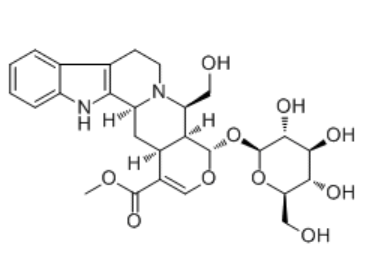
IsodihydrocadambineCAS# 55624-02-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 55624-02-7 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H34N2O10 | M.Wt | 546.6 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Isodihydrocadambine Dilution Calculator

Isodihydrocadambine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8295 mL | 9.1475 mL | 18.2949 mL | 36.5898 mL | 45.7373 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3659 mL | 1.8295 mL | 3.659 mL | 7.318 mL | 9.1475 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1829 mL | 0.9147 mL | 1.8295 mL | 3.659 mL | 4.5737 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0366 mL | 0.1829 mL | 0.3659 mL | 0.7318 mL | 0.9147 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0183 mL | 0.0915 mL | 0.1829 mL | 0.3659 mL | 0.4574 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4'-O-Methyllariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN9713
CAS No.:73354-09-3
- Aculeatin
Catalog No.:BCN9712
CAS No.:77636-05-6
- Isooxoflaccidin
Catalog No.:BCN9711
CAS No.:135010-50-3
- Inophyllum E
Catalog No.:BCN9710
CAS No.:17312-31-1
- Liquiridiolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9709
CAS No.:20528-70-5
- Alaternin
Catalog No.:BCN9708
CAS No.:641-90-7
- Adenostemmoside A
Catalog No.:BCN9707
CAS No.:130217-15-1
- Onjixanthone I
Catalog No.:BCN9706
CAS No.:136083-92-6
- 12-O-Methylinophyllum D
Catalog No.:BCN9705
CAS No.:40883-10-1
- Adenostemmoic acid G
Catalog No.:BCN9704
CAS No.:130217-26-4
- Indole-3-carboxylic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9703
CAS No.:106871-55-0
- Gancaonin J
Catalog No.:BCN9702
CAS No.:129280-37-1
- 5,6,4'-Trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9715
CAS No.:56226-95-0
- Blestriarene C
Catalog No.:BCN9716
CAS No.:120090-81-5
- Adenostemmoic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN9717
CAS No.:130217-16-2
- Hortiamide
Catalog No.:BCN9718
CAS No.:106055-13-4
- Adenostemmoic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN9719
CAS No.:130217-20-8
- Yukocitrine
Catalog No.:BCN9720
CAS No.:145940-32-5
- N-Methoxy-3-hydroxymethylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN9721
CAS No.:142768-49-8
- N-Methoxy-3-formylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN9722
CAS No.:117592-01-5
- O-Methylmurrayamine A
Catalog No.:BCN9723
CAS No.:134779-20-7
- Stephodeline
Catalog No.:BCN9724
CAS No.:56596-12-4
- Rossicaside B
Catalog No.:BCN9725
CAS No.:80458-55-5
- Pumiloside
Catalog No.:BCN9726
CAS No.:126722-26-7
Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Neolamarckia cadamba: A review.[Pubmed:26821190]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 2;181:118-35.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: There are more than 3000 officially documented plants in the Indian subcontinent that hold great medicinal potential. One such under-explored plant is an evergreen tropical tree Neolamarckia cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser (Rubiaceae). It is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world and has therapeutic potential against many diseases such as diabetes, anaemia, stomatitis, leprosy, cancer and infectious diseases. Neolamarckia cadamba has historical existence in India and it is mentioned in mythical stories. There are several reports on medicinal values of root, bark and leaves of N. cadamba; but the literature on its fruits is scanty. Therefore, the present review aims to provide updated comprehensive information on the phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of different parts of N. cadamba tree with special reference to its fruit, in order to open new perspectives for future food and pharmacological research. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A literature search was performed on N. cadamba using ethnobotanical textbooks, published articles in peer-reviewed journals, unpublished materials, government survey reports and scientific databases such as Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science Direct, Google Scholar and other web search engines (Google, Yahoo). The Plant List, International Plant Name Index and Kew Botanical Garden Plant name databases were used to validate the scientific names. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: Neolamarckia cadamba is one of the economically important trees, which is being exploited for paper, pulp and wood industry. In folk medicine, various parts of N. cadamba are used in the treatment of various ailments such as fever, uterine complaints, blood diseases, skin diseases, tumour, anaemia, eye inflammation and diarrhoea. Other reported uses of N. cadamba include antihepatotoxic, antimalarial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, diuretic and laxative. Various phytochemicals such as cadambine and its derivatives (dihydrocadambine and Isodihydrocadambine) and indole alkaloids (Neolamarckines) were isolated from the leaves; whereas the presence of quinovic acid derivatives have been reported in the bark of N. cadamba. CONCLUSION: The present review compiles information on an ethnopharmacologically useful plant N. cadamba. Bioactive compounds responsible for its various medicinal properties and their effects at the molecular level need to be investigated in more detail. Furthermore, the detailed study of toxicity and pharmacological properties of extracts as well as molecules in N. cadamba is required to confirm the ethnomedicinal claims of N. cadamba for food and pharmaceutical applications.
A possible solution for hair loss by inhibiting corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptor from traditional Chinese medicine.[Pubmed:23998289]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2014;32(10):1613-23.
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and corticotropin-releasing factor receptor (CRFR) play important roles in stress response, including anxiety and depression syndrome. The CRF expression also relates to chronic stress-related hair loss. This study utilizes the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) database and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate novel CRFR inhibitors for treatment of alopecia. The docking and screening from TCM database results indicate the vitamin B2, 3 beta-Isodihydrocadambine, and caribine display higher binding affinity than maltose in maltose binding protein (MBP). However, the results of MD simulation shows the caribine-facilitated CRFR approach closer to MBP, the 3D structure conformation of MBP and CRFR complex forms compact structure. Interestingly, the distance between the two proteins is reducing significantly after caribine dock into MBP binding site. Beside, from Ligand channel analysis, the paths of caribine demonstrate that residence time is increased in binding pocket. Hence, our finding suggests that caribine might be a potential lead compound to stimulate MBP and CRFR interaction, and help for baldless therapy in further study.
Gluco-indole alkaloids from Nauclea cadamba in Thailand and transformation of 3 alpha-dihydrocadambine into the indolopyridine alkaloid, 16-carbomethoxynaufoline.[Pubmed:12576667]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2003 Feb;51(2):232-3.
Three monoterpenoid gluco-indole alkaloids, 3beta-Isodihydrocadambine, cadambine, and 3alpha-dihydrocadambine, were isolated from Nauclea cadamba ROXB. growing in Thailand. The stereochemistry at C19 in 3beta-Isodihydrocadambine was elucidated to be R by spectroscopic analysis. Treatment of 3alpha-dihydrocadambine with beta-glucosidase in aqueous ammonium acetate solution gave an indolopyridine alkaloid, 16-carbomethoxynaufoline, and an unusually rearranged compound.


