Oroxylin ACAS# 480-11-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 480-11-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5320315 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C16H12O5 | M.Wt | 284.26 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Baicalein 6-methyl ether; 6-Methoxybaicalein | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (112.57 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
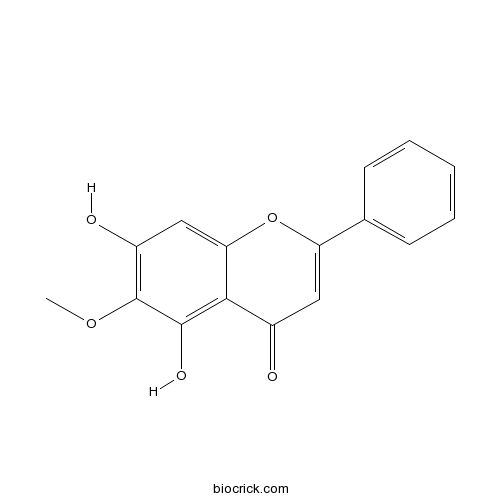
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C=C(O2)C3=CC=CC=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LKOJGSWUMISDOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O5/c1-20-16-11(18)8-13-14(15(16)19)10(17)7-12(21-13)9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-8,18-19H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Oroxylin A has anticancer,.anti-inflammation, antithrombotic,antibacterial, anti-pruritic effects, it can inhibit LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression by blocking NF-κB activation. Oroxylin A reverses MDR by G2/M arrest and the underlying mechanism attributed to the suppression of P-gp expression via Chk2/P53/NF-κB signaling pathway. Oroxylin A facilitates memory consolidation through brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-TrkB signaling. |
| Targets | TNF-α | ERK | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | NF-kB | Chk | p53 | P-gp | Akt | NOS | COX | PGE | Bcl-2/Bax | NO |
| In vitro | Antithrombotic activities of oroxylin A in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 23963976]Arch Pharm Res. 2014 May;37(5):679-86.
Oroxylin A suppresses invasion through down-regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 19100732]Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2009, 603(1-3):22-8.Our previous study revealed that Oroxylin A, a naturally occurring monoflavonoid isolated from Scutellariae radix, could inhibit the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inducing the apoptosis in these cells. However, the molecular mechanism of its anticancer activity remains poorly understood and warrants further investigations.
|
| In vivo | Oroxylin A enhances memory consolidation through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mice.[Pubmed: 25218897]Brain Res Bull. 2014 Sep;108:67-73.Memory consolidation is a process by which acquired information is transformed from a labile into a more stable state that can be retrieved at a later time. In the present study, we investigated the role of Oroxylin A on the memory consolidation process in mice.
Anti-pruritic effect of baicalin and its metabolites, baicalein and oroxylin A, in mice.[Pubmed: 20453872 ]Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Jun;31(6):718-24.To explore whether intestinal microflora plays a role in anti-pruritic activity of baicalin, a main constituent of the rhizome of Scutellaria baicalensis (SB).
|
| Cell Research | Oroxylin A inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation.[Pubmed: 10751555]Oroxylin A reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of MCF7/ADR cells by G2/M arrest.[Pubmed: 23470866]Toxicol Lett. 2013 May 23;219(2):107-15.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a refractory malignancy with a high incidence and large mortality. Current strategy for the chemotherapy of HCC focuses on developing agents with better efficacy and lower toxicity.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Jun 1;59(11):1445-57.Polyphenols are major components of many traditional herbal remedies, which exhibit several beneficial effects including anti-inflammation. The exact mechanism of the anti-inflammatory action of polyphenols, however, has not been determined.
|

Oroxylin A Dilution Calculator

Oroxylin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5179 mL | 17.5895 mL | 35.1791 mL | 70.3581 mL | 87.9477 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7036 mL | 3.5179 mL | 7.0358 mL | 14.0716 mL | 17.5895 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3518 mL | 1.759 mL | 3.5179 mL | 7.0358 mL | 8.7948 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0704 mL | 0.3518 mL | 0.7036 mL | 1.4072 mL | 1.759 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1759 mL | 0.3518 mL | 0.7036 mL | 0.8795 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Oroxylin A is a natural active flavonoid with strong anticancer effects. IC50 value: Target: In vitro: Oroxylin A suppressed the MDM2-mediated degradation of p53 via downregulating MDM2 transcription in wt-p53 cancer cells [1]. Oroxylin A remarkably reduced the generation of lactate and glucose uptake under hypoxia in HepG2 cells, inhibited HIF-1α expression and its stability [2]. Oroxylin A promotes superoxide dismutase (SOD2) gene expression through SIRT3-regulated DNA-binding activity of FOXO3a and increases the activity of SOD2 by promoting SIRT3-mediated deacetylation [3]. In vivo: Oroxylin A inhibited the tumor growth of nude mice-inoculated MCF-7 or HCT116 cells. The expression of MDM2 protein in tumor tissue was downregulated by oroxylin A as well [1].
References:
[1]. Zhao K, et al. Oroxylin A promotes PTEN-mediated negative regulation of MDM2 transcription via SIRT3-mediated deacetylation to stabilize p53 and inhibit glycolysis in wt-p53 cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Apr 23;8:41. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25902914
[2]. Dai Q, et al. Oroxylin A regulates glucose metabolism in response to hypoxic stress with the involvement of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Mol Carcinog. 2015 Aug 10.
[3]. Wei L, et al. Oroxylin A inhibits glycolysis-dependent proliferation of human breast cancer via promoting SIRT3-mediated SOD2 transcription and HIF1α destabilization. Cell Death Dis. 2015 Apr 9
- Astragalin
Catalog No.:BCN5549
CAS No.:480-10-4
- Eleutherol
Catalog No.:BCN8480
CAS No.:480-00-2
- CP-809101
Catalog No.:BCC1498
CAS No.:479683-64-2
- 1-O-galloyl-2-O-cinnamoyl-beta-d-glucose
Catalog No.:BCC3967
CAS No.:
- AUDA
Catalog No.:BCC4023
CAS No.:479413-70-2
- NBQX disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6907
CAS No.:479347-86-9
- CNQX disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6908
CAS No.:479347-85-8
- TC OT 39
Catalog No.:BCC7958
CAS No.:479232-57-0
- MMPIP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7528
CAS No.:479077-02-6
- [Orn8]-Urotensin II
Catalog No.:BCC5793
CAS No.:479065-85-5
- Aucubin
Catalog No.:BCN5355
CAS No.:479-98-1
- Vitexicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN5020
CAS No.:479-91-4
- Izalpinine
Catalog No.:BCN3682
CAS No.:480-14-8
- Morin
Catalog No.:BCN1028
CAS No.:480-16-0
- Taxifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5550
CAS No.:480-18-2
- Isorhamnetin
Catalog No.:BCN5551
CAS No.:480-19-3
- Aromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5552
CAS No.:480-20-6
- Orobol
Catalog No.:BCN5553
CAS No.:480-23-9
- Mellein
Catalog No.:BCN4785
CAS No.:480-33-1
- Eugenin
Catalog No.:BCN2921
CAS No.:480-34-2
- Linarin
Catalog No.:BCN5554
CAS No.:480-36-4
- Pinostrobin
Catalog No.:BCN5555
CAS No.:480-37-5
- Pinocembrin
Catalog No.:BCN5556
CAS No.:480-39-7
- Chrysin
Catalog No.:BCN5557
CAS No.:480-40-0
Synthesis and in vitro study of novel 7-O-acyl derivatives of Oroxylin A as antibacterial agents.[Pubmed:16046127]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Sep 1;15(17):3953-6.
A series of Oroxylin A derivatives, prepared by alkylation and condensation, were fully characterized by spectroscopic methods. All the derivatives were screened for antibacterial activity against a panel of susceptible and resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. It was observed that acylation of 7-OH group in Oroxylin A significantly enhanced the activity as compared to their parent compound (Oroxylin A).
Antithrombotic activities of oroxylin A in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:23963976]
Arch Pharm Res. 2014 May;37(5):679-86.
Here, the anticoagulant activities of Oroxylin A (OroA), a major component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, were examined by monitoring activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), prothrombin time (PT), and the activities of cell-based thrombin and activated factor X (FXa). Furthermore, the effects of OroA on the expressions of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) and tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) were tested in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with OroA resulted in prolonged aPTT and PT and inhibition of the activities of thrombin and FXa, and OroA inhibited production of thrombin and FXa in HUVECs. And OroA inhibited thrombin-catalyzed fibrin polymerization and platelet aggregation. In accordance with these anticoagulant activities, OroA elicited anticoagulant effects in mouse. In addition, treatment of OroA resulted in the inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced production of PAI-1, and treatment with OroA resulted in the significant reduction of the PAI-1 to t-PA ratio. Collectively, OroA possess antithrombotic activities and offer bases for development of a novel anticoagulant.
Oroxylin A suppresses invasion through down-regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:19100732]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan 28;603(1-3):22-8.
Our previous study revealed that Oroxylin A, a naturally occurring monoflavonoid isolated from Scutellariae radix, could inhibit the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inducing the apoptosis in these cells. However, the molecular mechanism of its anticancer activity remains poorly understood and warrants further investigations. In this study, we examined the anti-invasive activities of Oroxylin A in vitro. The results showed that Oroxylin A suppressed MDA-MB-435 cell adhesion to the fibronectin-coated substrate in a concentration-dependent manner. It inhibited the wound healing migration of MDA-MB-435 cells and invasion of MDA-MB-435 cells through reconstituted extracellular matrix (matrigel). Zymography revealed that Oroxylin A decreased the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2) and metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9). Oroxylin A also inhibited the expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in MDA-MB-435 cells. Additionally, Oroxylin A exerted an inhibitory effect on the phosphorylation of extracellular regulated proteinkinases1/2 (ERK1/2). Collectively, these data provided a molecular basis for the antiinvasive effects of Oroxylin A. Taken together, these findings strongly suggest that Oroxylin A had potential anti-metastatic effect in vitro and shed light on the investigation of Oroxylin A on breast cancer metastasis in vivo.
Activation of the unfolded protein response contributed to the selective cytotoxicity of oroxylin A in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.[Pubmed:22609744]
Toxicol Lett. 2012 Jul 20;212(2):113-25.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a refractory malignancy with a high incidence and large mortality. Current strategy for the chemotherapy of HCC focuses on developing agents with better efficacy and lower toxicity. In this study, we demonstrated that the natural flavonoid Oroxylin A preferentially inhibited the viability of HCC cell line HepG2 but not the normal hepatic cell line L02. In HepG2 but not L02 cells, Oroxylin A induced substantial production of intracellular H(2)O(2) and inordinate activation of the PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4-CHOP branch of the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway, which resulted in the induction of TRB3 and causal reduction of p-AKT1/2/3 (Ser473). Moreover, these effects were eliminated by either the stable knockdown of CHOP or the pretreatment and then co-incubation with the specific H(2)O(2) scavenger catalase. These results indicated that the H(2)O(2)-triggered overactivation of the UPR pathway and causal inactivation of AKT signaling contributed to the preferential cytotoxicity of Oroxylin A in malignant HepG2 cells. Therefore, present study proposed an underlying molecular mechanism that implicated the selective antitumor effect of Oroxylin A and recommended Oroxylin A as a prospect for improving the current chemotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC.
Oroxylin A inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation.[Pubmed:10751555]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Jun 1;59(11):1445-57.
Polyphenols are major components of many traditional herbal remedies, which exhibit several beneficial effects including anti-inflammation. The exact mechanism of the anti-inflammatory action of polyphenols, however, has not been determined. In the present study, we examined the effects of eight different polyphenols isolated from Chinese herbs, including two flavonoids (myricitrin and Oroxylin A), four ellagitannins (penta-O-galloyl-beta-glucopyranose, woodfordin C, oenothein B, and cuphiin D1), and two anthraquinones (emodin and physcion), on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) gene expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. The results indicated that only Oroxylin A and emodin concentration-dependently inhibited LPS-induced NO production. The remaining compounds slightly inhibited LPS-induced NO production only at the highest concentration examined. Furthermore, Oroxylin A inhibited the expression of LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 proteins and mRNAs without an appreciable cytotoxic effect on RAW264.7 cells. Emodin also inhibited LPS-induced iNOS protein as potently as Oroxylin A, but it inhibited LPS-induced iNOS mRNA expression only slightly and did not affect COX-2 mRNA and proteins. This was consistent with the findings that Oroxylin A but not emodin or physcion inhibited prostaglandin E(2) synthesis induced by LPS. The inhibitory effects of Oroxylin A on LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression were also demonstrated in Bcl-2-overexpressing RAW264.7 macrophages, suggesting that Oroxylin A inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression was not due to its antioxidant effect. Furthermore, Oroxylin A but not emodin blocked nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) binding and transcriptional activation associated with decreased p65 proteins in the nucleus induced by LPS. These results indicated that Oroxylin A, an active component in Huang Qin, inhibited LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression by blocking NF-kappaB activation, whereas emodin inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS expression may be mediated by a different transcription factor.
Oroxylin A enhances memory consolidation through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mice.[Pubmed:25218897]
Brain Res Bull. 2014 Sep;108:67-73.
Memory consolidation is a process by which acquired information is transformed from a labile into a more stable state that can be retrieved at a later time. In the present study, we investigated the role of Oroxylin A on the memory consolidation process in mice. Oroxylin A improved the memory retention administered at 0 h, 1 h and 3 h after training in a passive avoidance task, suggesting that Oroxylin A facilitates memory consolidation. Oroxylin A increased mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (mBDNF) levels in the hippocampus from 6h to 24h after administration. Moreover, 3h post-training administration of Oroxylin A enhanced the mBDNF level at 9h after the acquisition trial compared to the level at 6h after the acquisition trial. However, 6h post-training administration of Oroxylin A did not increase the mBDNF level at 9h after the acquisition trial. Blocking mBDNF signaling with recombinant tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB)-Fc or k252a at 9h after the acquisition trial obstructed the effect of Oroxylin A on memory consolidation. Taken together, our data suggest that Oroxylin A facilitates memory consolidation through BDNF-TrkB signaling and confirms that the increase of BDNF in a specific time window plays a crucial role in memory consolidation.
Anti-pruritic effect of baicalin and its metabolites, baicalein and oroxylin A, in mice.[Pubmed:20453872]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Jun;31(6):718-24.
AIM: To explore whether intestinal microflora plays a role in anti-pruritic activity of baicalin, a main constituent of the rhizome of Scutellaria baicalensis (SB). METHODS: Baicalin was anaerobically incubated with human fecal microflora, and its metabolites, baicalein and Oroxylin A, were isolated. The inhibitory effect of baicalin and its metabolites was accessed in histamine- or compound 48/80-induced scratching behavior in mice. RESULTS: Baicalin was metabolized to baicalein and Oroxylin A, with metabolic activities of 40.2+/-26.2 and 1.2+/-1.1 nmol.h(-1).mg(-1) wet weight of human fecal microflora, respectively. Baicalin (20, 50 mg/kg) showed more potent inhibitory effect on histamine-induced scratching behavior when orally administered than intraperitoneally. In contrast, baicalein and Oroxylin A had more potent inhibitory effect when the intraperitoneally administered. The anti-scratching behavior activity of oral baicalin and its metabolites was in proportion to their inhibition on histamine-induced increase of vascular permeability with Oroxylin A more potent than baicalein and baicalin. In Magnus test using guinea pig ileum, Oroxylin A is more potent than baicalein and baicalin in inhibition of histamine-induced contraction. The anti-scratching behavioral effect of oral baicalin was significantly reduced when oral antibiotics were simultaneously administered, whereas the effect of baicalein and Oroxylin A were not affected. CONCLUSION: Oral baicalin may be metabolized by intestinal microflora into baicalein and Oroxylin A, which ameliorate pruritic reactions through anti-histamine action.
Oroxylin A reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of MCF7/ADR cells by G2/M arrest.[Pubmed:23470866]
Toxicol Lett. 2013 May 23;219(2):107-15.
Oroxylin A is a naturally occurring monoflavonoid isolated from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, which has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties. The purpose of this study is to investigate the reversal effect and the fundamental mechanisms of Oroxylin A in MCF7/ADR cells. Data indicated that Oroxylin A showed strong reversal potency in MCF7/ADR cells and the reversal fold (RF) reached 4.68. After treatment with Oroxylin A, MCF7/ADR cells displayed reduced functional activity and expression of MDR1 at both the protein and mRNA levels. Meanwhile, Oroxylin A induced cells G2/M arrest in a concentration-dependent manner by increasing the expression of p-Chk2 (Thr68). Moreover, western blot and EMSA assays were used to reveal the inhibition of NF-kappaB in nucleus and the suppression of NF-kappaB binding activity by Oroxylin A. NSC 109555 ditosylate-Chk2 inhibitor partly dismissed G2/M arrest induced by Oroxylin A, reversed the increased trend of p-Chk2 and p-P53 (Ser20), inhibited the decreasing effect of Oroxylin A on the expression of P-gp and decreased the reversal fold of 90 muM Oroxylin A from 4.68 fold to 1.73 fold. In conclusion, we suggested that Oroxylin A reversed MDR by G2/M arrest and the underlying mechanism attributed to the suppression of P-gp expression via Chk2/P53/NF-kappaB signaling pathway.


