LosartanCAS# 114798-26-4 |
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- Candesartan
Catalog No.:BCC2558
CAS No.:139481-59-7
- Telmisattan
Catalog No.:BCC3863
CAS No.:144701-48-4
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Imidapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3792
CAS No.:89396-94-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 114798-26-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3961 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O | M.Wt | 422.91 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (236.46 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
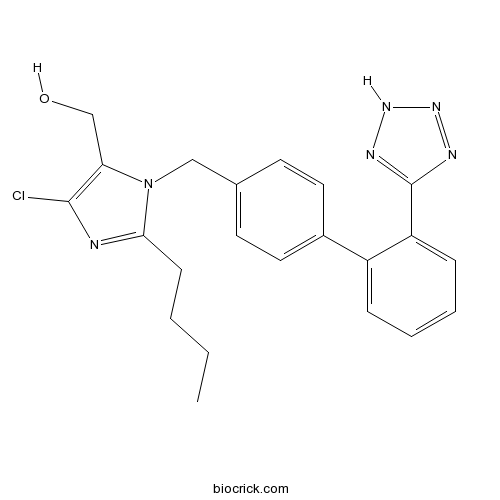
| Chemical Name | [2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol | ||
| SMILES | CCCCC1=NC(=C(N1CC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3C4=NNN=N4)CO)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PSIFNNKUMBGKDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H23ClN6O/c1-2-3-8-20-24-21(23)19(14-30)29(20)13-15-9-11-16(12-10-15)17-6-4-5-7-18(17)22-25-27-28-26-22/h4-7,9-12,30H,2-3,8,13-14H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Losartan Dilution Calculator

Losartan Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3646 mL | 11.8228 mL | 23.6457 mL | 47.2914 mL | 59.1142 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4729 mL | 2.3646 mL | 4.7291 mL | 9.4583 mL | 11.8228 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2365 mL | 1.1823 mL | 2.3646 mL | 4.7291 mL | 5.9114 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0473 mL | 0.2365 mL | 0.4729 mL | 0.9458 mL | 1.1823 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0236 mL | 0.1182 mL | 0.2365 mL | 0.4729 mL | 0.5911 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, competes with the binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 20 nM.
- 4-Bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl
Catalog No.:BCC8702
CAS No.:114772-54-2
- tert-Butyl4'-(bromomethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9164
CAS No.:114772-40-6
- Methyl 4'-bromomethyl biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9039
CAS No.:114772-38-2
- Methyl 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9040
CAS No.:114772-34-8
- 2-(2-Aminobenzoyl)-benzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8476
CAS No.:1147-43-9
- Columbianetin
Catalog No.:BCN8502
CAS No.:1147-29-1
- J 147
Catalog No.:BCC6360
CAS No.:1146963-51-0
- BMS-708163 (Avagacestat)
Catalog No.:BCC2104
CAS No.:1146699-66-2
- SNS-314 Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2177
CAS No.:1146618-41-8
- 3,4-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN6490
CAS No.:114637-83-1
- 17alpha-Thevebioside
Catalog No.:BCN6026
CAS No.:114613-59-1
- Moracin T
Catalog No.:BCN3291
CAS No.:1146113-27-0
- Z-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2754
CAS No.:1148-11-4
- ST-836
Catalog No.:BCC1968
CAS No.:1148156-63-1
- Boc-Phe(2-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3223
CAS No.:114873-00-6
- Boc-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2640
CAS No.:114873-03-9
- Trabectedin
Catalog No.:BCC2012
CAS No.:114899-77-3
- Z-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2734
CAS No.:1149-26-4
- Ciwujianoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1082
CAS No.:114902-16-8
- Ciwujianoside E
Catalog No.:BCN3505
CAS No.:114912-36-6
- Docetaxel intermediate
Catalog No.:BCN8360
CAS No.:114915-14-9
- 2-Chloro-1-(5'-(prop-1-ynyl)-2,2'-bithiophen-5-yl)ethanol
Catalog No.:BCN1614
CAS No.:114916-00-6
- N1,N10-Bis(p-coumaroyl)spermidine
Catalog No.:BCN6027
CAS No.:114916-05-1
- XL-888
Catalog No.:BCC2339
CAS No.:1149705-71-4
Protective effect of losartan and ramipril against stress induced insulin resistance and related complications: Anti-inflammatory mechanisms.[Pubmed:28259714]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Apr 15;801:54-61.
Chronic restraint stress (CRS) is known to cause various behavioural and biochemical alterations, leading to several negative health outcomes. The present study was designed to explore the impact of inhibiting Renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) and inflammatory pathways in stress pathophysiology. In the present study, male LACA mice were subjected to restraint stress daily for 30 days. Losartan, nimesulide, ramipril, minocycline and their combinations were administered 45min prior to restraint stress daily and their effects were observed. Restraint stressed mice depicted depression like behavior along with increased oxidative stress markers in their brains. CRS induced insulin resistance depicted by hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hypercholesteremia, increased glycosylated hemoglobin and HOMA-IR. Besides, treatment with Losartan, nimesulide, ramipril and minocycline significantly restored the behavioural and biochemical alterations and improved insulin sensitivity in stressed mice. Combination treatments synergistically reversed depression like behavior and decreased plasma glucose levels. Moreover they restored insulin levels, glycosylated hemoglobin levels and HOMA-IR values to the normal. This study signifies the synergistic effect of simultaneously blocking RAS and inflammatory pathways in stress pathophysiology.
Losartan Attenuates Scar Formation in Filtering Bleb After Trabeculectomy.[Pubmed:28273314]
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Mar 1;58(3):1478-1486.
Purpose: To examine the effects of Losartan on scar formation after trabeculectomy and on fibrotic changes of human Tenon's fibroblasts (HTFs). Methods: Trabeculectomy was performed on New Zealand rabbits. They were randomized to receive one of the following treatments: 0.9% normal saline, mitomycin-C, or one of the three doses of Losartan. Bleb morphology, IOP, and histopathology examination were performed. Primary cultured HTFs were treated with Losartan or vehicle, with or without angiotensin II (Ang II). Cell proliferation was assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, and cell migration was detected by scratch wound and transwell assay. Transdifferentiation was evaluated through the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) by immunofluorescence, real-time PCR, and Western blot. The expression of fibronectin (FN) was evaluated by real-time PCR and Western blot. Results: An amount of 5 mg/mL of Losartan subconjunctival injection significantly decreased IOP postoperatively and attenuated wound healing of the filtering bleb in the rabbit model. Immunostaining results showed less myofibroblast and collagen deposition around the bleb area in the Losartan-treated eyes. Losartan (10-5 M) in vitro significantly attenuated Ang II's stimulatory effects on proliferation and migration of HTFs. Expressions of alpha-SMA and FN in these cells were also decreased by Losartan pretreatment. Conclusions: Losartan attenuates scar formation of filtering bleb after trabeculectomy likely via decreasing proliferation, migration, transdifferentiation, and extracellular matrix deposition of Tenon's fibroblasts. These results indicate that Losartan may be an effective therapeutic agent in preventing bleb scar formation and in improving surgical outcome after trabeculectomy.
Dietary intervention, but not losartan, completely reverses non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese and insulin resistant mice.[Pubmed:28231800]
Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Feb 23;16(1):46.
BACKGROUND: Dietary intervention is the cornerstone of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) treatment. However, histological evidence of its efficacy is limited and its impact on hepatic pathways involved in NASH is underreported. The efficacy of the angiotensin receptor type 1 blocker Losartan is controversial because of varying results in a few animal and human studies. We evaluated the effect of dietary intervention versus Losartan on NASH and associated systemic metabolic features in a representative mouse model. METHODS: Male C57BL/6 J mice with high fat-high sucrose diet (HF-HSD) induced NASH, obesity, insulin resistance and hypercholesterolemia were subjected to dietary intervention (switch from HF-HSD to normal chow diet (NCD)) (n = 9), continuation HF-HSD together with Losartan (30 mg/kg/day) (n = 9) or continuation HF-HSD only (n = 9) for 8 weeks. 9 mice received NCD during the entire experiment (20 weeks). We assessed the systemic metabolic effects and performed a detailed hepatic histological and molecular profiling. A P-value of < 0.05, using the group with continuation of HF-HSD only as control, was considered as statistically significant. RESULTS: Dietary intervention normalized obesity, insulin resistance, and hypercholesterolemia (for all P < 0.001), and remarkably, completely reversed all histological features of pre-existent NASH (for all P < 0.001), including fibrosis measured by quantification of collagen proportional area (P < 0.01). At the hepatic molecular level, dietary intervention targeted fibrogenesis with a normalization of collagen type I alpha 1, transforming growth factor beta1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 mRNA levels (for all P < 0.01), lipid metabolism with a normalization of fatty acid translocase/CD36, fatty acid transport protein 5, fatty acid synthase mRNA levels (P < 0.05) and markers related to mitochondrial function with a normalization of hepatic ATP content (P < 0.05) together with sirtuin1 and uncoupling protein 2 mRNA levels (for both P < 0.001). Dietary intervention abolished p62 accumulation (P < 0.01), suggesting a restoration of autophagic flux. Losartan did not significantly affect obesity, insulin resistance, hypercholesterolemia or any histological NASH feature. CONCLUSIONS: Dietary intervention, and not Losartan, completely restores the metabolic phenotype in a representative mouse model with pre-existent NASH, obesity, insulin resistance and hypercholesterolemia.
The effect of tripterygium glucoside tablet on pharmacokinetics of losartan and its metabolite EXP3174 in rats.[Pubmed:28299812]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2017 Oct;31(10).
Losartan and tripterygium glucoside tablet (TGT) are often simultaneously used for reducing urine protein excretion in clinic. However, it is unknown whether there is potential herb-drug interaction between Losartan and TGT. The aim of this study was to investigate their potential herb-drug interaction, and clarify the mechanism of the effect of TGT on the pharmacokinetics of Losartan and its metabolite EXP3174 in rats. The plasma concentrations of Losartan and EXP3174 were determined by LC-MS, and the main pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated. The Cmax , t1/2 and AUC(0-t) of Losartan became larger after co-administration, while the Cmax and AUC(0-t) of EXP3174 became smaller, suggesting that TGT could influence the pharmacokinetics of Losartan and EXP3174. The effects of TGT and its main components on the metabolic rate of Losartan were further investigated in rat liver microsomes. Results indicated that TGT and its two main ingredients could decrease the metabolic rate of Losartan. Therefore, it was speculated that TGT might increase the plasma concentration of Losartan and decrease the concentration of EXP3174 by inhibiting the metabolism of Losartan. The results could provide references for clinical medication guidance of Losartan and TGT to avoid the occurrence of adverse reactions.


