KU-0063794MTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor CAS# 938440-64-3 |
- ETP-46464
Catalog No.:BCC3913
CAS No.:1345675-02-6
- NU 7026
Catalog No.:BCC3933
CAS No.:154447-35-5
- Daun02
Catalog No.:BCC1518
CAS No.:290304-24-4
- NU7441 (KU-57788)
Catalog No.:BCC3679
CAS No.:503468-95-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 938440-64-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16736978 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H31N5O4 | M.Wt | 465.54 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (35.81 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
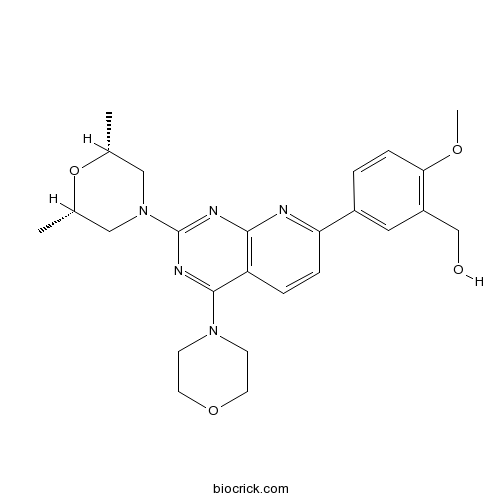
| Chemical Name | [5-[2-[(2R,6S)-2,6-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl]-4-morpholin-4-ylpyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl]-2-methoxyphenyl]methanol | ||
| SMILES | CC1CN(CC(O1)C)C2=NC3=C(C=CC(=N3)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)OC)CO)C(=N2)N5CCOCC5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RFSMUFRPPYDYRD-CALCHBBNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H31N5O4/c1-16-13-30(14-17(2)34-16)25-27-23-20(24(28-25)29-8-10-33-11-9-29)5-6-21(26-23)18-4-7-22(32-3)19(12-18)15-31/h4-7,12,16-17,31H,8-11,13-15H2,1-3H3/t16-,17+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (IC50 ~10 nM for mTORC1 and mTORC2). Displays no activity at PI 3-kinase or 76 other kinases tested. Inhibits activation and hydrophobic motif phosphorylation of Akt, S6K and SGK, but not RSK. Suppresses cell growth and induces G1 cell cycle arrest in vitro. | |||||

KU-0063794 Dilution Calculator

KU-0063794 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.148 mL | 10.7402 mL | 21.4804 mL | 42.9609 mL | 53.7011 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4296 mL | 2.148 mL | 4.2961 mL | 8.5922 mL | 10.7402 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2148 mL | 1.074 mL | 2.148 mL | 4.2961 mL | 5.3701 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.043 mL | 0.2148 mL | 0.4296 mL | 0.8592 mL | 1.074 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0215 mL | 0.1074 mL | 0.2148 mL | 0.4296 mL | 0.537 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ku-0063794 is a specific mTOR inhibitor, which inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2 with IC50 values of ~ 10nM.[1]
The mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) protein kinase lies at the nexus of signaling pathways that regulate cell growth and proliferation. Various cancer-driving mutations in genes such as receptor tyrosine kinases, Ras, PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) and PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10) stimulate proliferation, growth and survival by the activation of mTOR kinase. MTOR stimulates cell growth by phosphorylating and promoting activation of AGC (protein kinase A/protein kinase G/protein kinase C) family kinases such as Akt (protein kinase B), S6K (p70 ribosomal S6 kinase) and SGK(serum and glucocorticoid protein kinase). MTORC1 phosphorylates the hydrophobic motif of S6K, while mTORC2 phosphorylates the hydrophobic motif of Akt and SGK. Ku-0063794 inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2 in vitro and in vivo and can be used to dissect cellular functions of the mTOR pathway.[1]
In HEK-293 cells, Ku-0063794 inhibited the activity of endogenous immunoprecipitated mTORC1 and mTORC2, employing S6K1 and Akt as substrates, with IC50 values of ~10nM. The ability of Ku-0063794 to suppress S6K1 activity and phosphorylation was rapid,Concentrations
of 100–300 nM Ku-0063794 were required to fully suppress amino-acid-induced phosphorylation of S6K1 and S6 protein. Ku-0063794 inhibits phosphorylation of Akt at Thr 308. Ku-0063794 was also assessed for other targets. However, it does not significantly inhibit 76 other protein kinases tested as well as seven lipid kinases, including class 1a PI3K α and PI3K β.[1,2]
The antileukemic effects of Ku-0063794 of the PI3K signaling pathway were evaluated by methylcellulose colony assays with primary murine CML cells obtained from mice that underwent bone marrow reconstitution with hematopoietic cells transduced with a retrovirus vector-expressing BCR/ABL. It showed that Ku-0063794 fully suppressed colony formation of primary murine CML at 1000nM. Moreover, KU-0063794 strikingly reduces cell proliferation in BA/F3 cells expressing BCR/ABL independently of mutation status, which indicates Ku-0063794 is a desirable therapeutic strategy to affect oncogenes signaling downstream of BCR/ABL.[2]
References:
1.Garcia-Martinez J, Moran J, Clarke R, et al. Ku-0063794 is a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)[J]. Biochem. J, 2009, 421: 29-42.
2.Schuster K, Zheng J, Arbini A A, et al. Selective targeting of the mTORC1/2 protein kinase complexes leads to antileukemic effects in vitro and in vivo[J]. Blood cancer journal, 2011, 1(9): e34.
- ATPγS tetralithium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7855
CAS No.:93839-89-5
- 22-beta-Acetoxyglycyrrhizin
Catalog No.:BCN7904
CAS No.:938042-17-2
- 3-Prenyl-2,4,6-trihydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1303
CAS No.:93796-20-4
- Roxatidine Acetate HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4534
CAS No.:93793-83-0
- gamma-Secretase Modulators
Catalog No.:BCC1586
CAS No.:937812-80-1
- Neurodazine
Catalog No.:BCC7738
CAS No.:937807-66-4
- Neogambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2321
CAS No.:93772-31-7
- Jangomolide
Catalog No.:BCN4483
CAS No.:93767-25-0
- GRP (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5810
CAS No.:93755-85-2
- Magnaldehyde D
Catalog No.:BCN4070
CAS No.:93753-33-4
- Pacritinib (SB1518)
Catalog No.:BCC4558
CAS No.:937272-79-2
- SB1317
Catalog No.:BCC1925
CAS No.:937270-47-8
- Isochamaejasmine
Catalog No.:BCN3128
CAS No.:93859-63-3
- 9-Oxo-2,7-bisaboladien-15-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4484
CAS No.:93888-59-6
- FIPI
Catalog No.:BCC7721
CAS No.:939055-18-2
- Hirsutanonol 5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4485
CAS No.:93915-36-7
- Toonaciliatin M
Catalog No.:BCN7881
CAS No.:93930-04-2
- Fluvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC1579
CAS No.:93957-54-1
- Fluvastatin Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2317
CAS No.:93957-55-2
- [Ac-Tyr1,D-Phe2]GRF 1-29, amide (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5719
CAS No.:93965-89-0
- PF-00562271
Catalog No.:BCC3684
CAS No.:939791-38-5
- ACTB-1003
Catalog No.:BCC5587
CAS No.:939805-30-8
- BI 6015
Catalog No.:BCC6249
CAS No.:93987-29-2
- p53 and MDM2 proteins-interaction-inhibitor chiral
Catalog No.:BCC1830
CAS No.:939981-37-0
Ku-0063794 is a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR).[Pubmed:19402821]
Biochem J. 2009 Jun 12;421(1):29-42.
mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) stimulates cell growth by phosphorylating and promoting activation of AGC (protein kinase A/protein kinase G/protein kinase C) family kinases such as Akt (protein kinase B), S6K (p70 ribosomal S6 kinase) and SGK (serum and glucocorticoid protein kinase). mTORC1 (mTOR complex-1) phosphorylates the hydrophobic motif of S6K, whereas mTORC2 phosphorylates the hydrophobic motif of Akt and SGK. In the present paper we describe the small molecule KU-0063794, which inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2 with an IC50 of approximately 10 nM, but does not suppress the activity of 76 other protein kinases or seven lipid kinases, including Class 1 PI3Ks (phosphoinositide 3-kinases) at 1000-fold higher concentrations. KU-0063794 is cell permeant, suppresses activation and hydrophobic motif phosphorylation of Akt, S6K and SGK, but not RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase), an AGC kinase not regulated by mTOR. KU-0063794 also inhibited phosphorylation of the T-loop Thr308 residue of Akt phosphorylated by PDK1 (3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1). We interpret this as implying phosphorylation of Ser473 promotes phosphorylation of Thr308 and/or induces a conformational change that protects Thr308 from dephosphorylation. In contrast, KU-0063794 does not affect Thr308 phosphorylation in fibroblasts lacking essential mTORC2 subunits, suggesting that signalling processes have adapted to enable Thr308 phosphorylation to occur in the absence of Ser473 phosphorylation. We found that KU-0063794 induced a much greater dephosphorylation of the mTORC1 substrate 4E-BP1 (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1) than rapamycin, even in mTORC2-deficient cells, suggesting a form of mTOR distinct from mTORC1, or mTORC2 phosphorylates 4E-BP1. KU-0063794 also suppressed cell growth and induced a G1-cell-cycle arrest. Our results indicate that KU-0063794 will be useful in delineating the physiological roles of mTOR and may have utility in treatment of cancers in which this pathway is inappropriately activated.
Potent dual inhibitors of TORC1 and TORC2 complexes (KU-0063794 and KU-0068650) demonstrate in vitro and ex vivo anti-keloid scar activity.[Pubmed:23303455]
J Invest Dermatol. 2013 May;133(5):1340-50.
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is essential in controlling several cellular functions. This pathway is dysregulated in keloid disease (KD). KD is a common fibroproliferative dermal lesion with an ill-defined treatment strategy. KD demonstrates excessive matrix deposition, angiogenesis, and inflammatory cell infiltration. In KD, both total and phosphorylated forms of mTOR and p70(S6K)(Thr421/Ser424) are upregulated. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate adenosine triphosphate-competitive inhibitors of mTOR kinase previously unreported in keloid and their comparative efficacy with Rapamycin. Here, we present two mTOR kinase inhibitors, KU-0063794 and KU-0068650, that target both mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling. Treatment with either KU-0063794 or KU-0068650 resulted in complete suppression of Akt, mTORC1, and mTORC2, and inhibition of keloid cell spreading, proliferation, migration, and invasive properties at a very low concentration (2.5 mumol l(-1)). Both KU-0063794 and KU-0068650 significantly (P<0.05) inhibited cell cycle regulation and HIF1-alpha expression compared with that achieved with Rapamycin alone. In addition, both compounds induced shrinkage and growth arrest in KD, associated with the inhibition of angiogenesis, induction of apoptosis, and reduction in keloid phenotype-associated markers. In contrast, Rapamycin induced minimal antitumor activity. In conclusion, potent dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitors display therapeutic potential for the treatment of KD.
Autophagy inhibition sensitizes KU-0063794-mediated anti-HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell activity in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:26278819]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Sep 25;465(3):494-500.
Recent studies have indicated that mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling has a critical role in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In the current study, we investigated the activity of KU-0063794, a novel mTOR kinase inhibitor, against HepG2 HCC cells. Our results demonstrated that KU-0063794 blocked mTOR complex 1/2 (mTORC1/2) activation, and downregulated mTOR-regulated genes (Cyclin D1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha) in HepG2 cells. Consequently, KU-0063794 induced significant anti-survival and pro-apoptotic activities against HepG2 cells. When analyzing the possible KU-0063794-resistance factors, we showed that KU-0063794 induced cyto-protective autophagy activation in HepG2 cells, evidenced by GFP-light chain 3B (LC3B) puncta formation, p62 degradation, Beclin-1 expression and LC3B-I to LC3B-II conversion. Correspondingly, autophagy inhibitors, including bafliomycin A1, 3-methyladenine (3-MA) and chloroquine, dramatically enhanced KU-0063794-induced cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells. Further, RNAi knockdown of Beclin-1 also increased KU-0063794 sensitivity in HepG2 cells. In vivo, oral administration of KU-0063794 repressed HepG2 xenograft growth in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice, and its activity was further enhanced with co-administration of the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA. In summary, KU-0063794 inhibits HepG2 cell growth in vitro and in vivo, its activity could be further enhanced with autophagy inhibition.


