Hoechst 33258 analog 2Blue fluorescent dyes CAS# 23491-54-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23491-54-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44386468 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H26N6 | M.Wt | 422.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | 25℃: DMSO or water Protect from light | ||
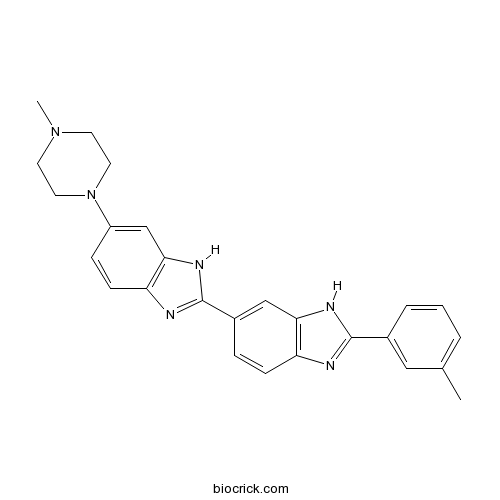
| Chemical Name | 2-(3-methylphenyl)-6-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-1H-benzimidazole | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=CC(=C1)C2=NC3=C(N2)C=C(C=C3)C4=NC5=C(N4)C=C(C=C5)N6CCN(CC6)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QGOKBFIFCYHFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H26N6/c1-17-4-3-5-18(14-17)25-27-21-8-6-19(15-23(21)29-25)26-28-22-9-7-20(16-24(22)30-26)32-12-10-31(2)11-13-32/h3-9,14-16H,10-13H2,1-2H3,(H,27,29)(H,28,30) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Hoechst 33258 analog 2 Dilution Calculator

Hoechst 33258 analog 2 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3668 mL | 11.8338 mL | 23.6675 mL | 47.335 mL | 59.1688 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4734 mL | 2.3668 mL | 4.7335 mL | 9.467 mL | 11.8338 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2367 mL | 1.1834 mL | 2.3668 mL | 4.7335 mL | 5.9169 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0473 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4734 mL | 0.9467 mL | 1.1834 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1183 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4734 mL | 0.5917 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Description: IC50 Value: N/A Hoechst stains are part of a family of blue fluorescent dyes used to stain DNA. These Bis-benzimides were originally developed by Hoechst AG, which numbered all their compounds so that the dye Hoechst 33342 is the 33342nd compound made by the company. There are three related Hoechst stains: Hoechst 33258, Hoechst 33342, and Hoechst 34580. The dyes Hoechst 33258 and Hoechst 33342 are the ones most commonly used and they have similarexcitation/emission spectra. Both dyes are excited by ultraviolet light at around 350 nm, and both emit blue/cyan fluorescent light around anemission maximum at 461 nm. Unbound dye has its maximum fluorescence emission in the 510-540 nm range. Hoechst dyes are soluble in water and in organic solvents such as dimethyl formamide or dimethyl sulfoxide. Concentrations can be achieved of up to 10 mg/mL. Aqueous solutions are stable at 2-6 °C for at least six months when protected from light. For long-term storage the solutions are instead frozen at ≤-20 °C. The dyes bind to the minor groove of double-stranded DNA with a preference for sequences rich in adenine andthymine. Although the dyes can bind to all nucleic acids, AT-rich double-stranded DNA strands enhance fluorescence considerably. Hoechst dyes are cell-permeable and can bind to DNA in live or fixed cells. Therefore, these stains are often called supravital, which means that cells survive a treatment with these compounds. Cells that express specific ATP-binding cassette transporter proteins can also actively transport these stains out of their cytoplasm. in vitro: N/A in vivo: N/A Clinical trial: N/A
- Hoechst 33342
Catalog No.:BCC1629
CAS No.:23491-52-3
- Hoechst 33258
Catalog No.:BCC1623
CAS No.:23491-45-4
- 2-Amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8536
CAS No.:2349-67-9
- U 99194 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7029
CAS No.:234757-41-6
- 2-Palmitoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCC7289
CAS No.:23470-00-0
- trans-Khellactone
Catalog No.:BCN6920
CAS No.:23458-04-0
- Decursinol
Catalog No.:BCN2638
CAS No.:23458-02-8
- alpha-Spinasterone
Catalog No.:BCN5086
CAS No.:23455-44-9
- Trenbolone cyclohexylmethylcarbonate
Catalog No.:BCC9185
CAS No.:23454-33-3
- Alternariol monomethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7384
CAS No.:23452-05-3
- Physcion 1-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8170
CAS No.:23451-01-6
- Irisolidone
Catalog No.:BCN8496
CAS No.:2345-17-7
- Hoechst 33258 analog 5
Catalog No.:BCC1627
CAS No.:23491-55-6
- Peimine
Catalog No.:BCN1094
CAS No.:23496-41-5
- Axillaridine
Catalog No.:BCN2060
CAS No.:23506-96-9
- MEN 11270
Catalog No.:BCC6094
CAS No.:235082-52-7
- Humulon
Catalog No.:BCC8186
CAS No.:23510-81-8
- 8-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN5921
CAS No.:23513-08-8
- 6-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN1030
CAS No.:23513-14-6
- 10-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN5922
CAS No.:23513-15-7
- (-)-licarin A
Catalog No.:BCN5087
CAS No.:23518-30-1
- Vomifoliol
Catalog No.:BCN5088
CAS No.:23526-45-6
- 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine
Catalog No.:BCN2169
CAS No.:2353-33-5
- 8-Debenzoylpaeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCC8787
CAS No.:23532-11-8
S-benzyl-cysteine-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involving activation of mitochondrial-dependent caspase cascade through the p53 pathway in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells.[Pubmed:24377536]
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(11):6379-84.
S-benzyl-cysteine (SBC) is a structural analog of S-allylcysteine (SAC), which is one of the major water- soluble compounds in aged garlic extract. In this study, anticancer activities and the underlying mechanisms of SBC action were investigated and compared these with those of SAC using human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. SBC significantly suppressed the survival rate of SGC-7901 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner, and the inhibitory activities of SBC were stronger than those of SAC. Flow cytometry revealed that SBC induced G2-phase arrest and apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells. Typical apoptotic morphological changes were observed by Hoechst 33258 dye assay. SBC-treatment dramatically induced the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (Deltapsim), and enhanced the enzymatic activities of caspase-9 and caspase-3 whilst hardly affecting caspase-8 activity. Furthermore, Western blotting indicated that SBC-induced apoptosis was accompanied by up-regulation of the expression of p53, Bax and the down-regulation of Bcl-2. Taken together, this study suggested that SBC exerts cytotoxic activity involving activation of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis through p53 and Bax/Bcl-2 pathways in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells.
Synthesis and antitumor activities of novel rhein alpha-aminophosphonates conjugates.[Pubmed:24378217]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jan 15;24(2):501-7.
Several rhein alpha-aminophosphonates conjugates (5a-5q) were synthesized and evaluated for in vitro cytotoxicity against HepG-2, CNE, Spca-2, Hela and Hct-116 cell lines. Some compounds showed relatively high cytotoxicity. Especially, compound 5i exhibited the strongest cytotoxicity against Hct-116 cells (IC50 was 5.32 muM). All the synthesized compounds exhibited low cytotoxicity against HUVEC cells. The mechanism of compound 5i was preliminarily investigated by Hoechst 33258 staining, JC-1 mitochondrial membrane potential staining and flow cytometry, which indicated that the compound 5i induced apoptosis in Hct-116 cancer cells. Cell cycle analysis showed that these compound 5i mainly arrested Hct-116 cells in G1 stage. The effects of 5i on the activation of caspases expression indicated that 5i might induce apoptosis via the membrane death receptor pathways. In addition, the binding properties of a model analog 5i to DNA were investigated by methods (UV-vis, fluorescence, CD spectroscopy and FRET-melting) in compare with that of rhein. Results indicated that 5i showed moderate ability to interact ct-DNA.
Da0324, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB activation, demonstrates selective antitumor activity on human gastric cancer cells.[Pubmed:27042000]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Mar 2;10:979-95.
BACKGROUND: The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is constitutively activated in a variety of human cancers, including gastric cancer. NF-kappaB inhibitors that selectively kill cancer cells are urgently needed for cancer treatment. Curcumin is a potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation. Unfortunately, the therapeutic potential of curcumin is limited by its relatively low potency and poor cellular bioavailability. In this study, we presented a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor named Da0324, a synthetic asymmetric mono-carbonyl analog of curcumin. The purpose of this study is to research the expression of NF-kappaB in gastric cancer and the antitumor activity and mechanism of Da0324 on human gastric cancer cells. METHODS: The expressions between gastric cancer tissues/cells and normal gastric tissues/cells of NF-kappaB were evaluated by Western blot. The inhibition viability of compounds on human gastric cancer cell lines SGC-7901, BGC-823, MGC-803, and normal gastric mucosa epithelial cell line GES-1 was assessed with the 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Absorption spectrum method and high-performance liquid chromatography method detected the stability of the compound in vitro. The compound-induced changes of inducible NF-kappaB activation in the SGC-7901 and BGC-823 cells were examined by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence methods. The antitumor activity of compound was performed by clonogenic assay, matrigel invasion assay, flow cytometric analysis, Western blot analysis, and Hoechst 33258 staining assay. RESULTS: High levels of p65 were found in gastric cancer tissues and cells. Da0324 displayed higher growth inhibition against several types of gastric cancer cell lines and showed relatively low toxicity to GES-1. Moreover, Da0324 was more stable than curcumin in vitro. Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence methods showed that Da0324 blocked NF-kappaB activation. In addition, Da0324 significantly inhibited tumor proliferation and invasion, arrested the cell cycle, and induced apoptosis in vitro. CONCLUSION: The asymmetric mono-carbonyl analog of curcumin Da0324 exhibited significantly improved antigastric cancer activity. Da0324 may be a promising NF-kappaB inhibitor for the selective targeting of cancer cells. However, further studies are needed in animals to validate these findings for the therapeutic use of Da0324.
Hydroquinone analog 4-[(Tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2yl) oxy] phenol induces C26 colon cancer cell apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.[Pubmed:25651526]
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jun;11(6):4671-7.
The 4[(Tetrahydro2Hpyran2yl) oxy] phenol (XGd) hydroquinone analog, is found in Vaccinium vitisidaea L. Although it is known for its antioxidant properties and high level of safety, its antitumor activity remains to be elucidated. In the present study, the anticancer effect of XGd was determined in vitro and in vivo. The cytotoxicity of XGd against C26 murine colon carcinoma cells was found to occur in a time and concentrationdependent manner, whereas little effect was observed in the two normal cell lines (HK2 and L02) investigated. Oral administration of XGd (100 mg/kg) had effects on the tumor growth of tumorbearing mice. Furthermore, marked apoptosis was observed using Hoechst 33258 staining and flow cytometric analysis with annexin V/propidium iodide double staining. XGd also downregulated the expression of Bcell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2), increased the expression levels of Bcl2associated X protein and activated caspase9, caspase3 and poly(adenosine diphosphateribose) polymerase. The present study demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that XGd inhibited cancer cell growth via the induction of apoptosis and was also able to inhibit tumor growth in vivo. These results demonstrated that XGd may be used as a potential natural agent for cancer therapy with low toxicity.
Mechanism of apoptotic induction in human breast cancer cell, MCF-7, by an analog of curcumin in comparison with curcumin--an in vitro and in silico approach.[Pubmed:24365254]
Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Mar 5;210:51-63.
In developing countries, survival rates for breast cancer are poor and it accounts for 22.9% of all cancers in women. Curcumin, a major constituent from turmeric, is one of the well-known chemopreventive agents. Reports have shown that curcumin induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. We synthesized an ortho-hydroxy substituted analog of curcumin (BDMC-A) and analyzed its cytotoxicity. The BDMC-A inhibited MCF-7 at a dose equivalent to that of curcumin (30 muM). The present study was aimed at delineating the apoptotic mechanism of BDMC-A in comparison to that of curcumin. In our study, BDMC-A exerted more potent effect on the modulation of selective apoptotic markers (intrinsic pathway: p53, Bcl-2, Bax, cyt c, Apaf-1, caspase-9, 3, PARP; extrinsic pathway: FasL, caspase 8) compared to curcumin. mRNA expression studies for Bcl2/Bax also supported the increased efficacy of BDMC-A. An in silico molecular docking study with PI3K revealed that the docking of BDMC-A was more potent compared to curcumin. Increased apoptotic induction by BDMC-A compared to curcumin was also demonstrated by Annexin V, Rh123 (DeltaPsim), PI, Hoechst 33258, AO/EB fluorescent staining studies which showed characteristic apoptotic features like nuclear fragmentation and chromatin condensation. Moreover, BDMC-A treated cells effectively induced apoptosis through ROS intermediates compared to curcumin, as measured by 2'-7'-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). Hence our overall results showed that BDMC-A induced apoptosis more effectively compared to curcumin and the activity can be attributed to the presence of hydroxyl group in the ortho position in its structure. Further researches are going on to delineate its molecular targets to evaluate its effect as a potent anticancer agent.


