IcotinibEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor CAS# 610798-31-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 610798-31-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 22024915 | Appearance | Powder |
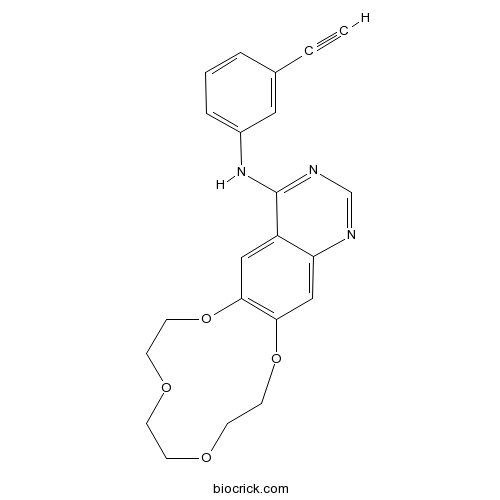
| Formula | C22H21N3O4 | M.Wt | 391.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | BPI-2009 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 155 mg/mL (395.99 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| SMILES | C#CC1=CC(=CC=C1)NC2=NC=NC3=CC4=C(C=C32)OCCOCCOCCO4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QQLKULDARVNMAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H21N3O4/c1-2-16-4-3-5-17(12-16)25-22-18-13-20-21(14-19(18)23-15-24-22)29-11-9-27-7-6-26-8-10-28-20/h1,3-5,12-15H,6-11H2,(H,23,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Icotinib (BPI-2009) is a potent and specific EGFR inhibitor with an IC50 of 5 nM; also inhibits mutant EGFRL858R, EGFRL858R/T790M, EGFRT790M and EGFRL861Q.In Vitro:Incubation with Iconitib at 0.5 μM results in kinase activity inhibition of 91%, 99%, 96%, 61% and 61%, respectively. Iconitib inhibits the proliferation of A431 and BGC-823 A549, H460 and KB cell lines with IC50s of 1, 4.06, 12.16, 16.08, 40.71 μM. When profiled with 88 kinases, Icotinib only shows meaningful inhibitory activity to EGFR and its mutants. Icotinib blocks EGFR-mediated intracellular tyrosine phosphorylation (IC50=45 nM) in the human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cell line and inhibits tumor cell proliferation[1].In Vivo:Icotinib exhibits potent dose-dependent antitumor effects in nude mice carrying a variety of human tumor-derived xenografts. The drug is well tolerated at doses up to 120 mg/kg/day in mice without mortality or significant body weight loss during the treatment. Icotinib inhibits tumor growth at a rate of 25.2%, 45.6% and 51.5% in the A431 cell line groups; 3.4%, 25.9% and 31.0% in the A549 cell line groups; 49.4%, 52.6% and 67.4% in the H460 cell line groups, and 30.3%, 36.4% and 46.5% in the HCT8 cell line groups, at 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg/dose, respectively[1]. References: | |||||

Icotinib Dilution Calculator

Icotinib Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5548 mL | 12.774 mL | 25.548 mL | 51.096 mL | 63.87 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.511 mL | 2.5548 mL | 5.1096 mL | 10.2192 mL | 12.774 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2555 mL | 1.2774 mL | 2.5548 mL | 5.1096 mL | 6.387 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0511 mL | 0.2555 mL | 0.511 mL | 1.0219 mL | 1.2774 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1277 mL | 0.2555 mL | 0.511 mL | 0.6387 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Icotinib is a potent and specific EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (IC50 = 5 nM) [1]
EGFR are family of receptor tyrosine kinase that is a transmembrane protein involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, motility and apoptosis. EGFR are expressed in various human cancer types, including breast, head & neck, NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer) and ovarian caners. [1]
In human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cell line, Icotinib inhibited EGF-induced EGFR phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. Icotinib inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of a variety of intracellular proteins. [1]
In different types of tumor xenograft mice models, Icotinib inhibited tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner without pronounced adverse effect in body weight loss and toxicity signs. In a randomized, double-blind, Gefitinib as control and multi-center phase III trial, Icotinib demonstrated efficacy on NSCLC in advanced stage. [1]
Reference:
[1] Tan F, Shen X, Wang D, Xie G, Zhang X, Ding L, Hu Y, He W, Wang Y, Wang Y. Icotinib (BPI-2009H), a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, displays potent efficacy in preclinical studies. Lung Cancer. 2012 May;76(2):177-82.
- Isobonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN4130
CAS No.:610778-85-3
- Boc-His(Nτ-Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2684
CAS No.:61070-22-2
- L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4283
CAS No.:6106-07-6
- N-Desmethylclozapine
Catalog No.:BCC6887
CAS No.:6104-71-8
- Teicoplanin
Catalog No.:BCC4731
CAS No.:61036-62-2
- c-JUN peptide
Catalog No.:BCC8085
CAS No.:610273-01-3
- Ferulamide
Catalog No.:BCN4129
CAS No.:61012-31-5
- Succinylcholine Chloride Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4564
CAS No.:6101-15-1
- Isoacetovanillone
Catalog No.:BCN7166
CAS No.:6100-74-9
- Tenuazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1859
CAS No.:610-88-8
- H-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2968
CAS No.:61-90-5
- Zoxazolamine
Catalog No.:BCC4751
CAS No.:61-80-3
- 4-Phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6769
CAS No.:6109-35-9
- Tectoridin
Catalog No.:BCN1020
CAS No.:611-40-5
- (R)-Mandelic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8532
CAS No.:611-71-2
- Bromhexine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8898
CAS No.:611-75-6
- Epipterosin L 2'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4614
CAS No.:61117-89-3
- 3,9-Dihydroxypterocarpan
Catalog No.:BCN4131
CAS No.:61135-91-9
- 6alpha-Hydroxymedicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3939
CAS No.:61135-92-0
- 4-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone
Catalog No.:BCN4132
CAS No.:61152-62-3
- Grandifloroside
Catalog No.:BCN4133
CAS No.:61186-24-1
- Quinine HCl Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4933
CAS No.:6119-47-7
- Uzarigenin digitaloside
Catalog No.:BCN4613
CAS No.:61217-80-9
- 6alpha-Hydroxymaackiain
Catalog No.:BCN3947
CAS No.:61218-44-8
Efficacy of icotinib in lung squamous-cell cancer: A real-world experience from single institution.[Pubmed:28276163]
Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;13(6):379-384.
AIM: Squamous cell carcinoma is a less common type of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) which associates with a poor clinical prognosis and lacks specific therapy. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Icotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has proven to be effective in EGFR-mutated NSCLC, in patients with lung squamous-cell cancer. METHODS: Retrospective analysis was conducted in patients who had advanced lung squamous-cell cancer confirmed by cytology or histology. Patients were treated orally with Icotinib (125 mg, three times daily) until event of unacceptable toxicity, disease progression or death. The primary endpoint was overall survival. The secondary endpoints were progression-free survival, overall response rate and disease control rate. RESULTS: Between January 2014 and May 2016, 20 patients were enrolled and evaluated for the efficacy and safety of Icotinib. Overall, the median overall survival and progression-free survival were 9.93 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 3.46-16.40) and 3.0 months (95% CI: 0.00-8.35), respectively. The overall response rate and disease control rate were 20% and 70%, respectively. For treatment-naive patients (n = 11), the overall survival and progression-free survival were 9.93 months (95% CI: 0.00-23.49) and 6.27 months (95% CI: 0.00-12.61); the response rate and disease control rate were 27.3% and 54.5%, respectively. The overall survival and progression-free survival of patients treated with second- or multiple-line Icotinib treatment (n = 9) were 6.5 months (95% CI: 0.80-12.20) and 1.2 months (95% CI: 1.10-1.30). A total of 11 patients experienced at least one treatment-related adverse event, most of which were mild to moderate. The most common manifestations were rash (n = 6, 30%) followed by diarrhea (n = 2, 10%). CONCLUSION: Icotinib has demonstrated a favorable efficacy and safety profile in patients with advanced lung squamous-cell cancer.
Complete remission through icotinib treatment in Non-small cell lung cancer epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patient with brain metastasis: A case report.[Pubmed:28352759]
Open Med (Wars). 2016 Feb 19;11(1):11-15.
Brain metastasis (BM) has been universally recognized as a poor prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have shown efficacy in treating BM with an EGFR mutation. This paper reports a case of BM patient with EGFR-mutated NSCLC. According to the findings, a complete remission (CR) of the BM was achieved by Icotinib treatment without conducting a radiotherapy, which was followed by a resection of the primary lung cancer lesion and lymph nodes. After one-year follow-up, the disease progressed to liver metastasis and liver lesion biopsy showed a T790M mutation. The patient responded well to the combination treatment of AZD9291 and Icotinib after the failure of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). This case report suggests that Icotinib has a sustainable anticancer response to BM and the combination with Icotinib and AZD9291 is effective for liver metastasis with T790M.
Effects of icotinib with and without radiation therapy on patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastases.[Pubmed:28332624]
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 23;7:45193.
EGFR-TKIs and radiation therapy (RT) are the principal treatment for patients with brain metastases (BM) and EGFR mutant NSCLC. However, the optimal use of brain RT for patients with asymptomatic BM remains undefined. A total of 152 patients were identified. 58 patients were excluded. Of the remaining 97 patients, 56 patients received upfront RT followed by Icotinib, including WBRT or SRS. 41 patients received Icotinib therapy alone. The mOS from diagnosis of BM was 27.0 months for the whole cohort (95% CI, 23.9-30.1 months). There was no difference in OS between the RT followed by Icotinib group and the Icotinib alone group (31.9 vs. 27.9 months, P = 0.237), and similar results were found in the SRS subgroup (35.5 vs. 27.9 months, P = 0.12). Patients with the EGFR Del19 mutation had a longer OS than patients with the exon 21 L858R mutation (32.7 vs. 27.4, P = 0.037). Intracranial progression-free survival (PFS) was improved in the patients who received RT followed by Icotinib compared to those receiving Icotinib alone (22.4 vs. 13.9 months, P = 0.043). Patients with EGFR-mutant adenocarcinoma and BM treated with Icotinib exhibited prolonged survival. A longer duration of intracranial control was observed with brain RT.
Erratum: Efficacy and safety of icotinib in patients with brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma [Corrigendum].[Pubmed:28356758]
Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Mar 21;10:1709.
[This corrects the article on p. 2911 in vol. 9, PMID: 27274284.].


