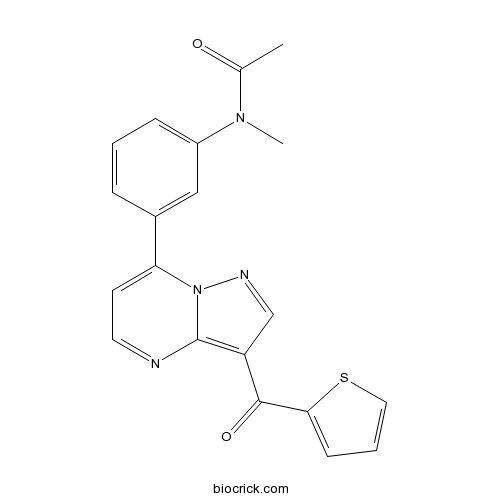
IndiplonSubtype-selective GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator CAS# 325715-02-4 |
- INCB3344
Catalog No.:BCC1648
CAS No.:1262238-11-8
- RS 504393
Catalog No.:BCC1910
CAS No.:300816-15-3
- MK-0812
Catalog No.:BCC1755
CAS No.:624733-88-6
- INCB 3284 dimesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1646
CAS No.:887401-93-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 325715-02-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6450813 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H16N4O2S | M.Wt | 376.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NBI 34060 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | N-methyl-N-[3-[3-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl]phenyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)N(C)C1=CC=CC(=C1)C2=CC=NC3=C(C=NN23)C(=O)C4=CC=CS4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CBIAWPMZSFFRGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H16N4O2S/c1-13(25)23(2)15-6-3-5-14(11-15)17-8-9-21-20-16(12-22-24(17)20)19(26)18-7-4-10-27-18/h3-12H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator that acts at the benzodiazepine site (Ki values are 1.2 and 1.7 nM in rat frontal cortex and cerebellum respectively). Displays ~ 10-fold selectivity for α1 subunit-containing receptors (EC50 values are 2.6, 24, 60 and 77 nM for α1β2γ2, α2β2γ2, α3β3γ2 and α5β2γ2 receptors respectively). Exhibits sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity in vivo and is orally active. |

Indiplon Dilution Calculator

Indiplon Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6565 mL | 13.2827 mL | 26.5654 mL | 53.1307 mL | 66.4134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5313 mL | 2.6565 mL | 5.3131 mL | 10.6261 mL | 13.2827 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2657 mL | 1.3283 mL | 2.6565 mL | 5.3131 mL | 6.6413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0531 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5313 mL | 1.0626 mL | 1.3283 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1328 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5313 mL | 0.6641 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ascleposide E
Catalog No.:BCN5244
CAS No.:325686-49-5
- 1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7792
CAS No.:325465-93-8
- ICA 110381
Catalog No.:BCC6338
CAS No.:325457-99-6
- Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3580
CAS No.:325143-98-4
- Ergosta-7,22-dien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN7088
CAS No.:32507-77-0
- Isorhapotogenin
Catalog No.:BCN3383
CAS No.:32507-66-7
- Myricanone
Catalog No.:BCN5243
CAS No.:32492-74-3
- Periplocymarin
Catalog No.:BCN8485
CAS No.:32476-67-8
- T 0156 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5803
CAS No.:324572-93-2
- 1-Indanamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8467
CAS No.:32457-23-1
- NPS-2143 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1808
CAS No.:324523-20-8
- Isochlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5910
CAS No.:534-61-2
- BPIPP
Catalog No.:BCC7730
CAS No.:325746-94-9
- GRI 977143
Catalog No.:BCC2401
CAS No.:325850-81-5
- Kaempferol 3-neohesperidoside
Catalog No.:BCN5245
CAS No.:32602-81-6
- Oleuropein
Catalog No.:BCN5246
CAS No.:32619-42-4
- Boc-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3439
CAS No.:3262-72-4
- Fraxamoside
Catalog No.:BCN5247
CAS No.:326594-34-7
- Mesoridazine Besylate
Catalog No.:BCC3975
CAS No.:32672-69-8
- H-Glu(OtBu)-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2934
CAS No.:32677-01-3
- Edpetiline
Catalog No.:BCN6771
CAS No.:32685-93-1
- FAAH inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4254
CAS No.:326866-17-5
- Shz 1
Catalog No.:BCC6334
CAS No.:326886-05-9
- MHY1485
Catalog No.:BCC6404
CAS No.:326914-06-1
Indiplon: a nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic for the treatment of insomnia.[Pubmed:18594049]
Ann Pharmacother. 2008 Jul;42(7):1070-9.
OBJECTIVE: To review the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy data, and adverse effects of Indiplon in the treatment of transient and chronic insomnia in adult and geriatric patients. DATA SOURCES: A literature search was conducted using MEDLINE (1966-May 2008), International Pharmaceutical Abstracts (1970-May 2008), and Cochrane database (2007) for the key words Indiplon or NBI-34060. References cited in the articles were reviewed for additional information. Abstract data were included only in the absence of significant published data. STUDY SELECTION AND DATA EXTRACTION: English-language literature reporting animal and human clinical studies was reviewed to evaluate data on the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy, and adverse effects of Indiplon. Clinical trials selected for inclusion were limited to those with human subjects, with the accepted inclusion of pharmacology data in animals. DATA SYNTHESIS: Indiplon is a nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic that exhibits its sedating activity through its interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acid alpha receptor complex. Indiplon immediate-release (IR) as well as modified-release (MR) forms have shown improvement compared with placebo in patients with DSM-IV-TR primary insomnia in various areas of subjective and objective sleep measurements. Specifically, improvements in total sleep time, latency to persistent sleep, latency to sleep onset, wake after sleep onset, and sleep quality have been noted in clinical trials. Trials evaluating both Indiplon IR and MR have so far not identified any major serious adverse effects. CONCLUSIONS: Limited clinical trial data exist on use of Indiplon in a "true" transient insomnia patient population. Based on recent Food and Drug Administration requests, clinical trial data assessing direct comparisons of Indiplon IR with other approved nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics are needed to clearly define the differences among these agents.
Preparation and characterization of a novel polymorph of indiplon, Form alpha.[Pubmed:22209207]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jan 15;22(2):963-8.
A new polymorph alpha of Indiplon was discovered, initially prepared by two methods, and further characterized by various means including single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), variable temperature powder X-ray diffraction (VT-PXRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetry analysis (TGA), Fourier transform Raman (FT-Raman) spectroscopy and solubility determination. The crystal structure of Form alpha as analyzed by SCXRD differ from the three previously reported polymorphs, Form I, II, and III. In addition, PXRD and solubility measurements could clearly distinguish between Form alpha and Form I. Slight differences between the two forms were also detected by FT-Raman. No differences between Form alpha and I were observed by DSC, which was explained by VT-PXRD results showing a solid-solid phase change from Form alpha to Form I during the heating process. Solubility measurements at various temperatures showed that the two polymorphs were mutually monotropic and that Form I was the relatively thermodynamically stable crystal form.
Indiplon is hydrolyzed by arylacetamide deacetylase in human liver.[Pubmed:24464802]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Apr;42(4):751-8.
Human arylacetamide deacetylase (AADAC) catalyzes the hydrolysis of some clinically used drugs, but the information available on its substrates is limited. To increase our knowledge of the AADAC substrates, we examined whether AADAC catalyzes the hydrolysis of Indiplon, which was initially developed as a hypnotic sedative drug. It has been reported that approximately 30-40% of the administered Indiplon was hydrolyzed to deacetylIndiplon in humans, but the enzyme responsible for this hydrolysis had not been identified. We detected high levels of Indiplon hydrolase activity in human liver microsomes (HLMs), but the levels found in human liver cytosol and plasma were scarcely detectable. Recombinant AADAC showed a high level of Indiplon hydrolase activity, whereas recombinant carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) and 2 (CES2) showed marginal activity. The Indiplon hydrolase activity of HLM was potently inhibited by vinblastine, a potent inhibitor of AADAC and CES2, but it was not inhibited by digitonin and telmisartan, inhibitors of CES1 and CES2, respectively. In a panel of 24 individual HLM samples, the Indiplon hydrolase activities were significantly correlated with the hydrolase activities of flutamide, phenacetin, and rifampicin, which are known AADAC substrates. An HLM sample with a homozygous AADAC*3 allele, which was previously found to exhibit decreased enzyme activity, showed the lowest Indiplon hydrolase activity among the 24 tested samples. Collectively, we found that human AADAC is responsible for the hydrolysis of Indiplon. Thus, we can add Indiplon to the list of human AADAC substrates.
Indiplon in the management of insomnia.[Pubmed:19920929]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2009 Sep 21;3:131-42.
Indiplon is a novel pyrazolopyrimidine, nonbenzodiazepine gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) agonist studied for the treatment of insomnia. This article reviews the chemistry, pharmacology, clinical pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, clinical trials, safety, tolerability, contraindications, use in special populations, and dosing of Indiplon. OVID, International Pharmaceutical Abstracts (IPA), and PubMed databases were searched (1966 to February 2009) for the keywords Indiplon, NBI-34060, and insomnia. References of key articles were also reviewed to identify additional publications. Only English language articles were selected for review. Indiplon has been shown to have high affinity and selectivity for the GABAalpha(1) receptor subunit associated with sedation. In clinical studies, Indiplon has demonstrated efficacy in improving latency to sleep onset, latency to persistent sleep, total sleep time, wake time after sleep onset, number of awakenings after sleep onset, and overall sleep quality when compared to placebo. Indiplon has a favorable safety profile with limited rebound insomnia and no tolerance. Neurocrine Biosciences, Incorporated received an Approvable Letter from the United States Food and Drug Administration in December 2007 for the Indiplon IR 5 mg and 10 mg capsules based on meeting three additional requirements. At the time of this writing, Indiplon remains unapproved.
Indiplon is a high-affinity positive allosteric modulator with selectivity for alpha1 subunit-containing GABAA receptors.[Pubmed:16399882]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Apr;317(1):369-77.
Indiplon (NBI 34060) is a novel pyrazolopyrimidine currently in development for the treatment of insomnia. We have previously shown that Indiplon exhibits high-affinity binding to native GABA(A) receptors from rat brain and acts as a positive allosteric modulator of GABA(A) receptor currents in cultured rat neurons (Sullivan et al., 2004). In this study, we examined the GABA(A) receptor alpha subunit selectivity of Indiplon using electrophysiological techniques to record GABA-activated chloride currents from recombinant rodent GABA(A) receptors expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Indiplon potentiated the GABA-activated chloride current in recombinant GABA(A) receptors in a dose-dependent and reversible manner and was approximately 10-fold selective for alpha1 subunit-containing receptors over GABA(A) receptors containing alpha2, alpha3, or alpha5 subunits. The EC(50) values were 2.6, 24, 60, and 77 nM for alpha1beta2gamma2, alpha2beta2gamma2, alpha3beta3gamma2, and alpha5beta2gamma2 receptors, respectively. Indiplon was approximately 10 times more potent than zolpidem and zopiclone and >100 times more potent than zaleplon. Moreover, Indiplon, up to 1 microM, did not potentiate GABA(A) receptors composed of alpha4beta2gamma2 and alpha6beta2gamma2 subunits. This mechanism of action is proposed to underlie the sedative-hypnotic effects of Indiplon in animals and humans.
In vivo pharmacological characterization of indiplon, a novel pyrazolopyrimidine sedative-hypnotic.[Pubmed:15256538]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Nov;311(2):547-59.
Indiplon (NBI 34060; N-methyl-N-[3-[3-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-pyrazolo[1,5-alpha]pyrimidin-7-yl]phenyl]ace tamide), a novel pyrazolopyrimidine and high-affinity allosteric potentiator of GABA(A) receptor function, was profiled for its effects in rodents after oral administration. In mice, Indiplon inhibited locomotor activity (ED(50) = 2.7 mg/kg p.o.) at doses lower than the nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics zolpidem (ED(50) = 6.1 mg/kg p.o.) and zaleplon (ED(50) = 24.6 mg/kg p.o.), a sedative effect that was reversed by the benzodiazepine site antagonist flumazenil. Indiplon inhibited retention in the mouse passive avoidance paradigm over a dose range and with a temporal profile that coincided with its sedative activity. Indiplon, zolpidem, and zaleplon were equally effective in inhibiting locomotor activity in the rat and produced dose-related deficits on the rotarod. In a rat vigilance paradigm, Indiplon, zolpidem, and zaleplon produced performance deficits over a dose range consistent with their sedative effects, although Indiplon alone showed no significant increase in response latency. Indiplon produced a small deficit in the delayed nonmatch to sample paradigm at a dose where sedative effects became apparent. Indiplon was active in the rat Vogel test of anxiety, but it showed only a sedative profile in the mouse open field test. The pharmacokinetic profile of Indiplon in both rat and mouse was consistent with its pharmacodynamic properties and indicated a rapid T(max), short t(1/2), and excellent blood-brain barrier penetration. Therefore, Indiplon has the in vivo profile of an efficacious sedative-hypnotic, in agreement with its in vitro receptor pharmacology as a high-affinity allosteric potentiator of GABA(A) receptor function, with selectivity for alpha1 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors.
Characterization of the interaction of indiplon, a novel pyrazolopyrimidine sedative-hypnotic, with the GABAA receptor.[Pubmed:15256540]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Nov;311(2):537-46.
Clinically used benzodiazepine and nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic agents for the treatment of insomnia produce their therapeutic effects through allosteric enhancement of the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA at the GABA(A) receptor. Indiplon is a novel pyrazolopyrimidine sedative-hypnotic agent, currently in development for insomnia. Using radioligand binding studies, Indiplon inhibited the binding of [(3)H]Ro 15-1788 (flumazenil) to rat cerebellar and cerebral cortex membranes with high affinity (K(i) values of 0.55 and 0.45 nM, respectively). [(3)H]Indiplon binding to rat cerebellar and cerebral cortex membranes was reversible and of high affinity, with K(D) values of 1.01 and 0.45 nM, respectively, with a pharmacological specificity consistent with preferential labeling of GABA(A) receptors containing alpha1 subunits. In "GABA shift" experiments and in measurements of GABA-induced chloride conductance in rat cortical neurons in culture, Indiplon behaved as an efficacious potentiator of GABA(A) receptor function. In both the radioligand binding and electrophysiological experiments, Indiplon had a higher affinity than zolpidem or zaleplon. These in vitro properties are consistent with the in vivo properties of Indiplon as an effective sedative-hypnotic acting through allosteric potentiation of the GABA(A) receptor.


