GGsTopγ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible CAS# 926281-37-0 |
- Pepstatin A
Catalog No.:BCC1218
CAS No.:26305-03-3
- Vicriviroc Malate
Catalog No.:BCC1230
CAS No.:541503-81-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 926281-37-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23582776 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H18NO7P | M.Wt | 331.26 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
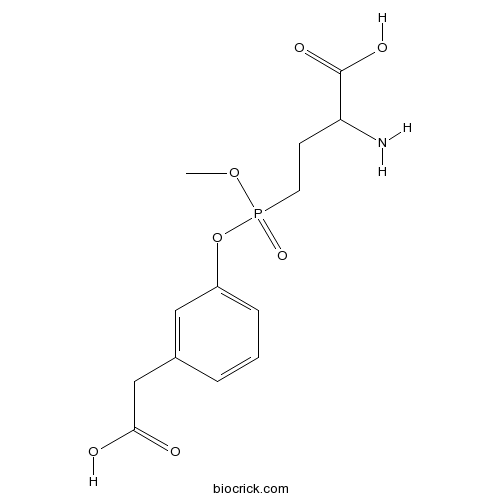
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-4-[[3-(carboxymethyl)phenoxy]-methoxyphosphoryl]butanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COP(=O)(CCC(C(=O)O)N)OC1=CC=CC(=C1)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NTFPDEDRMYYPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H18NO7P/c1-20-22(19,6-5-11(14)13(17)18)21-10-4-2-3-9(7-10)8-12(15)16/h2-4,7,11H,5-6,8,14H2,1H3,(H,15,16)(H,17,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, irreversible γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor; displays no inhibitory effects on glutamine amidotransferases or asparagine synthetase. Suppresses oxidative stress by inhibiting GGT activation. Prevents ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in rats in vivo. |

GGsTop Dilution Calculator

GGsTop Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0188 mL | 15.0939 mL | 30.1878 mL | 60.3755 mL | 75.4694 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6038 mL | 3.0188 mL | 6.0376 mL | 12.0751 mL | 15.0939 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3019 mL | 1.5094 mL | 3.0188 mL | 6.0376 mL | 7.5469 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0604 mL | 0.3019 mL | 0.6038 mL | 1.2075 mL | 1.5094 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0302 mL | 0.1509 mL | 0.3019 mL | 0.6038 mL | 0.7547 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GGsTop is a novel is a novel, highly selective, and irreversible γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor with Ki of 0.17 mM. [1]
GGT plays an important role in the metabolism of plasma glutathione (GSH) and its S-conjugates via the cleavage of the γ-glutamyl amide bond by hydrolysis and/or transpeptidation. GGT exists in the lung as a soluble enzyme in association with surfactant phospholipids and controls turnover of the extracellular pool of glutathione in LLF (lung lining fluid). In the human enzyme, a specific residue in the Cys - Gly binding site played a critical role in recognizing the Cys – Gly moiety or the acceptor molecules by interacting with the C-terminal carboxy group, whereas the Cys side chain and the Cys - Gly amide bond were not recognized significantly. GGsTop was found for its potency against GGT in a series of analogues designed for structure-activity relationships. [1, 2]
The inactivation rates of E. coli and human GGT by GGsTop were studied. GGsTop showed a good potency against GGT in both species. Furthermore, the kinetics of GGsTop for human GGT was also measured and its Ki value is 0.17 mM. [1]
In the IL-13 model, mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop exhibit a lung inflammatory response similar to that of mice administrated with IL-13 alone. However, mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop exhibit attenuation of methacholine-stimulated airway hyper-reactivity, inhibitory effect of Muc5ac and Muc5b gene induction, decreased epithelial cell mucous accumulation in the airway and a 4-fold increase in LLF glutathione content compared to mice in IL-13 group. The associated increase in LLF glutathione can protect lung airway epithelial cells against oxidant injury associated with inflammation in asthma. Moreover, ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) was induced by occlusion of the left renal artery and vein for 45 min followed by reperfusion 2 weeks after contralateral nephrectomy. Renal function in control significantly decreased at 1 day after reperfusion. Rats administrated with GGsTop at doses of 1 and 10 mg per kg i.v. 5 min before ischemia attenuated the I/R-induced renal dysfunction in a dose-dependent manner. Histopathological evaluation of the kidney of AKI rats revealed severe renal damages, whereas they were significantly suppressed by the GGsTop treatment. [2, 3]
References:
[1]. Han, Liyou, et al. "Design, synthesis, and evaluation of γ-phosphono diester analogues of glutamate as highly potent inhibitors and active site probes of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase." Biochemistry 46.5 (2007): 1432-1447.
[2]. Yamamoto, Shinya, et al. "Preventive effect of GGsTop, a novel and selective γ-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats." Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 339.3 (2011): 945-951.
[3]. Tuzova, Marina, et al. "Inhibiting lung lining fluid glutathione metabolism with GGsTop as a novel treatment for asthma." Frontiers in pharmacology 5 (2014)
- BG45
Catalog No.:BCC6469
CAS No.:926259-99-6
- Milnacipran
Catalog No.:BCC4194
CAS No.:92623-85-3
- O-Demethylforbexanthone
Catalog No.:BCN4469
CAS No.:92609-77-3
- Radotinib(IY-5511)
Catalog No.:BCC6398
CAS No.:926037-48-1
- AMTB hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7834
CAS No.:926023-82-7
- Dayecrystal A
Catalog No.:BCN4859
CAS No.:926010-24-4
- Secaubrytriol
Catalog No.:BCN4468
CAS No.:925932-10-1
- Secaubryenol
Catalog No.:BCN4467
CAS No.:925932-08-7
- TG100713
Catalog No.:BCC4985
CAS No.:925705-73-3
- 3-Isomangostin hydrate formate
Catalog No.:BCN4466
CAS No.:925705-36-8
- Acitretin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4299
CAS No.:925701-88-8
- KU-60019
Catalog No.:BCC3699
CAS No.:925701-49-1
- Deltatsine
Catalog No.:BCN8106
CAS No.:92631-66-8
- Germacrone 4,5-epoxide
Catalog No.:BCN6724
CAS No.:92691-35-5
- Toll-like receptor modulator
Catalog No.:BCC2007
CAS No.:926927-42-6
- Motolimod (VTX-2337)
Catalog No.:BCC6497
CAS No.:926927-61-9
- Glochicoccin D
Catalog No.:BCN4471
CAS No.:927812-23-5
- KC7F2
Catalog No.:BCC2434
CAS No.:927822-86-4
- DPNI-caged-GABA
Catalog No.:BCC5957
CAS No.:927866-58-8
- RAF265
Catalog No.:BCC3677
CAS No.:927880-90-8
- Golvatinib (E7050)
Catalog No.:BCC4423
CAS No.:928037-13-2
- Alisol O
Catalog No.:BCN3362
CAS No.:928148-51-0
- Tenacissoside F
Catalog No.:BCN4472
CAS No.:928151-78-4
- 3-Chloro-1-(4-octylphenyl)-propanone
Catalog No.:BCN2249
CAS No.:928165-59-7
Inhibiting lung lining fluid glutathione metabolism with GGsTop as a novel treatment for asthma.[Pubmed:25132819]
Front Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 31;5:179.
Asthma is characterized by airway inflammation. Inflammation is associated with oxidant stress. Airway epithelial cells are shielded from this stress by a thin layer of lung lining fluid (LLF) which contains an abundance of the antioxidant glutathione. LLF glutathione metabolism is regulated by gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Loss of LLF GGT activity in the mutant GGT(enu1) mouse causes an increase in baseline LLF glutathione content which is magnified in an IL-13 model of allergic airway inflammation and protective against asthma. Normal mice are susceptible to asthma in this model but can be protected with acivicin, a GGT inhibitor. GGT is a target to treat asthma but acivicin toxicity limits clinical use. GGsTop is a novel GGT inhibitor. GGsTop inhibits LLF GGT activity only when delivered through the airway. In the IL-13 model, mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop exhibit a lung inflammatory response similar to that of mice treated with IL-13 alone. But mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop show attenuation of methacholine-stimulated airway hyper-reactivity, inhibition of Muc5ac and Muc5b gene induction, decreased airway epithelial cell mucous accumulation and a fourfold increase in LLF glutathione content compared to mice treated with IL-13 alone. Mice treated with GGsTop alone are no different from that of mice treated with saline alone, and show no signs of toxicity. GGsTop could represent a valuable pharmacological tool to inhibit LLF GGT activity in pulmonary disease models. The associated increase in LLF glutathione can protect lung airway epithelial cells against oxidant injury associated with inflammation in asthma.
Phosphonate-based irreversible inhibitors of human gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT). GGsTop is a non-toxic and highly selective inhibitor with critical electrostatic interaction with an active-site residue Lys562 for enhanced inhibitory activity.[Pubmed:27622749]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 1;24(21):5340-5352.
gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT, EC 2.3.2.2) that catalyzes the hydrolysis and transpeptidation of glutathione and its S-conjugates is involved in a number of physiological and pathological processes through glutathione metabolism and is an attractive pharmaceutical target. We report here the evaluation of a phosphonate-based irreversible inhibitor, 2-amino-4-{[3-(carboxymethyl)phenoxy](methoyl)phosphoryl}butanoic acid (GGsTop) and its analogues as a mechanism-based inhibitor of human GGT. GGsTop is a stable compound, but inactivated the human enzyme significantly faster than the other phosphonates, and importantly did not inhibit a glutamine amidotransferase. The structure-activity relationships, X-ray crystallography with Escherichia coli GGT, sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis of human GGT revealed a critical electrostatic interaction between the terminal carboxylate of GGsTop and the active-site residue Lys562 of human GGT for potent inhibition. GGsTop showed no cytotoxicity toward human fibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells up to 1mM. GGsTop serves as a non-toxic, selective and highly potent irreversible GGT inhibitor that could be used for various in vivo as well as in vitro biochemical studies.
GGsTOP increases migration of human periodontal ligament cells in vitro via reactive oxygen species pathway.[Pubmed:27035100]
Mol Med Rep. 2016 May;13(5):3813-20.
GGsTop is a novel and selective inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), a cell-surface enzyme that has a key role in glutathione homeostasis and the maintenance of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS are essential for wound healing. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying the inhibition of GGT by GGsTop in human periodontal ligament cells (hPLCs). The present study assessed GGT expression in mouse periodontal ligament tissues, GGT activity in hPLCs, and the potential physiological effect of GGsTop on hPLC migration. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed that GGT was widely expressed in mouse periodontal ligament tissue. Treatment with GGsTop was associated with greater proliferation and migration of hPLCs, and higher levels of cellular ROS compared with untreated hPLCs. However, the increase in intracellular ROS was attenuated in hPLCs cocultured with the antioxidant Nacetylcysteine (NAC), a precursor of glutathione. The higher ROS levels associated with GGsTop treatment were in parallel with increases in the levels of type I collagen and alpha smooth muscle actin, which was inhibited in hPLCs cocultured with NAC. Thus, GGsTop may promote hPLC migration and participate in the maintenance of the periodontal ligament apparatus via the ROS pathway.
GGsTop, a novel and specific gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, protects hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed:27365338]
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):G305-12.
Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury is a major clinical problem and is associated with numerous adverse effects. GGsTop [2-amino-4{[3-(carboxymethyl)phenyl](methyl)phosphono}butanoic acid] is a highly specific and irreversible gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT) inhibitor. We studied the protective effects of GGsTop on IR-induced hepatic injury in rats. Ischemia was induced by clamping the portal vein and hepatic artery of left lateral and median lobes of the liver. Before clamping, saline (IR group) or saline containing 1 mg/kg body wt of GGsTop (IR-GGsTop group) was injected into the liver through the inferior vena cava. At 90 min of ischemia, blood flow was restored. Blood was collected before induction of ischemia and prior to restoration of blood flow and at 12, 24, and 48 h after reperfusion. All the animals were euthanized at 48 h after reperfusion and the livers were harvested. Serum levels of alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and gamma-GT were significantly lower after reperfusion in the IR-GGsTop group compared with the IR group. Massive hepatic necrosis was present in the IR group, while only few necroses were present in the IR-GGsTop group. Treatment with GGsTop increased hepatic GSH content, which was significantly reduced in the IR group. Furthermore, GGsTop prevented increase of hepatic gamma-GT, malondialdehyde, 4-hydroxynonenal, and TNF-alpha while all these molecules significantly increased in the IR group. In conclusion, treatment with GGsTop increased glutathione levels and prevented formation of free radicals in the hepatic tissue that led to decreased IR-induced liver injury. GGsTop could be used as a pharmacological agent to prevent IR-induced liver injury and the related adverse events.
Preventive effect of GGsTop, a novel and selective gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats.[Pubmed:21937737]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Dec;339(3):945-51.
GGsTop [2-amino-4-{[3-(carboxymethyl)phenyl](methyl)phosphono}butanoic acid], is a novel, highly selective, and irreversible gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor with no inhibitory activity on glutamine amidotransferases. In this study, we investigated the effects of treatment with GGsTop on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in uninephrectomized rats. Ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) was induced by occlusion of the left renal artery and vein for 45 min followed by reperfusion 2 weeks after contralateral nephrectomy. Renal function in vehicle-treated AKI rats markedly decreased at 1 day after reperfusion. Treatment with GGsTop (1 and 10 mg/kg i.v.) 5 min before ischemia attenuated the ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal dysfunction in a dose-dependent manner. Histopathological examination of the kidney of AKI rats revealed severe renal damage, which was significantly suppressed by the GGsTop treatment. In renal tissues exposed to ischemia/reperfusion, GGT activity was markedly increased immediately after reperfusion, whereas renal superoxide production and malondialdehyde level were significantly increased 6 h after reperfusion. These alterations were abolished by the treatment with GGsTop. In addition, renal glutathione content was decreased by the 45-min ischemia, but its level was markedly elevated by the GGsTop treatment. Our results demonstrate that the novel and highly selective GGT inhibitor GGsTop prevents ischemia/reperfusion-induced AKI. The renoprotective effect of GGsTop seems to be attributed to the suppression of oxidative stress by inhibiting GGT activation, thereby preventing the degradation of glutathione.
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of gamma-phosphono diester analogues of glutamate as highly potent inhibitors and active site probes of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.[Pubmed:17260973]
Biochemistry. 2007 Feb 6;46(5):1432-47.
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT, EC 2.3.2.2) catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl group of glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl amides to water (hydrolysis) or to amino acids and peptides (transpeptidation) and plays a central role in glutathione metabolism. GGT is involved in a number of biological events, such as drug resistance and metastasis of cancer cells by detoxification of xenobiotics and reactive oxygen species through glutathione metabolism, and is also implicated in physiological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, neurodegerative disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. In this study, we designed, synthesized, and evaluated a series of gamma-phosphono diester analogues of glutamate as transition-state mimic inhibitors of GGT. The electrophilic phosphonate diesters served as highly potent mechanism-based inhibitors that caused the time-dependent and irreversible inhibition of both the E. coli and human enzymes, probably by phosphonylating the catalytic Thr residue of the enzyme. In particular, one of the inhibitors exhibited more than 6000 times higher activity toward human GGT than acivicin, a classical but nonselective inhibitor of GGT. The dependence of the inactivation rate on the leaving group ability of the phosphonates (Bronsted plot) revealed that the phosphonylation of the catalytic Thr residue proceeded via a dissociative transition-state with substantial bond cleavage between the phosphorus and the leaving group for both E. coli and human GGTs. The binding site of GGT for the Cys-Gly moiety of glutathione or for the acceptor molecules was probed by the phosphonate diesters to reveal a significant difference in the mechanism of substrate recognition between E. coli and human GGT. Thus, in the human enzyme, a specific residue in the Cys-Gly binding site played a critical role in recognizing the Cys-Gly moiety or the acceptor molecules by interacting with the C-terminal carboxy group, whereas the Cys side chain and the Cys-Gly amide bond were not recognized significantly. In contrast, the E. coli enzyme was a nonselective enzyme that accommodated substrates without specifically recognizing the C-terminal carboxy group of the Cys-Gly moiety of gamma-glutamyl compounds or the acceptor molecules. The phosphonate diester-based GGT inhibitors shown here should serve as a blue print for the future design of highly selective GGT inhibitors for use as drug leads and biological probes that gain insight into the hitherto undefined physiological roles of GGT and the relationships between GGT and a variety of diseases.


