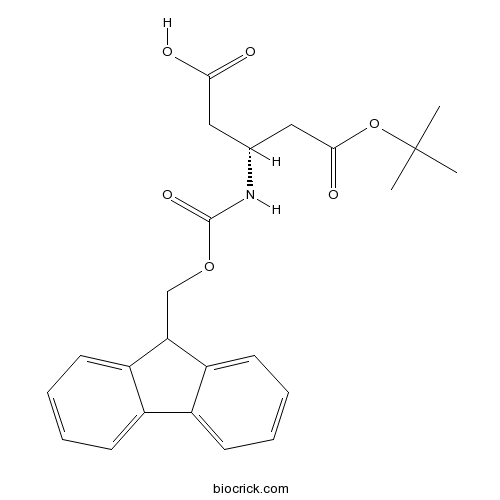
Fmoc- ß-HoAsp(OtBu)-OHCAS# 209252-17-5 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- CMK
Catalog No.:BCC1489
CAS No.:821794-90-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 209252-17-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2761514 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H27NO6 | M.Wt | 425.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3R)-3-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-5-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-5-oxopentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)CC(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)OCC1C2=CC=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C13 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XXXSUGLINJXRGT-OAHLLOKOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H27NO6/c1-24(2,3)31-22(28)13-15(12-21(26)27)25-23(29)30-14-20-18-10-6-4-8-16(18)17-9-5-7-11-19(17)20/h4-11,15,20H,12-14H2,1-3H3,(H,25,29)(H,26,27)/t15-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Fmoc- ß-HoAsp(OtBu)-OH Dilution Calculator

Fmoc- ß-HoAsp(OtBu)-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3502 mL | 11.7509 mL | 23.5018 mL | 47.0035 mL | 58.7544 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.47 mL | 2.3502 mL | 4.7004 mL | 9.4007 mL | 11.7509 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.235 mL | 1.1751 mL | 2.3502 mL | 4.7004 mL | 5.8754 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.047 mL | 0.235 mL | 0.47 mL | 0.9401 mL | 1.1751 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0235 mL | 0.1175 mL | 0.235 mL | 0.47 mL | 0.5875 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fmoc- ß-HoAsp(OtBu)-OH
- Entecavir Hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1109
CAS No.:209216-23-9
- Obtucarbamate B
Catalog No.:BCN3937
CAS No.:20913-18-2
- Mangochinine
Catalog No.:BCN4913
CAS No.:209115-67-3
- JWH 073
Catalog No.:BCC1674
CAS No.:208987-48-8
- Swertianin
Catalog No.:BCC8258
CAS No.:20882-75-1
- Testosterone benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9166
CAS No.:2088-71-3
- Saikosaponin D
Catalog No.:BCN1088
CAS No.:20874-52-6
- (1R,1'S,3'R/1R,1'R,3'S)-L-054,264
Catalog No.:BCC7364
CAS No.:208706-12-1
- Ermanin
Catalog No.:BCN4912
CAS No.:20869-95-8
- Boc-His(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3399
CAS No.:20866-46-0
- Berberine
Catalog No.:BCN4911
CAS No.:2086-83-1
- Primulic Acid 2
Catalog No.:BCC8237
CAS No.:208599-88-6
- Neocryptomerin
Catalog No.:BCN8023
CAS No.:20931-36-6
- Beta-mangostin
Catalog No.:BCN1213
CAS No.:20931-37-7
- Platycoside A
Catalog No.:BCN3241
CAS No.:209404-00-2
- VX-745
Catalog No.:BCC3966
CAS No.:209410-46-8
- 1-(2-Amino-5-chlorophenyl)-1-(trifluoromethyl)-3-cyclopropyl-2-propyn-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8404
CAS No.:209414-27-7
- SB271046
Catalog No.:BCC5057
CAS No.:209481-20-9
- SB 271046 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1924
CAS No.:209481-24-3
- Isotanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN2501
CAS No.:20958-15-0
- Isotanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2500
CAS No.:20958-17-2
- Dihydroisotanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2308
CAS No.:20958-18-3
- CART (55-102) (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6006
CAS No.:209615-79-2
- Sodium Aescinate
Catalog No.:BCN6266
CAS No.:20977-05-3
New t-butyl based aspartate protecting groups preventing aspartimide formation in Fmoc SPPS.[Pubmed:26077723]
J Pept Sci. 2015 Aug;21(8):680-7.
Obtaining homogenous aspartyl-containing peptides via Fmoc/tBu chemistry is often an insurmountable obstacle. A generic solution for this issue utilising an optimised side-chain protection strategy that minimises aspartimide formation would therefore be most desirable. To this end, we developed the following new derivatives: Fmoc-Asp(OEpe)-OH (Epe = 3-ethyl-3-pentyl), Fmoc-Asp(OPhp)-OH (Php = 4-n-propyl-4-heptyl) and Fmoc-Asp(OBno)-OH (Bno = 5-n-butyl-5-nonyl). We have compared their effectiveness against that of Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)-OH and Fmoc-Asp(OMpe)-OH in the well-established scorpion toxin II model peptide variants H-Val-Lys-Asp-Asn/Arg-Tyr-Ile-OH by treatments of the peptidyl resins with the Fmoc removal reagents containing piperidine and DBU at both room and elevated temperatures. The new derivatives proved to be extremely effective in minimising aspartimide by-products in each application.
Innovative chemical synthesis and conformational hints on the lipopeptide liraglutide.[Pubmed:27238390]
J Pept Sci. 2016 Jul;22(7):471-9.
Liraglutide is a new generation lipopeptide drug used for the treatment of type II diabetes. In this work, we describe new approaches for its preparation fully by chemical methods. The key step of these strategies is the synthesis in solution of the Lys/gamma-Glu building block, Fmoc-Lys-(Pal-gamma-Glu-OtBu)-OH, in which Lys and Glu residues are linked through their side chains and gamma-Glu is N(alpha) -palmitoylated. This dipeptide derivative is then inserted into the peptide sequence on solid phase. As liraglutide is obtained with great purity and high yield, our approach can be particularly attractive for an industrial production. We also report here the results of a circular dichroism conformational analysis in a membrane mimetic environment that offers new insights into the mechanism of action of liraglutide. Copyright (c) 2016 European Peptide Society and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Synthesis of complex head-to-side-chain cyclodepsipeptides.[Pubmed:27658010]
Nat Protoc. 2016 Oct;11(10):1924-1947.
Cyclodepsipeptides are cyclic peptides in which at least one amide link on the backbone is replaced with an ester link. These natural products present a high structural diversity that corresponds to a broad range of biological activities. Therefore, they are very promising pharmaceutical candidates. Most of the cyclodepsipeptides have been isolated from marine organisms, but they can also originate from terrestrial sources. Within the family of cyclodepsipeptides, 'head-to-side-chain' cyclodepsipeptides have, in addition to the macrocyclic core closed by the ester bond, an arm terminated with a polyketide moiety or a branched amino acid, which makes their synthesis a challenge. This protocol provides guidelines for the synthesis of 'head-to-side-chain cyclodepsipeptides' and includes-as an example-a detailed procedure for preparing pipecolidepsin A. Pipecolidepsin was chosen because it is a very complex 'head-to-side-chain cyclodepsipeptide' of marine origin that shows cytotoxicity in several human cancer cell lines. The procedure begins with the synthesis of the noncommercial protected amino acids (2R,3R,4R)-2-{[(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy]carbonylamino}-3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethylhexa noic acid (Fmoc-AHDMHA-OH), Alloc-pipecolic-OH, (4R,5R)-5-((((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-4-oxo-4-(tritylamino)butyl)- 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolane-4-carboxylic acid (Fmoc-DADHOHA(acetonide, Trt))-OH and the pseudodipeptide (2R,3R,4R)-3-hydroxy-2,4,6-trimethylheptanoic acid ((HTMHA)-D-Asp(OtBu)-OH). It details the assembly of the depsipeptidic skeleton using a fully solid-phase approach (typically on an amino polystyrene resin coupled to 3-(4-hydroxymethylphenoxy)propionic acid (AB linker)), including the key ester formation step. It concludes by describing the macrocyclization step performed on solid phase, and the global deprotection and cleavage of the cyclodepsipeptide from the resin using a trifluoroacetic acid-H2O-triisopropylsilane (TFA-H2O-TIS; 95:2.5:2.5) cocktail, as well as the final purification by semipreparative HPLC. The entire procedure takes approximately 2 months to complete.
A 'conovenomic' analysis of the milked venom from the mollusk-hunting cone snail Conus textile--the pharmacological importance of post-translational modifications.[Pubmed:24055806]
Peptides. 2013 Nov;49:145-58.
Cone snail venoms provide a largely untapped source of novel peptide drug leads. To enhance the discovery phase, a detailed comparative proteomic analysis was undertaken on milked venom from the mollusk-hunting cone snail, Conus textile, from three different geographic locations (Hawai'i, American Samoa and Australia's Great Barrier Reef). A novel milked venom conopeptide rich in post-translational modifications was discovered, characterized and named alpha-conotoxin TxIC. We assign this conopeptide to the 4/7 alpha-conotoxin family based on the peptide's sequence homology and cDNA pre-propeptide alignment. Pharmacologically, alpha-conotoxin TxIC demonstrates minimal activity on human acetylcholine receptor models (100 muM, <5% inhibition), compared to its high paralytic potency in invertebrates, PD50 = 34.2 nMol kg(-1). The non-post-translationally modified form, [Pro](2,8)[Glu](16)alpha-conotoxin TxIC, demonstrates differential selectivity for the alpha3beta2 isoform of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with maximal inhibition of 96% and an observed IC50 of 5.4 +/- 0.5 muM. Interestingly its comparative PD50 (3.6 muMol kg(-1)) in invertebrates was ~100 fold more than that of the native peptide. Differentiating alpha-conotoxin TxIC from other alpha-conotoxins is the high degree of post-translational modification (44% of residues). This includes the incorporation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid, two moieties of 4-trans hydroxyproline, two disulfide bond linkages, and C-terminal amidation. These findings expand upon the known chemical diversity of alpha-conotoxins and illustrate a potential driver of toxin phyla-selectivity within Conus.
A paclitaxel-conjugated adenovirus vector for targeted drug delivery for tumor therapy.[Pubmed:21959006]
Biomaterials. 2012 Jan;33(1):146-62.
Tumor-targeted drug delivery is an attractive strategy in cancer treatment. Our previous study demonstrated that modified adenovirus has strong tumor targeting ability and less toxicity to surrounding normal tissue. In this study, Paclitaxel (PTX), a widely used clinical anticancer drug, was conjugated to folate-modified adenovirus (Ad) nanoparticles by using succinic anhydride and Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH linkers to form two prodrugs, FA-Ad-Suc-PTX and FA-Ad-ICG02-Glu-PTX. Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent dye ICG-Der-02 was attached to -NH(2)-Glu(OtBu)-PTX for in vivo optical imaging. In vitro and acute toxicity study demonstrates the low toxicity of the prodrug FA-Ad-Suc-PTX and FA-Ad-ICG02-Glu-PTX compared to the free drug. The dynamic behaviors and targeting ability of FA-Ad-ICG02-Glu-PTX on MDA-MB-231 tumor-bearing mice were investigated by NIR fluorescence imaging. The result show that PTX-conjugated Ad vector could enhance the targeting and residence time in tumor site. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that Coxsackie adenovirus receptor (CAR) or foliate receptor (FR)-mediated uptake of FA-Ad-loaded PTX induced highly anti-tumor activity. The results support the potential of using chemically modified Ad vector as drug-loaded tumor-targeting delivery system.


