EleutherolCAS# 480-00-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 480-00-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 120697 | Appearance | Yellow crystalline powder |
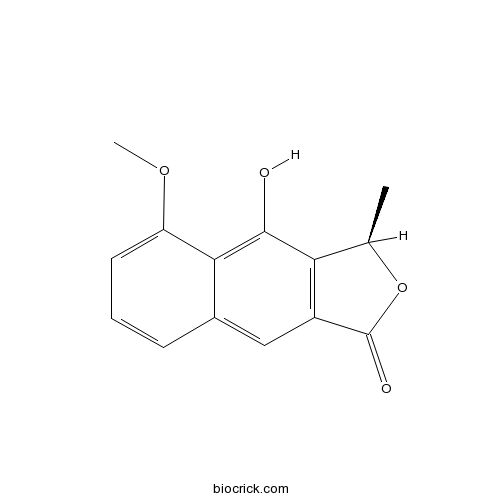
| Formula | C14H12O4 | M.Wt | 244.24 |
| Type of Compound | Quinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3R)-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-methyl-3H-benzo[f][2]benzofuran-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C2=C(C=C3C=CC=C(C3=C2O)OC)C(=O)O1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KNLHGXVYZRQSJZ-SSDOTTSWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12O4/c1-7-11-9(14(16)18-7)6-8-4-3-5-10(17-2)12(8)13(11)15/h3-7,15H,1-2H3/t7-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Eleutherol Dilution Calculator

Eleutherol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0943 mL | 20.4717 mL | 40.9433 mL | 81.8867 mL | 102.3583 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8189 mL | 4.0943 mL | 8.1887 mL | 16.3773 mL | 20.4717 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4094 mL | 2.0472 mL | 4.0943 mL | 8.1887 mL | 10.2358 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0819 mL | 0.4094 mL | 0.8189 mL | 1.6377 mL | 2.0472 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0409 mL | 0.2047 mL | 0.4094 mL | 0.8189 mL | 1.0236 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- CP-809101
Catalog No.:BCC1498
CAS No.:479683-64-2
- 1-O-galloyl-2-O-cinnamoyl-beta-d-glucose
Catalog No.:BCC3967
CAS No.:
- AUDA
Catalog No.:BCC4023
CAS No.:479413-70-2
- NBQX disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6907
CAS No.:479347-86-9
- CNQX disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6908
CAS No.:479347-85-8
- TC OT 39
Catalog No.:BCC7958
CAS No.:479232-57-0
- MMPIP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7528
CAS No.:479077-02-6
- [Orn8]-Urotensin II
Catalog No.:BCC5793
CAS No.:479065-85-5
- Aucubin
Catalog No.:BCN5355
CAS No.:479-98-1
- Vitexicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN5020
CAS No.:479-91-4
- Artemetin
Catalog No.:BCN5547
CAS No.:479-90-3
- Canthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN5546
CAS No.:479-43-6
- Astragalin
Catalog No.:BCN5549
CAS No.:480-10-4
- Oroxylin A
Catalog No.:BCN5363
CAS No.:480-11-5
- Izalpinine
Catalog No.:BCN3682
CAS No.:480-14-8
- Morin
Catalog No.:BCN1028
CAS No.:480-16-0
- Taxifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5550
CAS No.:480-18-2
- Isorhamnetin
Catalog No.:BCN5551
CAS No.:480-19-3
- Aromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5552
CAS No.:480-20-6
- Orobol
Catalog No.:BCN5553
CAS No.:480-23-9
- Mellein
Catalog No.:BCN4785
CAS No.:480-33-1
- Eugenin
Catalog No.:BCN2921
CAS No.:480-34-2
- Linarin
Catalog No.:BCN5554
CAS No.:480-36-4
- Pinostrobin
Catalog No.:BCN5555
CAS No.:480-37-5
Application of MEKC and monolithic CEC for the analysis of bioactive naphthoquinones in Eleutherine americana.[Pubmed:19862752]
Electrophoresis. 2009 Nov;30(21):3757-63.
Two microscale separation techniques for the analysis of bioactive naphthoquinones in Eleutherine americana were developed and validated. By MEKC four compounds (eleuthoside B, isoeleutherin, Eleutherol and eleutherinoside A) could be determined in plant extracts using an aqueous electrolyte solution composed of 25 mM sodium tetraborate, 50 mM sodium cholate and 20% THF. CEC on a polymeric methacrylate-based monolith with strong cationic properties showed promising results, as it additionally enabled the separation of two enantiomers, eleutherin and isoeleutherin. The mobile phase for CEC experiments comprised 3 mM ammonium formate in a mixture of ACN and water. At an applied voltage of -25 kV, all five markers were baseline separated in less than 12 min. Both methods were successfully validated for linearity (MEKC: R(2) > or = 0.999; CEC: R(2) > or = 0.997), sensitivity (MEKC: LOD = 4-5 microg/mL; CEC: LOD=2-8 microg/mL), accuracy (MEKC: 96.5-102.7% recovery; CEC: 97.1-103.5% recovery) and precision (MEKC: sigma(rel) < or = 2.43%; CEC: sigma(rel) < or = 2.21%). The quantitative analysis of naphthoquinone derivatives in several E. americana samples showed that both methods are suitable for practical applications, because the results were well comparable to those obtained by established techniques such as HPLC.
Antifungal Activity of Pyranonaphthoquinones Obtained from Cipura paludosa Bulbs.[Pubmed:26594766]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Sep;10(9):1589-92.
Previous studies with the bulbs of Cipura paludosa (Iridaceae) showed the presence of pyranonaphthoquinones, including eleutherine, isoeleutherine and Eleutherol. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antifungal properties of these compounds. The activity was tested against the clinically relevant yeasts Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Cryptococcus neoformans with the microbroth dilution method, following the guidelines of CLSI. Eleutherine, isoeleutherine and Eleutherol all presented significant antifungal activity, especially the first two, the major components, with MIC values between 7.8 and 250 microg/mL. In conclusion, these results demonstrate that C. paludosa bulbs produce active principles with relevant antifungal potential, contributing, at least in part, to the antimicrobial effect evidenced for this plant and justifying its popular use against infections.
Polyketides from Eleutherine bulbosa.[Pubmed:20835959]
Nat Prod Res. 2010 Oct;24(16):1578-86.
Four new polyketides, (R)-4-hydroxyeleutherin, eleuthone, eleutherinol-8-O-beta-D-glucoside and isoeleuthoside C (dihydroisoeleutherin-5-O-beta-D-gentiobioside) were isolated from the bulbs of Eleutherine bulbosa, to join eleutherin, isoeleutherin, eleutherinol, Eleutherol, eleuthoside B (Eleutherol-4-O-beta-D-gentiobioside), eleuthoside C (dihydroeleutherin-5-O-beta-D-gentiobioside), hongconin (4-oxodihydroisoeleutherin) and elecanacin, which have already been isolated from the same plant. The structures of the new polyketides, based on oxydated cyclic systems, have been elucidated by chemical and spectroscopic methods.
Eleutherinone, a novel fungitoxic naphthoquinone from Eleutherine bulbosa (Iridaceae).[Pubmed:12973542]
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2003 Jul;98(5):709-12. Epub 2003 Sep 8.
The dichloromethane extract prepared from the underground parts of Eleutherine bulbosa (Miller) Urban (Iridaceae) showed strong activity in the direct bioautography assay with the phytopathogenic fungus Cladosporium sphaerospermum. This assay was used to guide the fractionation of this extract and allowed the isolation of four compounds: the new naphthoquinone eleutherinone[8-methoxy-1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-naphtho(2,3-c)furan-4,9 -dione] and the known compounds, previously isolated from this species, eleutherin [9-methoxy-1(R),3(S)-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo(g)isochromene-5,10-dione], isoeleutherin [9-methoxy-1(R),3(R)-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo(g)isochromene-5,10-dione], and Eleutherol [4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3(R)-methyl-3H-naphtho(2,3-c)furan-1 -one]. All quinonoid compounds showed strong antifungal activity in the bioautography assay at 100 g/spot, while Eleutherol was inactive.
alpha-Glucosidase inhibitors from the bulb of Eleutherine americana.[Pubmed:25212136]
Food Chem. 2011 Sep 15;128(2):308-11.
One effective way to treat diabetes is by suppressing carbohydrate digestion due to the utilisation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs). The determination of prospective herbs, done in vitro by using enzyme assay, resulted in the finding of Eleutherine americana, which showed a potent inhibitory activity. A 50% aqueous methanol-soluble extract of bulbs of E. americana was chromatographed successively and the active fractions were further purified with preparative high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to isolate active compounds against alpha-glucosidase. Structure determination by mass and NMR analysis revealed that these isolated compounds were Eleutherol (1), eleutherinoside A (2), and eleuthoside B (3) based on comparisons with the reference data. Considering the amount and the inhibitory activity of each naphthalene in the whole extracts, the bulb of E. americana inhibitory activity against alpha-glucosidase might be a result of compound 2 (IC50=0.5mM, yield=5mg/50g plant sample, with a characteristic structure which has never been found in other AGIs. AGIs play an important role for the treatment of diabetes, therefore these results may suggest novel alternatives for diabetes treatment management.
Analysis of naphthoquinone derivatives in the Asian medicinal plant Eleutherine americana by RP-HPLC and LC-MS.[Pubmed:18486396]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Aug 5;47(4-5):990-3.
The first analytical procedure for the determination of a new naphthopyrone, eleutherinoside A, together with the known bioactive compounds eleuthoside B, isoeleutherin, eleutherin and Eleutherol in Eleutherine americana was established. Optimum HPLC separation of these naphthoquinone derivatives was possible on RP-12 column material, using water and acetonitrile as mobile phase. Flow-rate, detection wavelength and temperature were adjusted to 1.0 mL/min, 254 nm and 40 degrees C, respectively. Validation results indicated that the HPLC method is well suited for the determination of naphthoquinone derivatives in the bulbs of E. americana with a good linearity (r2>0.9996), precision (intra-day R.S.D. <4.70%, inter-day R.S.D. <5.68%) and recovery rates from 96.26 to 103.48%. Limit of detection (LOD) was found to be below 0.84 microg/mL for all five compounds. LC-MS analyses performed in positive and negative electrospray ionization mode assured peak purity and identity. The analysis of different E. americana samples from Thailand revealed that Eleutherol (0.10-0.20%) was dominant in all specimens, followed by isoeleutherin and eleutherin. The new natural product 2,5-dimethyl-10-hydroxynaphthopyrone 8-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside occurred in percentages of less than 0.05%.
Assessment of antistaphylococcal activity of partially purified fractions and pure compounds from Eleutherine americana.[Pubmed:19350980]
J Food Prot. 2009 Feb;72(2):354-9.
Ready-to-eat foods were investigated for contamination with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and the partially purified fractions from the bulb of Eleutherine americana were evaluated for their anti-MRSA activity. Partially purified fractions Ea6.3 and Ea9 demonstrated good antibacterial activity with a MIC of 125 to 500 microg/ml and MBC of 250 to > or =1000 microg/ml against all the food isolates. Fraction Ea6.3 produced a MIC and MBC of 250 and 500 microg/ml, respectively, whereas fraction Ea9 yielded MIC and MBC of 125 and > or =1000 microg/ml, respectively, against the enterotoxin-producing reference strains. Growth curves in the presence of fraction Ea6.3 at 4 x MIC resulted in total elimination of all the test strains between 20 and 24 h, while fraction Ea9 reduced bacterial population by at least 6 log relative to the control. The partially purified fractions were further purified to obtain pure compounds identified as Eleutherol, eleutherin, isoeleutherin, hongconin, two anthraquinones, and elecanacin. The antibacterial activities of these compounds were also investigated; they produced MICs ranging from 31.25 to > or =1000 microg/ml. This study suggests that E. americana crude extract or its partially purified fractions have potentials for application as natural food preservatives.


