NU 7026DNPK inhibitor,ATP-competitive and potent CAS# 154447-35-5 |
- BEZ235 Tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC1416
CAS No.:1028385-32-1
- ETP-46464
Catalog No.:BCC3913
CAS No.:1345675-02-6
- NU7441 (KU-57788)
Catalog No.:BCC3679
CAS No.:503468-95-9
- CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)
Catalog No.:BCC1270
CAS No.:870281-82-6
- BKM120
Catalog No.:BCC1279
CAS No.:944396-07-0
- GDC-0941
Catalog No.:BCC3626
CAS No.:957054-30-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 154447-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9860529 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H15NO3 | M.Wt | 281.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | LY293646 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 2.9 mg/mL (10.31 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
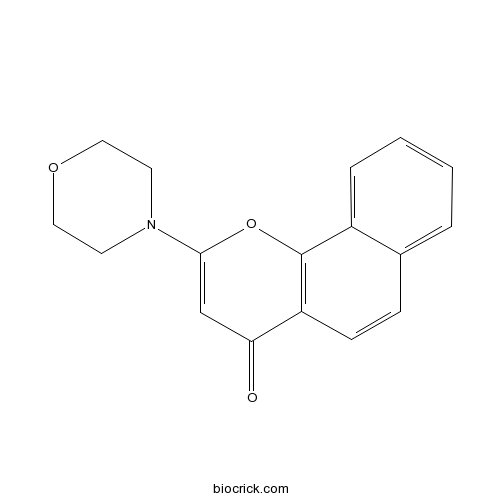
| Chemical Name | 2-morpholin-4-ylbenzo[h]chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1COCCN1C2=CC(=O)C3=C(O2)C4=CC=CC=C4C=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KKTZALUTXUZPSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H15NO3/c19-15-11-16(18-7-9-20-10-8-18)21-17-13-4-2-1-3-12(13)5-6-14(15)17/h1-6,11H,7-10H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | ATP-competitive inhibitor of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Displays selectivity over other PIKK family enzymes (IC50 values are 0.23, 13.0, > 100 and > 100 μM for DNA-PK, PI3K, ATM and ATR respectively). Radiosensitizes both proliferating and quiescent mouse embryonic fibroblast cells to IR and inhibits DSB repair. |

NU 7026 Dilution Calculator

NU 7026 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5548 mL | 17.774 mL | 35.548 mL | 71.0959 mL | 88.8699 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.711 mL | 3.5548 mL | 7.1096 mL | 14.2192 mL | 17.774 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3555 mL | 1.7774 mL | 3.5548 mL | 7.1096 mL | 8.887 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0711 mL | 0.3555 mL | 0.711 mL | 1.4219 mL | 1.7774 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0355 mL | 0.1777 mL | 0.3555 mL | 0.711 mL | 0.8887 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NU 7026 is a selective inhibitor of DNA-PK with IC50 value of 0.23 μM [1].
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase and involves in a variety of cellular processes, like, DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, V(D)J recombination apparatus, chromatin structure and telomere maintenance. It has been shown that increased DNA-PK expression resulted in tumor cells resistance to radio- or chemo- therapy [2].
NU 7026 is a potent DNA-PK inhibitor and often is used combined with PARP-1 inhibitor AG14361 to sensitize tumor cells to radio- or chemo-therapy. When tested with primary PARP-1-/- and cells PARP-1+/+ cells, NU 7026 treatment (<50 μM) sensitized cells to IR-induced cytotoxicity and reduced clonogenic survival by inhibiting DNA-PK [1]. In N87 gastric cancer cells, administration NU 7026 combined with radiation increased DNA double-srand break, cell apoptosis and reduced cell survival through inhibiting DNA-PK [2]. When tested with CH1 human ovarian cancer cells, administration of NU 7026 combined with radiation reduced cell survival rate and clonogenic ability [3].
In female BALB/c mice model with CH1 cells subcutaneous xenograft, administration of NU 7026 orally or intraperitoneally sensitized mice to the radiotherapy with the dose of 100 mg/kg [3].
It has also been reported that NU 7026 is a potent inhibitor of PI-3K, ATM and ATR with IC50 value of 13 μM, >100μM and >100μM, respectively [1].
References:
[1]. Veuger, S.J., et al., Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res, 2003. 63(18): p. 6008-15.
[2]. Niazi, M.T., et al., Effects of dna-dependent protein kinase inhibition by NU7026 on dna repair and cell survival in irradiated gastric cancer cell line N87. Curr Oncol, 2014. 21(2): p. 91-6.
[3]. Nutley, B.P., et al., Preclinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of a novel prototype DNA-PK inhibitor NU7026. Br J Cancer, 2005. 93(9): p. 1011-8.
- Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3040
CAS No.:154445-77-9
- Pramanicin
Catalog No.:BCN1853
CAS No.:154445-05-3
- Lysicamine
Catalog No.:BCN6523
CAS No.:15444-20-9
- Zinc protoporphyrin IX
Catalog No.:BCC6775
CAS No.:15442-64-5
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol 4-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1556
CAS No.:154418-16-3
- Methyl 3-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCN3403
CAS No.:154418-15-2
- Capecitabine
Catalog No.:BCN2168
CAS No.:154361-50-9
- Echistatin, α1 isoform
Catalog No.:BCC5988
CAS No.:154303-05-6
- CB-5083
Catalog No.:BCC6528
CAS No.:1542705-92-9
- Ampalex
Catalog No.:BCC1359
CAS No.:154235-83-3
- Abiraterone
Catalog No.:BCC2259
CAS No.:154229-19-3
- Abiraterone Acotate
Catalog No.:BCN2184
CAS No.:154229-18-2
- LY 294002
Catalog No.:BCC3659
CAS No.:154447-36-6
- LY 303511
Catalog No.:BCC1715
CAS No.:154447-38-8
- Methyl 5-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCN3402
CAS No.:154461-64-0
- Sinapaldehyde glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1689
CAS No.:154461-65-1
- CHM 1
Catalog No.:BCC2387
CAS No.:154554-41-3
- SB 204990
Catalog No.:BCC6342
CAS No.:154566-12-8
- Stauprimide
Catalog No.:BCC7768
CAS No.:154589-96-5
- Efavirenz
Catalog No.:BCC4135
CAS No.:154598-52-4
- Tezampanel
Catalog No.:BCC1993
CAS No.:154652-83-2
- 3-Methoxymollugin
Catalog No.:BCN7164
CAS No.:154706-44-2
- 2-(2'-Hydroxytetracosanoylamino)-octadecane-1,3,4-triol
Catalog No.:BCN1555
CAS No.:154801-30-6
- Cimiside E
Catalog No.:BCN7951
CAS No.:154822-57-8
DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase As Molecular Target for Radiosensitization of Neuroblastoma Cells.[Pubmed:26716839]
PLoS One. 2015 Dec 30;10(12):e0145744.
Tumor cells might resist therapy with ionizing radiation (IR) by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) of IR-induced double-strand breaks. One of the key players in NHEJ is DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). The catalytic subunit of DNA-PK, i.e. DNA-PKcs, can be inhibited with the small-molecule inhibitor NU7026. In the current study, the in vitro potential of NU7026 to radiosensitize neuroblastoma cells was investigated. DNA-PKcs is encoded by the PRKDC (protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide) gene. We showed that PRKDC levels were enhanced in neuroblastoma patients and correlated with a more advanced tumor stage and poor prognosis, making DNA-PKcs an interesting target for radiosensitization of neuroblastoma tumors. Optimal dose finding for combination treatment with NU7026 and IR was performed using NGP cells. One hour pre-treatment with 10 muM NU7026 synergistically sensitized NGP cells to 0.63 Gy IR. Radiosensitizing effects of NU7026 increased in time, with maximum effects observed from 96 h after IR-exposure on. Combined treatment of NGP cells with 10 muM NU7026 and 0.63 Gy IR resulted in apoptosis, while no apoptotic response was observed for either of the therapies alone. Inhibition of IR-induced DNA-PK activation by NU7026 confirmed the capability of NGP cells to, at least partially, resist IR by NHEJ. NU7026 also synergistically radiosensitized other neuroblastoma cell lines, while no synergistic effect was observed for low DNA-PKcs-expressing non-cancerous fibroblasts. Results obtained for NU7026 were confirmed by PRKDC knockdown in NGP cells. Taken together, the current study shows that DNA-PKcs is a promising target for neuroblastoma radiosensitization.
Combining carbon ion irradiation and non-homologous end-joining repair inhibitor NU7026 efficiently kills cancer cells.[Pubmed:26553138]
Radiat Oncol. 2015 Nov 9;10:225.
BACKGROUND: Our previous data demonstrated that targeting non-homologous end-joining repair (NHEJR) yields a higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair (HRR) to heavy ions using DNA repair gene knockouts (KO) in mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF). In this study, we determined if combining the use of an NHEJR inhibitor with carbon (C) ion irradiation was more efficient in killing human cancer cells compared with only targeting a HRR inhibitor. METHODS: The TP53-null human non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1299 was used for testing the radiosensitizing effect of NHEJR-related DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) inhibitor NU7026, HRR-related Rad51 inhibitor B02, or both to C ion irradiation using colony forming assays. The mechanism underlying the inhibitor radiosensitization was determined by flow cytometry after H2AX phosphorylation staining. HRR-related Rad54-KO, NHEJR-related Lig4-KO, and wild-type TP53-KO MEF were also included to confirm the suppressing effect specificity of these inhibitors. RESULTS: NU7026 showed significant sensitizing effect to C ion irradiation in a concentration-dependent manner. In contrast, B02 showed a slight sensitizing effect to C ion irradiation. The addition of NU7026 significantly increased H2AX phosphorylation after C ion and x-ray irradiations in H1299 cells, but not B02. NU7026 had no effect on radiosensitivity to Lig4-KO MEF and B02 had no effect on radiosensitivity to Rad54-KO MEF in both irradiations. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that inhibitors targeting the NHEJR pathway could significantly enhance radiosensitivity of human cancer cells to C ion irradiation, rather than targeting the HRR pathway.
The modulating effect of ATM, ATR, DNA-PK inhibitors on the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of benzo[a]pyrene in human hepatocellular cancer cell line HepG2.[Pubmed:26595742]
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;40(3):988-96.
The effect of inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-related kinases (PIKK): ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM), ATM- and Rad3-related (ATR) and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) on response of HepG2 human liver cancer cells to benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) was investigated. PIKK inhibitors: KU55933 (5 muM), NU7026 (10 muM) or caffeine (1 and 2mM) when used as single agents or in combinations (KU55933/NU7026 and caffeine/NU7026) did not significantly influence the BaP (3 muM) cytotoxicity (MTT reduction test). BaP induced a weak proapoptotic effect which was moderately enhanced by both inhibitor combinations. HepG2 cells exposed to BaP showed a strong S-phase arrest which was considerably diminished by both inhibitor combinations. The DNA damage (comet assay) induced after continuous 24h exposure to BaP was significantly diminished by both inhibitor combinations. Weak induction of reactive oxygen species by BaP was observed, which was not modulated by the inhibitor combinations. Similarly, no modulation of the glutathione levels was observed.
DNA-PK activity is associated with caspase-dependent myogenic differentiation.[Pubmed:27513301]
FEBS J. 2016 Oct;283(19):3626-3636.
Differentiation of myoblasts into myotubes is essential for skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Caspase-3 and caspase-9 are required for efficient myoblast differentiation. The caspase-activated endonuclease activity, CAD, and the DNA-damage repair protein XRCC1 have also been shown to be required to complete differentiation. DNA-damage associated with differentiation is accompanied by phosphorylation of Histone 2AX, an event normally catalysed by kinases ATR, ATM or DNA-PK. However, the kinase responsible for phosphorylation during differentiation is not known. Here we show that inhibition of DNA-PK, but not of ATR or ATM, blocked histone phosphorylation during differentiation. We also show that DNA-PK inhibition and siRNA-mediated DNA-PK knockdown blocked cell fusion. These data implicate a new role for DNA-PK in myogenic differentiation.
micorRNA-101 silences DNA-PKcs and sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine.[Pubmed:27988337]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Jan 29;483(1):725-731.
Gemcitabine sensitization is important for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. We have previously shown that DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) over-expression causes Akt activation and gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Here, we aim to downregulate DNA-PKcs via introduction of micorRNA-101 ("miR-101"). We showed that forced-expression of miR-101 downregulated DNA-PKcs and potentiated gemcitabine-induced PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell death and apoptosis. Contrarily, miR-101 depletion through expressing antagomiR-101 in PANC-1 cells resulted in DNA-PKcs upregulation and gemcitabine resistance. DNA-PKcs downregulation is the primary reason of gemcitabine-sensitization by miR-101. DNA-PKcs inhibition (by NU7026) or silence (by targeted siRNAs) disabled miR-101-mediaetd gemcitabine sensitization. Significantly, Akt Ser-473 phosphorylation in PANC-1 cells was also inhibited by miR-101, but was augmented with antagomiR-101 expression. Importantly, we showed that miR-101 level was downregulated in gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer tissues, which was correlated with DNA-PKcs upregulation. Together, these results suggest that miR-101 sensitizes PANC-1 cells to gemcitabine possibly via downregulating DNA-PKcs.
Chlorambucil cytotoxicity in malignant B lymphocytes is synergistically increased by 2-(morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chomen-4-one (NU7026)-mediated inhibition of DNA double-strand break repair via inhibition of DNA-dependent protein kinase.[Pubmed:17351105]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jun;321(3):848-55.
Chlorambucil (CLB) treatment is used in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) but resistance to CLB develops in association with accelerated repair of CLB-induced DNA damage. Phosphorylated histone H2AX (gammaH2AX) is located at DNA double-strand break (DSB) sites; furthermore, it recruits and retains damage-responsive proteins. This damage can be repaired by nonhomologous DNA end-joining (NHEJ) and/or homologous recombinational repair (HR) pathways. A key component of NHEJ is the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) complex. Increased DNA-PK activity is associated with resistance to CLB in CLL. We used the specific DNA-PK inhibitor 2-(morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chomen-4-one (NU7026) to sensitize CLL cells to chlorambucil. Our results indicate that in a CLL cell line (I83) and in primary CLL-lymphocytes, chlorambucil plus NU7026 has synergistic cytotoxic activity at nontoxic doses of NU7026. CLB treatment results in G(2)/M phase arrest, and NU7026 increases this CLB-induced G(2)/M arrest. Moreover, a kinetic time course demonstrates that CLB-induced DNA-PK activity was inhibited by NU7026, providing direct evidence of the ability of NU7026 to inhibit DNA-PK function. DSBs, visualized as gammaH2AX, were enhanced 24 to 48 h after CLB and further increased by CLB plus NU7026, suggesting that the synergy of the combination is mediated by NU7026 inhibition of DNA-PK with subsequent inhibition of DSB repair.


