DimethylolureaCAS# 140-95-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 140-95-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 8827 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C3H8N2O3 | M.Wt | 120 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
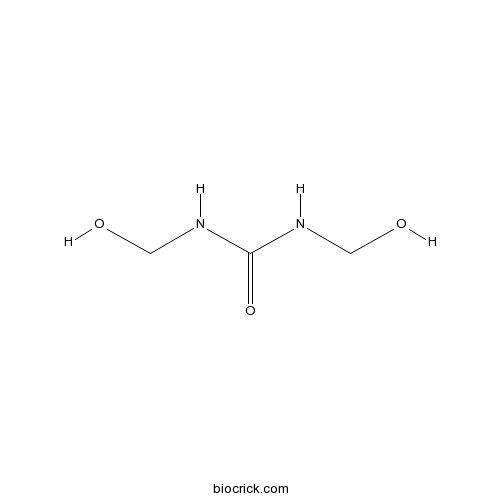
| Chemical Name | 1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)urea | ||
| SMILES | C(NC(=O)NCO)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QUBQYFYWUJJAAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C3H8N2O3/c6-1-4-3(8)5-2-7/h6-7H,1-2H2,(H2,4,5,8) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Dimethylolurea Dilution Calculator

Dimethylolurea Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.3333 mL | 41.6667 mL | 83.3333 mL | 166.6667 mL | 208.3333 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.6667 mL | 8.3333 mL | 16.6667 mL | 33.3333 mL | 41.6667 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.8333 mL | 4.1667 mL | 8.3333 mL | 16.6667 mL | 20.8333 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1667 mL | 0.8333 mL | 1.6667 mL | 3.3333 mL | 4.1667 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0833 mL | 0.4167 mL | 0.8333 mL | 1.6667 mL | 2.0833 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4-Allylanisole
Catalog No.:BCC8674
CAS No.:140-67-0
- Pentamidine isethionate
Catalog No.:BCC5644
CAS No.:140-64-7
- Nithiamide
Catalog No.:BCC4687
CAS No.:140-40-9
- Cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6217
CAS No.:140-10-3
- Palbinone
Catalog No.:BCN3930
CAS No.:139954-00-0
- Alpinone 3-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7768
CAS No.:139906-49-3
- Drahebenine
Catalog No.:BCN7044
CAS No.:1399049-43-4
- Globularin
Catalog No.:BCN6215
CAS No.:1399-49-1
- 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose
Catalog No.:BCN2719
CAS No.:139891-98-8
- Milameline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7427
CAS No.:139886-04-7
- Cucurbitacin E-2-O-Glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8156
CAS No.:1398-78-3
- Sildenafil
Catalog No.:BCC1947
CAS No.:139755-83-2
- Nystatin (Fungicidin)
Catalog No.:BCC4813
CAS No.:1400-61-9
- 4μ8C
Catalog No.:BCC4754
CAS No.:14003-96-4
- Eucalyptin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6216
CAS No.:14004-35-4
- PB-22
Catalog No.:BCC1840
CAS No.:1400742-17-7
- 3-CPMT
Catalog No.:BCC6845
CAS No.:14008-79-8
- Tannic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2643
CAS No.:1401-55-4
- AMG 925
Catalog No.:BCC5150
CAS No.:1401033-86-0
- 3'-Hydroxygynuramide II
Catalog No.:BCC8634
CAS No.:1401093-57-9
- PI-1840
Catalog No.:BCC5453
CAS No.:1401223-22-0
- ML 277
Catalog No.:BCC7976
CAS No.:1401242-74-7
- 15,16-Dihydroxyoctadeca-9Z,12Z-dienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8438
CAS No.:140129-22-2
- Pterisolic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN4842
CAS No.:1401419-85-9
Utilization of wheat straw for the preparation of coated controlled-release fertilizer with the function of water retention.[Pubmed:22730900]
J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Jul 18;60(28):6921-8.
With the aim of improving fertilizer use efficiency and minimizing the negative impact on the environment, a new coated controlled-release fertilizer with the function of water retention was prepared. A novel low water solubility macromolecular fertilizer, poly(dimethylourea phosphate) (PDUP), was "designed" and formulated from N,N'-Dimethylolurea (DMU) and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Simultaneously, an eco-friendly superabsorbent composite based on wheat straw (WS), acrylic acid (AA), 2-acryloylamino-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid (AMPS), and N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide (NHMAAm) was synthesized and used as the coating to control the release of nutrient. The nitrogen release profile and water retention capacity of the product were also investigated. The degradation of the coating material in soil solution was studied. Meanwhile, the impact of the content of N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide on the degradation extent was examined. The experimental data showed that the product with good water retention and controlled-release capacities, being economical and eco-friendly, could be promising for applications in agriculture and horticulture.
Patch testing with components of water-based metalworking fluids: results of a multicentre study with a second series.[Pubmed:17101005]
Contact Dermatitis. 2006 Dec;55(6):322-9.
BACKGROUND: Although many allergens in metalworking fluids (MWF) are identified, there are still some MWF components, which are not sufficiently investigated concerning their sensitizing properties. OBJECTIVES: To investigate sensitization to 10 frequently used MWF components, which are not part of the established MWF test series, in metalworkers with suspected occupational dermatitis due to MWF. PATIENTS/METHODS: Oleyl alcohol, myristyl alcohol, Dimethylolurea, 4,4'-methylenebis morpholine, imazalil, 1-amino-2-propanol (monoisopropanolamine; MIPA), 2-amino-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol (AEPD), 2,5-bis(n-octyldithio)-1,3,4-thiadiazole, zinc alkyl dithiophosphate and dibenzyl disulfide have been patch tested in 144 patients. RESULTS: 7 patients reacted positively to the formaldehyde releaser 4,4'-methylenebis morpholine, and 6 of these patients also reacted to formaldehyde and/or other formaldehyde releasers. 4 patients reacted positively to myristyl alcohol tested at 10% petrolatum (pet.). Additionally, 20 doubtful or irritant reactions occurred. 1 patient each reacted positively to oleyl alcohol, MIPA, and AEPD. None of the other test substances mentioned above elicited any clear-cut positive reaction. Patch testing with well-known MWF allergens showed proportions of positive reactions, which were comparable to those from other studies, e.g. 11% to monoethanolamine, 8% to colophonium and 3%-5% to various preservatives. CONCLUSIONS: 4,4'-methylenebis morpholine may be an important MWF allergen, although clinical relevance could not be stated definitely in every case. Myristyl alcohol should not be patch tested at 10% pet., but at a lesser concentration, due to irritant properties.


