GAP-134Gap junction modifier CAS# 943134-39-2 |
- GAP-134 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1589
CAS No.:943133-81-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 943134-39-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16656685 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H17N3O4 | M.Wt | 291.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Danegaptide; ZP 1609 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO | ||
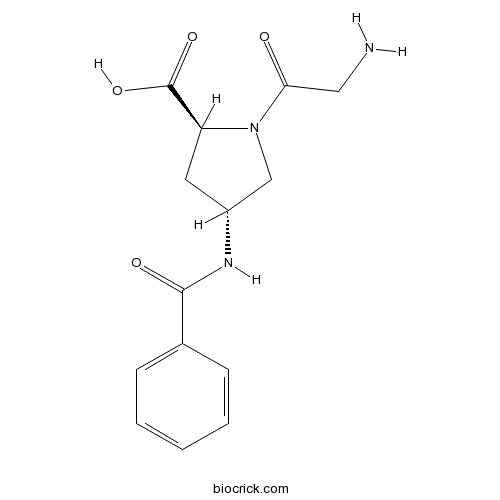
| Chemical Name | (2S,4R)-1-(2-aminoacetyl)-4-benzamidopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(CN(C1C(=O)O)C(=O)CN)NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BIZKIHUJGMSVFD-MNOVXSKESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H17N3O4/c15-7-12(18)17-8-10(6-11(17)14(20)21)16-13(19)9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5,10-11H,6-8,15H2,(H,16,19)(H,20,21)/t10-,11+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | GAP-134 (Danegaptide, ZP 1609), a small modified dipeptide, has been identified as a potent and selective second generation gap junction modifier with oral bioavailability.
IC50 value:
Target: gap junction
Gap junction uncoupling can alter conduction pathways and promote cardiac re-entry mechanisms that potentiate many supraventricular arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter (AFL). Gap junction modifier GAP-134, showed consistent efficacy on measures of conduction and AF/AFL inducibility in the canine sterile pericarditis model. GAP-134 is a pharmalogical agent with a favorable clinical safety profile and potential antiarrhythmic efficacy, as already confirmed in phase I clinical trials. References: | |||||

GAP-134 Dilution Calculator

GAP-134 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4329 mL | 17.1644 mL | 34.3289 mL | 68.6577 mL | 85.8222 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6866 mL | 3.4329 mL | 6.8658 mL | 13.7315 mL | 17.1644 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3433 mL | 1.7164 mL | 3.4329 mL | 6.8658 mL | 8.5822 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0687 mL | 0.3433 mL | 0.6866 mL | 1.3732 mL | 1.7164 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0343 mL | 0.1716 mL | 0.3433 mL | 0.6866 mL | 0.8582 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Gap junction uncoupling can alter conduction pathways and promote cardiac re-entry mechanisms that potentiate many supraventricular arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter (AFL). GAP-134 (Danegaptide), a small modified dipeptide, has been identified as a potent and selective second generation gap junction modifier with oral bioavailability. Gap junction modifier GAP-134, showed consistent efficacy on measures of conduction and AF/AFL inducibility in the canine sterile pericarditis model. GAP-134 is a pharmalogical agent with a favorable clinical safety profile and potential antiarrhythmic efficacy, as already confirmed in phase I clinical trials.
- GAP-134 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1589
CAS No.:943133-81-1
- H-Phe(4-NH2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3152
CAS No.:943-80-6
- DGAT-1 inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1530
CAS No.:942999-61-3
- 3beta-(2-O-alpha-L-Rhamnopyranosyl-beta-D-xylopyranosyloxy)-23-hydroxyoleana-12-ene-28-oic acid 6-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8948
CAS No.:942997-00-4
- 12-Hydroxyganoderic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN8051
CAS No.:942950-96-1
- CCT129202
Catalog No.:BCC2187
CAS No.:942947-93-5
- GSK1070916
Catalog No.:BCC2183
CAS No.:942918-07-2
- Acetyldihydromicromelin A
Catalog No.:BCN4492
CAS No.:94285-22-0
- Dihydromicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN4491
CAS No.:94285-06-0
- 5-Hydroxy-7,8,2',5'-tetramethoxyflavone 5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1302
CAS No.:942626-75-7
- 1,5,15-Tri-O-methylmorindol
Catalog No.:BCN4490
CAS No.:942609-65-6
- Walsuronoid B
Catalog No.:BCN4489
CAS No.:942582-15-2
- Chlorahololide D
Catalog No.:BCN4493
CAS No.:943136-39-8
- Peroxydehydrotumulosic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3739
CAS No.:943225-53-4
- Ponatinib (AP24534)
Catalog No.:BCC2522
CAS No.:943319-70-8
- Ethyl p-nitrobenzyl carbonate
Catalog No.:BCN3285
CAS No.:943409-69-6
- Sappanchalcone
Catalog No.:BCN4494
CAS No.:94344-54-4
- JNJ-38877605
Catalog No.:BCC2485
CAS No.:943540-75-8
- Rhapontigenin 3'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2873
CAS No.:94356-22-6
- Piceatannol 3'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2874
CAS No.:94356-26-0
- Methylnissolin-3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3829
CAS No.:94367-42-7
- Isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3845
CAS No.:94367-43-8
- Sebiferenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4495
CAS No.:94390-09-7
- Ophiopogoside A
Catalog No.:BCC8346
CAS No.:943914-99-6
The gap junction modifier, GAP-134 [(2S,4R)-1-(2-aminoacetyl)-4-benzamido-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid], improves conduction and reduces atrial fibrillation/flutter in the canine sterile pericarditis model.[Pubmed:19252062]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Jun;329(3):1127-33.
Gap junction uncoupling can alter conduction pathways and promote cardiac re-entry mechanisms that potentiate many supraventricular arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter (AFL). Our objective was to determine whether GAP-134 [(2S,4R)-1-(2-aminoacetyl)-4-benzamido-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid], a small dipeptide gap junction modifier, can improve conduction and ultimately prevent AF/AFL. In rat atrial strips subjected to metabolic stress, GAP-134 prevented significantly conduction velocity slowing at 10 nM compared with vehicle (p < 0.01). In the canine sterile pericarditis model, conduction time (CT; n = 5), atrial effective refractory period (AERP; n = 3), and AF/AFL duration/inducibility (n = 16) were measured 2 to 3 days postoperatively in conscious dogs. CT was significantly faster after GAP-134 infusion (average plasma concentration, 250 nM) at cycle lengths of 300 ms (66.2 +/- 1.0 versus 62.0 +/- 1.0 ms; p < 0.001) and 200 ms (64.4 +/- 0.9 versus 61.0 +/- 1.3 ms; p < 0.001). No significant changes in AERP were noted after GAP-134 infusion. The mean number of AF/AFL inductions per animal was significantly decreased after GAP-134 infusion (2.7 +/- 0.6 versus 1.6 +/- 0.8; p < 0.01), with total AF/AFL burden being decreased from 12,280 to 6063 s. Western blot experiments showed no change in connexin 43 expression. At concentrations exceeding those described in the AF/AFL experiments, GAP-134 had no effect on heart rate, blood pressure, or any electrocardiogram parameters. In conclusion, GAP-134 shows consistent efficacy on measures of conduction and AF/AFL inducibility in the canine sterile pericarditis model. These findings, along with its oral bioavailability, underscore its potential antiarrhythmic efficacy.
Effects of chronic gap junction conduction-enhancing antiarrhythmic peptide GAP-134 administration on experimental atrial fibrillation in dogs.[Pubmed:19808462]
Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009 Apr;2(2):171-8.
BACKGROUND: Abnormal intercellular communication caused by connexin dysfunction may contribute to atrial fibrillation (AF). The present study assessed the effect of the gap junction conduction-enhancing antiarrhythmic peptide GAP-134 on AF inducibility and maintenance in a dog model of atrial cardiomyopathy. METHODS AND RESULTS: Twenty-four dogs subject to simultaneous atrioventricular pacing (220 bpm for 14 days) were randomly assigned to placebo treatment (PACED-CTRL; 12 dogs) or oral GAP-134 (2.9 mg/kg BID; PACED-GAP-134; 12 dogs) starting on day 0. UNPACED-CTRL (4 dogs) and UNPACED-GAP-134 (4 dogs) served as additional control groups. Change in left atrial (LA) systolic area from baseline to 14 days was calculated using transoesophageal echocardiography. At 14 days, animals underwent an open-chest electrophysiological study. PACED-CTRL dogs (versus UNPACED-CTRL) had a shorter estimated LA wavelength (8.0+/-1.4 versus 24.4+/-2.5 cm, P<0.05) and a greater AF vulnerability (mean AF duration, 1588+/-329 versus 25+/-34 seconds, P<0.05). Oral GAP-134 had no effect on AF vulnerability in UNPACED dogs. Compared with PACED-CTRL dogs, PACED-GAP-134 dogs had a longer estimated LA wavelength (10.2+/-2.8 versus 8.0+/-1.4 cm, respectively, P<0.05). Oral GAP-134 did not significantly reduce AF inducibility or maintenance in the entire group of 24 PACED dogs; in a subgroup of dogs (n=11) with less than 100% increase in LA systolic area, oral GAP-134 reduced AF induction from 100% to 40% and mean AF duration from 1737+/-120 to 615+/-280 seconds (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: Oral GAP-134 reduces pacing-induced decrease in LA wavelength and appears to attenuate AF vulnerability in dogs with less atrial mechanical remodeling. Gap junction modulation may affect AF in some circumstances.
GAP-134 ([2S,4R]-1-[2-aminoacetyl]4-benzamidopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid) prevents spontaneous ventricular arrhythmias and reduces infarct size during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in open-chest dogs.[Pubmed:19721133]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Sep;14(3):207-14.
The antiarrhythmic dipeptide, GAP-134, ([2S,4R]-1[2-aminoacetyl]-4-benzamido-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid) was evaluated in canine ischemia/reperfusion model. In dogs subjected to 60-minute ischemia and 4-hour reperfusion, GAP-134 was administered 10 minutes before reperfusion as a bolus + intravenous (IV) infusion. The doses administered were 0.25 microg/kg bolus + 0.19 microg/kg per hour infusion; 2.5 microg/kg + 1.9 microg/kg per hour; 25 mg/kg + 19 mg/kg per hour; 75 mg/kg + 57 mg/kg per hour. Ventricular ectopy was quantified during reperfusion, including premature ventricular contractions (PVC) and ventricular tachycardia (VT). Total incidence of VT was reduced significantly with the 2 highest doses of GAP-134 (1.7 + 0.8; 2.2 + 1.4 events; P < .05) compared to controls (23.0 + 6.1). Total PVCs were reduced significantly from 11.1 + 1.6% in control animals to 2.0% + 0.7% and 1.8% + 0.8% after the 2 highest doses of GAP-134. Infarct size, expressed as percentage of left ventricle, was reduced significantly from 19.0% + 3.5% in controls to 7.9% + 1.5% and 7.1% + 0.8% (P < .05) at the 2 highest doses of GAP-134. GAP-134 is an effective antiarrhythmic agent with potential to reduce ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Discovery of (2S,4R)-1-(2-aminoacetyl)-4-benzamidopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (GAP-134)13, an orally active small molecule gap-junction modifier for the treatment of atrial fibrillation.[Pubmed:19175320]
J Med Chem. 2009 Feb 26;52(4):908-11.
Rotigaptide (3) is an antiarrhythmic peptide that improves cardiac conduction by modifying gap-junction communication. Small molecule gap-junction modifiers with improved physical properties were identified from a Zealand Pharma peptide library using pharmaceutical profiling, established SAR around 3, and a putative pharmacophore model for rotigaptide. Activity of the compounds was confirmed in a mouse cardiac conduction block model of arrhythmia. Dipeptide 9f (GAP-134) was identified as a potent, orally active gap-junction modifier for clinical development.


