J 147CAS# 1146963-51-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1146963-51-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25229652 | Appearance | Powder |
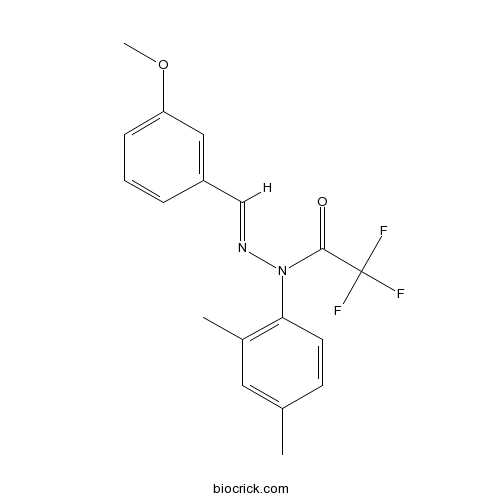
| Formula | C18H17F3N2O2 | M.Wt | 350.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (285.44 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-N-[(E)-(3-methoxyphenyl)methylideneamino]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)N(C(=O)C(F)(F)F)N=CC2=CC(=CC=C2)OC)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HYMZAYGFKNNHDN-SSDVNMTOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H17F3N2O2/c1-12-7-8-16(13(2)9-12)23(17(24)18(19,20)21)22-11-14-5-4-6-15(10-14)25-3/h4-11H,1-3H3/b22-11+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent neuroprotective and neurotrophic compound. Protects against neurotoxicity in cortical neurons in vitro (EC50 = 25 - 200 nM). Reduces soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels and increases BDNF levels in the hippocampus in vivo. Enhances memory in wild type rats. Prevents memory deficits and rescues cognitive deficits in young and aged transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice, respectively. Orally active. |

J 147 Dilution Calculator

J 147 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8545 mL | 14.2723 mL | 28.5445 mL | 57.089 mL | 71.3613 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5709 mL | 2.8545 mL | 5.7089 mL | 11.4178 mL | 14.2723 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2854 mL | 1.4272 mL | 2.8545 mL | 5.7089 mL | 7.1361 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0571 mL | 0.2854 mL | 0.5709 mL | 1.1418 mL | 1.4272 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0285 mL | 0.1427 mL | 0.2854 mL | 0.5709 mL | 0.7136 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
J-147 is a broad spectrum neuroprotective phenyl hydrazide compound(EC50=60-115 nM) with significant neurotrophic properties related to the induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). IC50 value: 60-115 nM in vitro assay [1] Target: J-147 has been shown to promotes HT22 and primary cell survival in a dose-dependent manner (EC50 value range of 0.06 – 0.115 μM) when applied to cell exposed to the mitochondrial neurotoxin, iodoacetic acid (IAA), toxicity mediated by the excitatory amino acid glutamate, which causes HT22 cell death by an oxytosis mechanism. In the preclinical in vitro development assays, the EC50 value for J-147-induced cell survival is 25 nM. J-147 was metabolically unstable (highly metabolized) with only 12% of parent remaining after incubation with rat microsomes (phase 1 metabolism).
References:
[1]. Lapchak PA, et al. J-147 a Novel Hydrazide Lead Compound to Treat Neurodegeneration: CeeToxTM Safety and Genotoxicity Analysis. J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2013 Aug;4(3). pii: 158.
- BMS-708163 (Avagacestat)
Catalog No.:BCC2104
CAS No.:1146699-66-2
- SNS-314 Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2177
CAS No.:1146618-41-8
- 3,4-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN6490
CAS No.:114637-83-1
- 17alpha-Thevebioside
Catalog No.:BCN6026
CAS No.:114613-59-1
- Moracin T
Catalog No.:BCN3291
CAS No.:1146113-27-0
- Kisspeptin 234
Catalog No.:BCC6077
CAS No.:1145998-81-7
- Soyasaponin Ba
Catalog No.:BCN2854
CAS No.:114590-20-4
- Thevebioside
Catalog No.:BCN6025
CAS No.:114586-47-9
- Coronadiene
Catalog No.:BCN3683
CAS No.:1145689-64-0
- Ganoderiol F
Catalog No.:BCN6024
CAS No.:114567-47-4
- Boeravinone B
Catalog No.:BCN6466
CAS No.:114567-34-9
- Galanin (1-29) (rat, mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC5928
CAS No.:114547-31-8
- Columbianetin
Catalog No.:BCN8502
CAS No.:1147-29-1
- 2-(2-Aminobenzoyl)-benzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8476
CAS No.:1147-43-9
- Methyl 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9040
CAS No.:114772-34-8
- Methyl 4'-bromomethyl biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9039
CAS No.:114772-38-2
- tert-Butyl4'-(bromomethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9164
CAS No.:114772-40-6
- 4-Bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl
Catalog No.:BCC8702
CAS No.:114772-54-2
- Losartan
Catalog No.:BCC4090
CAS No.:114798-26-4
- Z-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2754
CAS No.:1148-11-4
- ST-836
Catalog No.:BCC1968
CAS No.:1148156-63-1
- Boc-Phe(2-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3223
CAS No.:114873-00-6
- Boc-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2640
CAS No.:114873-03-9
- Trabectedin
Catalog No.:BCC2012
CAS No.:114899-77-3
Metabolism of a potent neuroprotective hydrazide.[Pubmed:23582448]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 May 15;21(10):2733-41.
Using a drug discovery scheme for Alzheimer's disease (AD) that is based upon multiple pathologies of old age, we identified a potent compound with efficacy in rodent memory and AD animal models. Since this compound, J147, is a phenyl hydrazide, there was concern that it can be metabolized to aromatic amines/hydrazines that are potentially carcinogenic. To explore this possibility, we examined the metabolites of J147 in human and mouse microsomes and mouse plasma. It is shown that J147 is not metabolized to aromatic amines or hydrazines, that the scaffold is exceptionally stable, and that the oxidative metabolites are also neuroprotective. It is concluded that the major metabolites of J147 may contribute to its biological activity in animals.
The neurotrophic compound J147 reverses cognitive impairment in aged Alzheimer's disease mice.[Pubmed:23673233]
Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013 May 14;5(3):25.
INTRODUCTION: Despite years of research, there are no disease-modifying drugs for Alzheimer's disease (AD), a fatal, age-related neurodegenerative disorder. Screening for potential therapeutics in rodent models of AD has generally relied on testing compounds before pathology is present, thereby modeling disease prevention rather than disease modification. Furthermore, this approach to screening does not reflect the clinical presentation of AD patients which could explain the failure to translate compounds identified as beneficial in animal models to disease modifying compounds in clinical trials. Clearly a better approach to pre-clinical drug screening for AD is required. METHODS: To more accurately reflect the clinical setting, we used an alternative screening strategy involving the treatment of AD mice at a stage in the disease when pathology is already advanced. Aged (20-month-old) transgenic AD mice (APP/swePS1DeltaE9) were fed an exceptionally potent, orally active, memory enhancing and neurotrophic molecule called J147. Cognitive behavioral assays, histology, ELISA and Western blotting were used to assay the effect of J147 on memory, amyloid metabolism and neuroprotective pathways. J147 was also investigated in a scopolamine-induced model of memory impairment in C57Bl/6J mice and compared to donepezil. Details on the pharmacology and safety of J147 are also included. RESULTS: Data presented here demonstrate that J147 has the ability to rescue cognitive deficits when administered at a late stage in the disease. The ability of J147 to improve memory in aged AD mice is correlated with its induction of the neurotrophic factors NGF (nerve growth factor) and BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) as well as several BDNF-responsive proteins which are important for learning and memory. The comparison between J147 and donepezil in the scopolamine model showed that while both compounds were comparable at rescuing short term memory, J147 was superior at rescuing spatial memory and a combination of the two worked best for contextual and cued memory. CONCLUSION: J147 is an exciting new compound that is extremely potent, safe in animal studies and orally active. J147 is a potential AD therapeutic due to its ability to provide immediate cognition benefits, and it also has the potential to halt and perhaps reverse disease progression in symptomatic animals as demonstrated in these studies.
A novel neurotrophic drug for cognitive enhancement and Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:22194796]
PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e27865.
Currently, the major drug discovery paradigm for neurodegenerative diseases is based upon high affinity ligands for single disease-specific targets. For Alzheimer's disease (AD), the focus is the amyloid beta peptide (Ass) that mediates familial Alzheimer's disease pathology. However, given that age is the greatest risk factor for AD, we explored an alternative drug discovery scheme that is based upon efficacy in multiple cell culture models of age-associated pathologies rather than exclusively amyloid metabolism. Using this approach, we identified an exceptionally potent, orally active, neurotrophic molecule that facilitates memory in normal rodents, and prevents the loss of synaptic proteins and cognitive decline in a transgenic AD mouse model.


