Dihydroisotanshinone ICAS# 20958-18-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
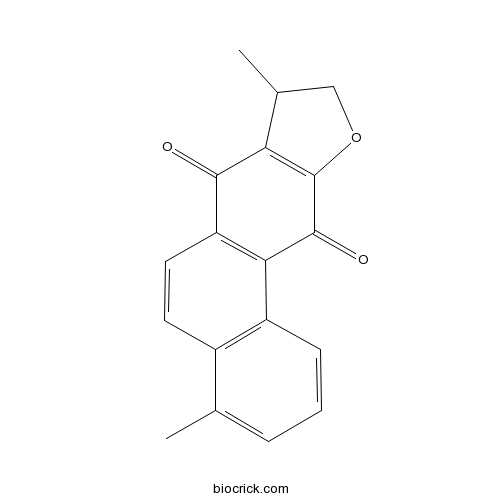
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20958-18-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 89406 | Appearance | Red powder |
| Formula | C18H14O3 | M.Wt | 278.30 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 3.33 mg/mL (11.97 mM; ultrasonic and warming and heat to 40°C) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 4,8-dimethyl-8,9-dihydronaphtho[2,1-f][1]benzofuran-7,11-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1COC2=C1C(=O)C3=C(C2=O)C4=C(C=C3)C(=CC=C4)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KXNYCALHDXGJSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H14O3/c1-9-4-3-5-12-11(9)6-7-13-15(12)17(20)18-14(16(13)19)10(2)8-21-18/h3-7,10H,8H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dihydroisotanshinone I has protective action against menadione-induced hepatotoxicity, attributed to its antioxidant properties including the free radical scavenging activity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation. |
| Targets | Calcium Channel | ATPase | Potassium Channel |
| In vitro | Dihydroisotanshinone I protects against menadione-induced toxicity in a primary culture of rat hepatocytes.[Pubmed: 12494333]Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1077-81.Dihydroisotanshinone I is a phenanthrenequinone derivative isolated from the roots of Salvia trijuga Diels. |
| Kinase Assay | Activation of the iberiotoxin-sensitive BKCa channels by salvianolic acid B of the porcine coronary artery smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed: 16928370]Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 28;546(1-3):28-35.
|

Dihydroisotanshinone I Dilution Calculator

Dihydroisotanshinone I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5932 mL | 17.9662 mL | 35.9324 mL | 71.8649 mL | 89.8311 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7186 mL | 3.5932 mL | 7.1865 mL | 14.373 mL | 17.9662 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3593 mL | 1.7966 mL | 3.5932 mL | 7.1865 mL | 8.9831 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0719 mL | 0.3593 mL | 0.7186 mL | 1.4373 mL | 1.7966 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0359 mL | 0.1797 mL | 0.3593 mL | 0.7186 mL | 0.8983 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dihydroisotanshinone I is a bioactive compound present in a widely used traditional Chinese medicine named danshen.
In Vitro:Dihydroisotanshinone I can inhibit the migration of both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Dihydroisotanshinone diminishes the ability of prostate cancer cells to recruit macrophages and reduces the secretion of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) from both macrophages and prostate cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. It inhibits the protein expression of p-STAT3 and decreases the translocation of STAT3 into nuclear chromatin. It also suppresses the expression of tumor epithelial-mesenchymal transition genes, including RhoA and SNAI1[1]. Pretreating the cells with dihydroisotanshinone I at concentrations ranging from 2.5 μM to 20 μM for 24 hours cause dose-dependent protection against hepatotoxicity induced by menadione. Adding dihydroisotanshinone I to freshly isolated hepatocytes at concentrations between 50 nM to 200 nM inhibit NADH-induced superoxide production dose-dependently[2].
References:
[1]. Wu CY, et al. Anti-cancer effect of danshen and dihydroisotanshinone I on prostate cancer: targeting the crosstalk between macrophages and cancer cells via inhibition of the STAT3/CCL2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 1.
[2]. Ip SP, et al. Dihydroisotanshinone I protects against menadione-induced toxicity in a primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1077-81.
- Isotanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2500
CAS No.:20958-17-2
- Isotanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN2501
CAS No.:20958-15-0
- SB 271046 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1924
CAS No.:209481-24-3
- SB271046
Catalog No.:BCC5057
CAS No.:209481-20-9
- 1-(2-Amino-5-chlorophenyl)-1-(trifluoromethyl)-3-cyclopropyl-2-propyn-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8404
CAS No.:209414-27-7
- VX-745
Catalog No.:BCC3966
CAS No.:209410-46-8
- Platycoside A
Catalog No.:BCN3241
CAS No.:209404-00-2
- Beta-mangostin
Catalog No.:BCN1213
CAS No.:20931-37-7
- Neocryptomerin
Catalog No.:BCN8023
CAS No.:20931-36-6
- Fmoc- ß-HoAsp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3230
CAS No.:209252-17-5
- Entecavir Hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1109
CAS No.:209216-23-9
- Obtucarbamate B
Catalog No.:BCN3937
CAS No.:20913-18-2
- CART (55-102) (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6006
CAS No.:209615-79-2
- Sodium Aescinate
Catalog No.:BCN6266
CAS No.:20977-05-3
- Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275)
Catalog No.:BCC3595
CAS No.:209783-80-2
- AR-M 1000390 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6143
CAS No.:209808-47-9
- Tafluprost
Catalog No.:BCC5270
CAS No.:209860-87-7
- Resibufagin
Catalog No.:BCN8230
CAS No.:20987-24-0
- H-Phenylglycinol
Catalog No.:BCC2713
CAS No.:20989-17-7
- Androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3,17-diacetate
Catalog No.:BCC8823
CAS No.:2099-26-5
- YO-01027 (Dibenzazepine, DBZ)
Catalog No.:BCC2100
CAS No.:209984-56-5
- LY-411575
Catalog No.:BCC2101
CAS No.:209984-57-6
- LY-411575 isomer 1
Catalog No.:BCC5443
CAS No.:209984-58-7
- LY-900009
Catalog No.:BCC2103
CAS No.:209984-68-9
Activation of the iberiotoxin-sensitive BKCa channels by salvianolic acid B of the porcine coronary artery smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:16928370]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 28;546(1-3):28-35.
In this study, we examined the effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) crude extract, some of its lipid-soluble components (tanshinone I, tanshinone II(A), cryptotanshinone, Dihydroisotanshinone I) and the water-soluble compounds (danshensu and salvianolic acid B) on the K(+) channels such as the iberiotoxin-sensitive Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK(Ca)) channels and the glibenclamide-sensitive ATP-dependent K(+) (IK(ATP)) channels of the porcine left anterior descending coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Cumulative application of salvianolic acid B (30-300 microM) caused a l-NNA (100 microM)-insensitive, potentiation of the outward BK(Ca) current amplitude with no apparent effect on the IK(ATP) channels opening. Salvianolic acid B (300 microM) caused an ODQ (10 microM, a guanylate cyclase inhibitor)-sensitive enhancement of the outward BK(Ca) current amplitude. In contrast, none of the other isolated chemical constituents of S. miltiorrhiza modified the openings of the two types of K(+) channels studied. In conclusion, our results suggest that salvianolic acid B, a major hydrophilic constituent found in Radix S. miltiorrhiza, activated the opening of the BK(Ca) channels of the porcine coronary artery smooth muscle cells through the activation of guanylate cyclase without the involvement of the nitric oxide synthase activation.
Dihydroisotanshinone I protects against menadione-induced toxicity in a primary culture of rat hepatocytes.[Pubmed:12494333]
Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1077-81.
Dihydroisotanshinone I is a phenanthrenequinone derivative isolated from the roots of Salvia trijuga Diels. The present study demonstrated the hepatoprotective effect of Dihydroisotanshinone I against menadione-induced cytotoxicity in a primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Pretreating the cells with Dihydroisotanshinone I at concentrations ranging from 2.5 microM to 20 microM for 24 hours caused dose-dependent protection against hepatotoxicity induced by menadione. Intracellular glutathione level and activity of DT-diaphorase have been suggested to play important roles in menadione-induced cytotoxicity. However, treating the hepatocytes with 20 microM Dihydroisotanshinone I for 24 hours did not cause a significant change in glutathione level and DT-diaphorase activity. On the contrary, adding Dihydroisotanshinone I to freshly isolated hepatocytes at concentrations between 50 nM to 200 nM inhibited NADH-induced superoxide production dose-dependently as indicated by the decrease of lucigenin-amplified chemiluminescence. In addition, Dihydroisotanshinone I at concentrations ranging from 5 microM to 20 microM inhibited tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation dose-dependently in isolated hepatocytes as indicated by the level of malondialdehyde. These results suggest that the protective action of Dihydroisotanshinone I against menadione-induced hepatotoxicity is attributed to its antioxidant properties including the free radical scavenging activity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Abbreviations. DTD:DT-diaphorase GSH:glutathione LDH:lactate dehydrogenase MDA:malondialdehyde MTT:3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide TBHP: tert-butyl hydroperoxide


