Galanin (1-29) (rat, mouse)Non-selective galanin receptor agonist CAS# 114547-31-8 |
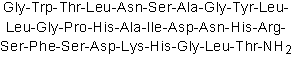
- Etifoxine
Catalog No.:BCC1560
CAS No.:21715-46-8
- Etomidate
Catalog No.:BCC1150
CAS No.:33125-97-2
- Acamprosate calcium
Catalog No.:BCC1327
CAS No.:77337-73-6
- Flumazenil
Catalog No.:BCC1259
CAS No.:78755-81-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 114547-31-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488777 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C141H211N43O41 | M.Wt | 3164.48 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | GWTLNSAGYLLGPHAIDNHRSFSDKHGLT (Modifications: Thr-29 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]amino]-5-carbamimidamidopentanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-4-[[(2S)-6-amino-1-[[(2S)-1-[[2-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3R)-1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC=N1)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CC3=CNC=N3)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CNC=N4)NC(=O)C5CCCN5C(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CC=C(C=C6)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC7=CNC8=CC=CC=C87)NC(=O)CN | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JHQDYHHNJBOXKP-UPNHMZDKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C141H211N43O41/c1-15-71(10)113(139(224)177-100(52-112(199)200)132(217)173-97(49-105(144)191)129(214)171-96(48-81-57-151-66-159-81)128(213)166-86(30-23-37-152-141(147)148)122(207)178-102(62-186)136(221)169-92(43-76-25-17-16-18-26-76)127(212)180-103(63-187)137(222)174-99(51-111(197)198)131(216)165-85(29-21-22-36-142)121(206)170-94(46-79-55-149-64-157-79)120(205)155-59-109(195)163-88(40-68(4)5)133(218)182-114(74(13)188)116(146)201)181-118(203)73(12)161-123(208)95(47-80-56-150-65-158-80)175-138(223)104-31-24-38-184(104)110(196)60-156-119(204)87(39-67(2)3)167-124(209)89(41-69(6)7)168-126(211)91(44-77-32-34-82(190)35-33-77)164-108(194)58-154-117(202)72(11)160-135(220)101(61-185)179-130(215)98(50-106(145)192)172-125(210)90(42-70(8)9)176-140(225)115(75(14)189)183-134(219)93(162-107(193)53-143)45-78-54-153-84-28-20-19-27-83(78)84/h16-20,25-28,32-35,54-57,64-75,85-104,113-115,153,185-190H,15,21-24,29-31,36-53,58-63,142-143H2,1-14H3,(H2,144,191)(H2,145,192)(H2,146,201)(H,149,157)(H,150,158)(H,151,159)(H,154,202)(H,155,205)(H,156,204)(H,160,220)(H,161,208)(H,162,193)(H,163,195)(H,164,194)(H,165,216)(H,166,213)(H,167,209)(H,168,211)(H,169,221)(H,170,206)(H,171,214)(H,172,210)(H,173,217)(H,174,222)(H,175,223)(H,176,225)(H,177,224)(H,178,207)(H,179,215)(H,180,212)(H,181,203)(H,182,218)(H,183,219)(H,197,198)(H,199,200)(H4,147,148,152)/t71-,72-,73-,74+,75+,85-,86-,87-,88-,89-,90-,91-,92-,93-,94-,95-,96-,97-,98-,99-,100-,101-,102-,103-,104-,113-,114-,115-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Non-selective galanin receptor agonist (Ki values are 0.98, 1.48 and 1.47 nM for GAL1, GAL2 and GAL3 respectively). Anticonvulsant; prevents the occurrence of full kindled seizures in rats. |

Galanin (1-29) (rat, mouse) Dilution Calculator

Galanin (1-29) (rat, mouse) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Regelidine
Catalog No.:BCN3094
CAS No.:114542-54-0
- Honyucitrin
Catalog No.:BCN4728
CAS No.:114542-44-8
- Spiramine A
Catalog No.:BCN6023
CAS No.:114531-28-1
- (+)-U-50488 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6656
CAS No.:114528-81-3
- (-)-U-50488 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6666
CAS No.:114528-79-9
- Z-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2743
CAS No.:1145-80-8
- Oroxin B
Catalog No.:BCN1203
CAS No.:114482-86-9
- BNP (1-32), human
Catalog No.:BCC1039
CAS No.:114471-18-0
- Beta-Furoyleupatolide
Catalog No.:BCN6407
CAS No.:114437-24-0
- WYE-125132 (WYE-132)
Catalog No.:BCC4608
CAS No.:1144068-46-1
- PF-8380
Catalog No.:BCC1857
CAS No.:1144035-53-9
- Fmoc-D-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3511
CAS No.:114360-54-2
- Boeravinone B
Catalog No.:BCN6466
CAS No.:114567-34-9
- Ganoderiol F
Catalog No.:BCN6024
CAS No.:114567-47-4
- Coronadiene
Catalog No.:BCN3683
CAS No.:1145689-64-0
- Thevebioside
Catalog No.:BCN6025
CAS No.:114586-47-9
- Soyasaponin Ba
Catalog No.:BCN2854
CAS No.:114590-20-4
- Kisspeptin 234
Catalog No.:BCC6077
CAS No.:1145998-81-7
- Moracin T
Catalog No.:BCN3291
CAS No.:1146113-27-0
- 17alpha-Thevebioside
Catalog No.:BCN6026
CAS No.:114613-59-1
- 3,4-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN6490
CAS No.:114637-83-1
- SNS-314 Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2177
CAS No.:1146618-41-8
- BMS-708163 (Avagacestat)
Catalog No.:BCC2104
CAS No.:1146699-66-2
- J 147
Catalog No.:BCC6360
CAS No.:1146963-51-0
Regulation of kindling epileptogenesis by hippocampal galanin type 1 and type 2 receptors: The effects of subtype-selective agonists and the role of G-protein-mediated signaling.[Pubmed:16699066]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):700-8.
The search for antiepileptic drugs that are capable of blocking the progression of epilepsy (epileptogenesis) is an important problem of translational epilepsy research. The neuropeptide galanin effectively suppresses acute seizures. We examined the ability of hippocampal galanin receptor type 1 (GalR1) and type 2 (GalR2) to inhibit kindling epileptogenesis and studied signaling cascades that mediate their effects. Wistar rats received 24-h-long intrahippocampal infusion of a GalR1/2 agonist galanin(1-29), GalR1 agonist M617 [galanin(1-13)-Gln14-bradykinin(2-9)-amide], or GalR2 agonist galanin(2-11). The peptides were administered alone or combined with an inhibitor of Gi protein pertussis toxin (PTX), Gi-protein activated K+ channels (GIRK) inhibitor tertiapin Q (TPQ), G(q/11) protein inhibitor [D-Arg1,D-Trp(5,7,9),Leu11]-substance P (dSP), or an inhibitor of intracellular Ca2+ release dantrolene. Sixteen hours into drug delivery, the animals were subjected to rapid kindling-60 electrical trains administered to ventral hippocampus every 5 min. M617 delayed epileptogenesis, whereas galanin(1-29) and galanin(2-11) completely prevented the occurrence of full kindled seizures. TPQ abolished anticonvulsant effect of M617 but not of galanin(2-11). PTX blocked anticonvulsant effects of M617 and inversed the action of galanin(1-29) and galanin(2-11) to proconvulsant. dSP and dantrolene did not modify seizure suppression through GalR1 and GalR2, but eliminated the proconvulsant effect of PTX + galanin(1-29) and PTX + galanin(2-11) combinations. We conclude that hippocampal GalR1 exert their disease-modifying effect through the Gi-GIRK pathway. GalR2 is antiepileptogenic through the Gi mechanism independent of GIRK. A secondary proconvulsant pathway coupled to GalR2 involves G(q/11) and intracellular Ca2+. The data are important for understanding endogenous mechanisms regulating epileptogenesis and for the development of novel antiepileptogenic drugs.
DUB-2 is a member of a novel family of cytokine-inducible deubiquitinating enzymes.[Pubmed:8995226]
J Biol Chem. 1997 Jan 3;272(1):51-7.
Cytokines regulate cell growth by inducing the expression of specific target genes. We have recently identified a cytokine-inducible, immediate-early gene, DUB-1, that encodes a deubiquitinating enzyme with growth regulatory activity. In the current study, we have isolated a highly related gene, DUB-2, that is induced by interleukin-2. The DUB-2 mRNA was induced in T cells as an immediate-early gene and was rapidly down-regulated. Like DUB-1, the DUB-2 protein had deubiquitinating activity in vitro. When a conserved cysteine residue of DUB-2, required for ubiquitin-specific thiol protease activity, was mutated to serine (C60S), deubiquitinating activity was abolished. DUB-1 and DUB-2 proteins are highly related throughout their primary amino acid sequence except for a hypervariable region at their COOH terminus. Moreover, the DUB genes co-localize to a region of mouse chromosome 7, suggesting that they arose by a tandem duplication of an ancestral DUB gene. Additional DUB genes co-localize to this region, suggesting a larger family of cytokine-inducible DUB enzymes. We propose that different cytokines induce specific DUB genes. Each induced DUB enzyme thereby regulates the degradation or the ubiquitination state of an unknown growth regulatory factor, resulting in a cytokine-specific growth response.


