ala-(pI)Phe-Glu-Ile-Ile-Gly-NH2 3 (GATE3-8), based on the [d-Ala(2)]Deltorphin II template, which is delta-selective in in vitro radioligand binding assays over the mu- and kappa-opioid receptors. It is a full agonist in [(35)S]GTPgammaS functional assays and analgesic when administered supraspinally to mice. Analgesia of 3 (GATE3-8) is blocked by the selective delta receptor antagonist naltrindole, indicating that the analgesic action of 3 is mediated by the delta-opioid receptor. We have established a radioligand in which (125)I is incorporated into 3 (GATE3-8). The radioligand has a KD of 0.1 nM in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the delta receptor. Additionally, a series of peptides based on 3 (GATE3-8) was synthesized by incorporating various halogens in the para position on the aromatic ring of Phe(3). The peptides were characterized for binding affinity at the mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors, which showed a linear correlation between binding affinity and the size of the halogen substituent. These peptides may be interesting tools for probing delta-opioid receptor pharmacology.
Synthesis, Biological Activity, and NMR-Based Structural Studies of Deltorphin I Analogs Modified in Message Domain with a New alpha,alpha-Disubstituted Glycines.[Pubmed:26808639]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2016 Jun;87(6):824-32.
This article describes new Deltorphin I analogs in which phenylalanine residues were replaced by the corresponding (R) or (S)-alpha-benzyl-beta-azidoalanine, alpha-benzyl-beta-(1-pyrrolidinyl)alanine, alpha-benzyl-beta-(1-piperidinyl)alanine, and alpha-benzyl-beta-(4-morpholinyl)-alanine residues. The potency and selectivity of the new analogs were evaluated by a competitive receptor binding assay in the rat brain using [(3) H]DAMGO (a mu ligand) and [(3) H]DELT (a delta ligand). The affinity of analogs containing (R) or (S)-alpha-benzyl-beta-azidoalanine in position 3 to delta-receptors strongly depended on the chirality of the alpha,alpha-disubstituted residue. The conformational behavior of peptides modified with (R) or (S)-alpha-benzyl-beta-(1-piperidinyl)Ala, which displays the opposite selectivity, was analyzed by (1) H and (13) C NMR. The mu-selective Tyr-d-Ala-(R)-alpha-benzyl-beta-(1-piperidinyl)Ala-Asp-Val-Val-Gly-NH2 lacks the helical conformation observed in the delta-selective Tyr-d-Ala-(S)-alpha-benzyl-beta-(1-piperidinyl)Ala-Asp-Val-Val-Gly-NH2 . Our results support the proposal that differences between delta- and mu-selective opioid peptides are attributable to the presence or absence of a spatial overlap between the N-terminal message domain and the C-terminal address domain.
Deltorphin transport across the blood-brain barrier.[Pubmed:9256506]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Aug 19;94(17):9469-74.
In vivo antinociception studies demonstrate that deltorphins are opioid peptides with an unusually high blood-brain barrier penetration rate. In vitro, isolated bovine brain microvessels can take up deltorphins through a saturable nonconcentrative permeation system, which is apparently distinct from previously described systems involved in the transport of neutral amino acids or of enkephalins. Removing Na+ ions from the incubation medium decreases the carrier affinity for deltorphins (-25%), but does not affect the Vmax value of the transport. The nonselective opiate antagonist naloxone inhibits deltorphin uptake by brain microvessels, but neither the selective delta-opioid antagonist naltrindole nor a number of opioid peptides with different affinities for delta- or mu-opioid receptors compete with deltorphins for the transport. Binding studies demonstrate that mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors are undetectable in the microvessel preparation. Preloading of the microvessels with L-glutamine results in a transient stimulation of deltorphin uptake. Glutamine-accelerated deltorphin uptake correlates to the rate of glutamine efflux from the microvessels and is abolished by naloxone.
[D-Ala2]deltorphin I binding and pharmacological evidence for a special subtype of delta opioid receptor on human and invertebrate immune cells.[Pubmed:1329092]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9316-20.
The effects of the opioid neuropeptide [D-Ala2]Deltorphin I, isolated from amphibian skin, on immunoregulatory activities were studied in representatives of vertebrates and invertebrates. The high potency of this compound parallels that of [Met]enkephalin, which was previously demonstrated in vertebrate plasma and invertebrate hemolymph. The addition of [D-Ala2]Deltorphin I at 10(-11) M to human granulocytes or immunocytes of the mollusc Mytilus edulis resulted in cellular adherence and conformational changes indicative of cellular activation. This value is in line with the concentrations obtained with [Met]enkephalin, tested in the presence of the specific neutral endopeptidase 24.11 inhibitor phosphoramidon, and this opioid's synthetic analog [D-Ala2, Met5]enkephalin which, like [D-Ala2]Deltorphin I, is resistant to proteolytic degradation. Both ligands appear to be acting on the same population of immunocytes. The same relationship was estimated to exist in the insect Leucophaea maderae, in which the high viscosity of the hemolymph makes the quantification of reactive cells more difficult than in Mytilus. In addition, [D-Ala2]Deltorphin I is as potent as beta-endorphin in affecting the proliferation of lymphocytes in response to mitogen. Saturation experiments with unlabeled ligands and the radioligands [3H][D-Ala2]Deltorphin I and [3H][D-Ala2,Met5]enkephalinamide revealed the presence of two high-affinity binding sites on human granulocytes, one sensitive to the nonequilibrium delta opioid antagonist [D-Ala2,Leu5,Cys6]enkephalinamide and the other relatively insensitive. The results obtained with [D-Ala2]Deltorphin I support the view that the special role played by endogenous [Met]enkephalin in immunobiological activities of vertebrates and invertebrates is mediated by a special subtype of delta opioid receptor.
Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites.[Pubmed:2544892]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5188-92.
Deltorphins are endogenous linear heptapeptides, isolated from skin extracts of frogs belonging to the genus Phyllomedusa, that have a higher affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites than any other natural compound known. Two deltorphins with the sequence Tyr-Ala-Phe-Asp(or Glu)-Val-Val-Gly-NH2 have been isolated from skin extracts of Phyllomedusa bicolor. The alanine in position 2 is in the D configuration. These peptides, [D-Ala2]deltorphins I and II, show an even higher affinity for delta receptors than the previously characterized deltorphin, which contains D-methionine as the second amino acid. These peptides show some similarity to another constituent of Phyllomedusa skin, dermorphin, which is highly selective for mu-opioid receptors. These peptides all have the N-terminal sequence Tyr-D-Xaa-Phe, where D-Xaa is either D-alanine or D-methionine. While this structure seems to be capable of activating both mu and delta opioid receptors, differences in the C-terminal regions of these peptides are probably responsible for the observed high receptor selectivity of dermorphin and deltorphin.


