PumilosideCAS# 126722-26-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

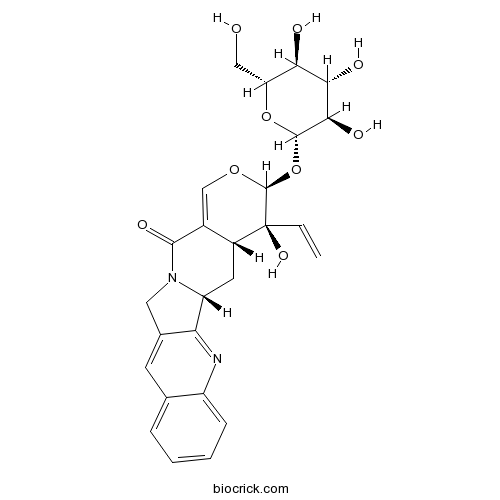
| Cas No. | 126722-26-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101012337 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C26H28N2O9 | M.Wt | 512.5 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (3S)-Pumiloside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,18S,19S,20R)-19-ethenyl-19-hydroxy-18-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-2,4,6,8,10,15-hexaen-14-one | ||
| SMILES | C=CC1(C2CC3C4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4CN3C(=O)C2=COC1OC6C(C(C(C(O6)CO)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CMLUTPKMPFDRAX-PJKCNYDSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H28N2O9/c1-2-26(34)15-8-17-19-13(7-12-5-3-4-6-16(12)27-19)9-28(17)23(33)14(15)11-35-25(26)37-24-22(32)21(31)20(30)18(10-29)36-24/h2-7,11,15,17-18,20-22,24-25,29-32,34H,1,8-10H2/t15-,17-,18-,20-,21+,22-,24+,25+,26+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Pumiloside Dilution Calculator

Pumiloside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9512 mL | 9.7561 mL | 19.5122 mL | 39.0244 mL | 48.7805 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3902 mL | 1.9512 mL | 3.9024 mL | 7.8049 mL | 9.7561 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1951 mL | 0.9756 mL | 1.9512 mL | 3.9024 mL | 4.878 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.039 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3902 mL | 0.7805 mL | 0.9756 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0195 mL | 0.0976 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3902 mL | 0.4878 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rossicaside B
Catalog No.:BCN9725
CAS No.:80458-55-5
- Stephodeline
Catalog No.:BCN9724
CAS No.:56596-12-4
- O-Methylmurrayamine A
Catalog No.:BCN9723
CAS No.:134779-20-7
- N-Methoxy-3-formylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN9722
CAS No.:117592-01-5
- N-Methoxy-3-hydroxymethylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN9721
CAS No.:142768-49-8
- Yukocitrine
Catalog No.:BCN9720
CAS No.:145940-32-5
- Adenostemmoic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN9719
CAS No.:130217-20-8
- Hortiamide
Catalog No.:BCN9718
CAS No.:106055-13-4
- Adenostemmoic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN9717
CAS No.:130217-16-2
- Blestriarene C
Catalog No.:BCN9716
CAS No.:120090-81-5
- 5,6,4'-Trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9715
CAS No.:56226-95-0
- Isodihydrocadambine
Catalog No.:BCN9714
CAS No.:55624-02-7
- Phyllanthurinolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9727
CAS No.:168180-12-9
- Artanomaloide
Catalog No.:BCN9728
CAS No.:112823-41-3
- 4-(2,6,6-Trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-3-buten-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN9909
CAS No.:79-77-6
- 11-Oxomogroside IIIE
Catalog No.:BCN9730
CAS No.:2096516-68-4
- Rauhimbine
Catalog No.:BCN9731
CAS No.:66634-44-4
- Carvacryl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9732
CAS No.:6380-28-5
- Furfuryl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN9733
CAS No.:98-00-0
- gamma-Nonanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9734
CAS No.:104-61-0
- 1-(3',5'-dimethoxy)phenyl-2-[4''-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (6->1)-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl]phenylethane
Catalog No.:BCN9735
CAS No.:1338076-61-1
- Tripalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN9736
CAS No.:555-44-2
- Capsanthin
Catalog No.:BCN9737
CAS No.:465-42-9
- Uzarin
Catalog No.:BCN9738
CAS No.:20231-81-6
Biosynthesis-inspired mining and identification of untapped alkaloids in Camptotheca acuminate for enzyme discovery using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time of flight-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:32201039]
J Chromatogr A. 2020 Jun 7;1620:461036.
Leaves, flowers, fruits and stems (44 sample groups) were collected from mature Camptotheca acuminate during 2017.3-2018.3 and classified by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time of flight-mass spectrometry based metabolomics. One hundred metabolites including forty-seven alkaloids, fifteen terpenes, thirty-two polyphenols and six other metabolites were rapidly identified through the in-house database alignment at first glance. Thirty-three alkaloids classified into five groups including camptothecin group (CG1-13), Pumiloside group (PG1-5), strictosidinic acid group (SG1-3), vincosamide group (VG1-7), and a new hybrid group, vincosamide-camptothecin group (VC1-5) were mined and further characterized by MS/MS analyses. The identification of two untapped biosynthetic precursors, 2-hydroxyPumiloside (PG2) and 16hydroxy15, 16-dihydrocamptothecoside (CG3), along with sixteen new alkaloids enables us for a better understanding of camptothecin biogenetic reasoning. The underlying enzymes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis were also proposed according to the guiding metabolic map, thus purposefully mining of enzymes involved in the downstream biosynthetic pathway of camptothecin could be initiated with the help of this map.
Ethanol extract of Ophiorrhiza pumila suppresses liver cancer cell proliferation and migration.[Pubmed:32021647]
Chin Med. 2020 Jan 31;15:11.
Background: Ophiorrhiza pumila, belonging to the genus Ophiorrhiza (Rubiaceae), is distributed throughout tropical and subtropical Asia. In this study, we evaluated for the first time the anti-proliferation and anti-migration effects of ethanol extract of O. pumila (OPE) on HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells, and explored the related mechanism. Methods: OPE was prepared by percolation with 95% ethanol and its main compounds were analyzed by HPLC-MS(2). The anti-proliferation effect of OPE was evaluated by the CCK-8 assay and colony formation assay. Cell cycle distribution, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level were detected by flow cytometry. Migration and invasion abilities were detected by Transwell migration/invasion assays. The expression of correlated proteins was determined using western blotting. Results: A total of 5 tentative compounds were identified from OPE, including Pumiloside, deoxyPumiloside, camptothecin, aknadinine, and beta-stigmasterol. OPE displayed strong cytostatic effects on HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells. OPE induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, increased apoptosis, and augmented ROS production in these cell lines. In addition, OPE possessed a significant inhibition on cell migration and invasion by reduction of MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression. Moreover, OPE significantly suppressed the phosphorylation of p65. Conclusions: Our data showed that OPE suppresses liver cancer cell proliferation and migration, which is possibly involved with the inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway.
A new indole alkaloid with HUVEC proliferation activities from Nauclea officinalis.[Pubmed:31707857]
Nat Prod Res. 2019 Nov 11:1-7.
A new indole alkaloid, namely naucleofficine H (1), was obtained from the aqueous extract of Nauclea officinalis, together with four known alkaloids, vincosamide (2), strictosamide (3), angustoline (4) and Pumiloside (5). Their structures were characterized by analyzing their physicochemical data including NMR, and HRMS. In addition, five compounds were tested for their proliferation activities. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), extra-cellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1 and 2 (ERK) and phosphorylation of ERK 1/2 (p-ERK) were also detected in HUVEC treated withbioactive compounds using western blotting. The result showed that these compounds could promote HUVEC cell proliferation. Compounds 3 and 5 could up-regulate VEGF and p-ERK in HUVEC.
Distribution of camptothecin biosynthetic intermediates and identification the rate-limiting step of camptothecin biosynthesis.[Pubmed:31537116]
Nat Prod Res. 2019 Sep 19:1-8.
Two key biosynthetic intermediates (Pumiloside and strictosamide) of camptothecin were isolated. A high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV) method was developed to determine four main alkaloid compounds (Pumiloside, strictosamide, camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin) and estimate two minor compounds (deoxyPumiloside, 9-methoxycamptothecin) simultaneously in different parts of Camptotheca acuminata, with a good linearity and R(2) > 0.999 for all curves. The results indicated that there was a positive correlation between the two key intermediates (strictosamide and Pumiloside) and camptothecin in vivo. The speculation that the root was the synthetic position of camptothecin in vivo was confirmed. The rate-limiting step of camptothecin biosynthesis was estimated the step from Pumiloside to deoxyPumiloside based on its concentration fall sharply.
Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Multiple Trace Levels of Intermediate Metabolites for Camptothecin Biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata and Their Simultaneous Determination by HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS/MS and HPLC-TSQ-MS.[Pubmed:30823523]
Molecules. 2019 Feb 25;24(4). pii: molecules24040815.
Camptothecin (CPT) has strong antitumor activity and is used as an anticancer therapeutic agent. To better understand and decipher the pathway of CPT biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata, the main purpose here was focused on creating an effective extraction strategy for a rich intermediate metabolite profile. In the present study, a 70% aqueous acetonitrile was verified as an optimal extraction solvent for microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) of metabolites by spiking experiments. Based on multi-objective optimization, the best extraction conditions of a solid-liquid ratio of 1:20, microwave power of 230 W, and a time of 4 min were achieved using a full factorial 3(4) experimental design. Crude extracts obtained from the shoot apex of C. acuminata using MAE have been qualitatively profiled by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry (HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS/MS) and a HPLC triple quadrupole-MS (HPLC-TSQ-MS) analysis was conducted for their metabolite content in different tissues. CPT, and ten related metabolites and their isomers, including tryptamine, loganic acid, secologanic acid, strictosidinic acid, strictosamide, strictosamide epoxide, strictosamide diol, strictosamide ketolactam, Pumiloside, and deoxyPumiloside, were detected and tentatively identified. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging of the shoot apex demonstrated that severe cell disruption was evident after intensified extraction processes. The study showed the difference of metabolite profiles and the enhancement of metabolite content after microwave-pretreated techniques, and the established MAE procedure is an effective methodology to preserve valuable metabolite compounds for analysis.
A new benzofuran derivative from the leaves of Ficus pumila L.[Pubmed:29072969]
Nat Prod Res. 2018 Jul;32(14):1648-1652.
A new benzofuran derivative, Pumiloside (1), together with seven known flavonoid glycosides, afzelin (2), astragalin (3), quercitrin (4), isoquercitrin (5), kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (6), rutin (7) and kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside (8) were isolated from the leaves of Ficus pumila. Their structures were established by spectroscopic data and comparison with the literature values.
Anti-inflammatory effect of the six compounds isolated from Nauclea officinalis Pierrc ex Pitard, and molecular mechanism of strictosamide via suppressing the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed:27989509]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 20;196:66-74.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Nauclea officinalis Pierrc ex Pitard. is a Chinese medicinal herb that contains high level of alkaloids which is the most abundant and active constituent. Strictosamide isolated from Nauclea officinalis Pierrc ex Pitard. showed significant effects on inflammatory response, compared with Pumiloside, 3-epi-Pumiloside, vincosamide, 3alpha,5alpha-tetrahydrodeoxycordifoline lactam and naucleamide A-10-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside of this plant. AIM OF STUDY: we investigated the biological activities of the six compounds mentioned-above, and the underlying molecular mechanism exerted by the most potent one, strictosamide. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The effects of strictosamide and other five compounds on the inhibitory activity of nitric oxide (NO) were screened by Griess test. The contents of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) in media were detected by using Enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) kits. The effects on the mRNA expression of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), TNF-alpha and IL-1beta of strictosamide were further investigated by RT-qPCR. Western blot assay was conducted to illustrate the effects of strictosamide on iNOS and phosphorylation of p65, inhibitor of NF-kappaB (IkappaB)-alpha, IkappaB-kinase (IKK)-alpha as well as p-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p-c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p-p38 in the protein levels. RESULTS: Strictosamide potently suppressed the productions of NO, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages, and it dose-dependently alleviated the LPS-simulated protein level of iNOS as well as the mRNA expressions of iNOS, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. In addition, molecular data revealed that strictosamide markedly decreased the expressions of p-p65, p-IkappaBalpha and p-IKKalpha. Furthermore, strictosamide significantly attenuated LPS-induced the phosphorylation of p38, ERK and JNK. CONCLUSIONS: At present study, the results indicated that the anti-inflammatory activity of strictosamide was associated with the restraint of NO, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta via negative regulation of both NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells.
[Effect of rat intestinal flora on in vitro metabolic transformation of pumiloside].[Pubmed:28895344]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 May;41(10):1921-1925.
To study the metabolic transformation of Pumiloside by rat intestinal flora in vitro and identify its metabolites. Pumiloside was incubated in the rat intestinal flora in vitro. HPLC was used to monitor the metabolic process, and HPLC-Q-TOF-MS was used to identify the structures of biotransformation products. In vitro, Pumiloside was easily metabolized by rat intestinal flora, and with the prolongation of metabolic time, Pumiloside was transformed into several metabolites. Three metabolites were initially identified in this experiment. The study indicated that Pumiloside could be extensively metabolized in the rat intestinal flora in vitro.
New cycloartane saponin and monoterpenoid glucoindole alkaloids from Mussaenda luteola.[Pubmed:26969788]
Fitoterapia. 2016 Apr;110:129-34.
A new cycloartane-type saponin with unusual hydroxylation at C-17 and a unique side chain, 9 (R), 19, 22 (S), 24 (R) bicyclolanost-3beta, 12alpha, 16beta, 17alpha tetrol-25-one 3-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-d-glucopyranoside (1) and two new monoterpenoid glucoindole alkaloids, 10-methoxy Pumiloside (2) and the previously chemically synthesized, 10-methoxy strictosidine (3) along with other five known compounds, 7alpha-morroniside (4), 7-epi-loganin (5), (7beta)-7-O-methylmorroniside (6), 5(S)-5-carboxystrictisidine (7) and apigenin-7-O-neohesperidoside (8) were isolated from the aerial parts of Mussaenda luteola (Rubiaceae). The structural elucidation of the isolates was accomplished by extensive (1D and 2D NMR) spectroscopic data analysis and HR-ESI-MS. Compounds 4-8 were reported for the first time from the genus Mussaenda. Interestingly, this is the first report for the occurrence of the monoterpenoid glucoindole-type alkaloids in the genus which might be useful for the chemotaxonomic evaluation of the genus Mussaenda. All isolates were evaluated for their antiprotozoal activities. Compound 7 showed good antitrypanosomal activity with IC50 and IC90 values of 13.7 and 16.6 muM compared to IC50 and IC90 values of 13.06 and 28.99 muM for the positive control DFMO, difluoromethylornithine.
A novel 10-hydroxycamptothecin-glucoside from the fruit of Camptotheca acuminata.[Pubmed:26609763]
Nat Prod Res. 2016;30(9):1053-9.
Glycosides were isolated from the fruit of Camptotheca acuminata and identified using NMR, MS, UV and IR spectrometries. 10-O-(1-beta-D-glycosyl) camptothecin (1) was identified for the first time in a natural material. In addition, compounds 2-4 were firstly reported from the fruits of C. acuminata and indentified as syringaresinol-4, 4'-O-bis-beta-D-glucoside (2), hyperoside (3) and Pumiloside (4), respectively. Two known compounds, vincoside-lactam (5) and strictosidinic acid (6), were also obtained.
New indole glucosides as biosynthetic intermediates of camptothecin from the fruits of Camptotheca acuminata.[Pubmed:25771119]
Fitoterapia. 2015 Jun;103:1-8.
Six new indole glucosides (1-6) and fifteen known alkaloids (7-21) were isolated from the fruit of Camptotheca acuminata. The planar structures of 1-6 were determined on the basis of spectroscopic data analysis and their absolute configurations were established by CD. The isolated indole glucosides showed a clear biosynthetic pathway of camptothecin (7), which started from tryptamine and secologanin and was proposed by synthetic chemists previously. Particularly, compound 1 supplemented the process of the transformation from Pumiloside (20) or 3-epi-Pumiloside (21) to camptothecin (7). In addition, camptothecin 10-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (13) and norcamptothecin (17), synthesized in the early structural modification of 7, were first isolated from the natural resources. The new compounds 1-6 were screened for their in vitro cytotoxicity but they did not show any exciting result.
Natural indole butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors from Nauclea officinalis.[Pubmed:25636869]
Phytomedicine. 2015 Jan 15;22(1):45-8.
Nine monoterpenoid indole alkaloids; naucletine (1), angustidine (2), nauclefine (3), angustine (4), naucline (5), angustoline (6), harmane (7), 3,14-dihydroangustoline (8), strictosamide (9) and one quinoline alkaloid glycoside; Pumiloside (10) from Nauclea officinalis were tested for cholinesterase inhibitory activity. All the alkaloids except for Pumiloside (10) showed strong to weak BChE inhibitory effect with IC50 values ranging between 1.02-168.55 muM. Angustidine (2), nauclefine (3), angustine (4), angustoline (6) and harmane (7) showed higher BChE inhibiting potency compared to galanthamine. Angustidine (2) was the most potent inhibitor towards both AChE and BChE. Molecular docking (MD) studies showed that angustidine (2) docked deep into the bottom gorge of hBChE and formed hydrogen bonding with Ser 198 and His 438. Kinetic study of angustidine (2) on BChE suggested a mixed inhibition mode with an inhibition constant (Ki) of 6.12 muM.
Simultaneous determination of six alkaloid components in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study of Danmu preparations by an ultra fast liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:25612771]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Mar 1;983-984:10-7.
Danmu injection and Danmu tablet are two widely used traditional Chinese medicine made of Nauclea officinalis (commonly known as Danmu), in which the alkaloids are the major active substances. In this paper, an ultra fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS/MS) method was developed for simultaneous determination and the pharmacokinetic characteristics study of six main active alkaloids (naucleamide A-10-O-beta-d-glucopyranosid, naucleamide G, Pumiloside, 3-epi-Pumiloside, strictosamide and vincosamide) of the two above-mentioned Danmu preparations in rat plasma. In the course of the experiment, following sample preparation by protein precipitation with methanol-ethyl acetate (2:1, v/v), the nitrogen-dried extraction was reconstituted in methanol and assayed on a C18 column using a gradient elution program with mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and water containing 0.1% formic acid. The MS detection was performed in positive ionization mode with selected ion transitions. The established method was fully validated and proved to be sensitive and specific with lower limits of quantification (LLOQs) all less than 0.32ng/mL in rat plasma and matrix effects ranged from 88.87 to 108.27%. Good linearities of six alkaloids were obtained in respective concentration ranges (r(2)>0.995). The average extract recoveries for each compound at three quality control concentration levels were no less than 79.70%, and the precision and accuracy were within the acceptable limits. The validated method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of six alkaloid components of Danmu injection and tablet in rat plasma. The obtained results may be helpful to reveal the action mechanism and guide the clinical application of Danmu preparations.
In vitro anti-Herpes simplex virus activity of crude extract of the roots of Nauclea latifolia Smith (Rubiaceae).[Pubmed:24131916]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Oct 16;13:266.
BACKGROUND: Nauclea latifolia Smith, a shrub belonging to the family Rubiaceae is a very popular medicinal plant in Cameroon and neighboring countries where it is used to treat jaundice, yellow fever, rheumatism, abdominal pains, hepatitis, diarrhea, dysentery, hypertension, as well as diabetes. The ethno-medicinal use against yellow fever, jaundice and diarrhea prompted us to investigate on the antiviral activity of the root bark of N. latifolia. In this study, HSV-2 was chosen as a viral model because of its strong impact on HIV transmission and acquisition. METHODS: The crude extract under study was prepared by maceration of air-dried and powdered roots barks of N. latifolia in CH2Cl2/MeOH (50:50) mixture for 48 hours, then it was subjected to filtration and evaporation under vacuum. A phytochemical analysis of the crude extract was performed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled with a photodiode array and mass spectrometry (HPLC-PDA-ESI-qMS). The anti-HSV-2 activity was assayed in vitro by plaque reduction and virus yield assays and the major mechanism of action was investigated by virucidal and time of addition assays. Data values were compared using the Extra sum of squares F test of program GraphPad PRISM 4. RESULTS: The main components detected in the extract belong to the class of indole alkaloids characteristic of Nauclea genus. Strictosamide, vincosamide and Pumiloside were tentatively identified together with quinovic acid glycoside. N. latifolia crude extract inhibited both acyclovir sensitive and acyclovir resistant HSV-2 strains, with IC50 values of 5.38 mug/ml for the former and 7.17 mug/ml for the latter. The extract was found to be most active when added post-infection, with IC50 of 3.63 mug/ml. CONCLUSION: The results of this work partly justify the empirical use of N. latifolia in traditional medicine for the treatment of viral diseases. This extract could be a promising rough material for the development of a new and more effective modern anti-HSV-2 medication also active against acyclovir-resistant HSV-2 strains.


