Lappaol ACAS# 62333-08-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 62333-08-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 323894 | Appearance | Yellow crystalline powder |
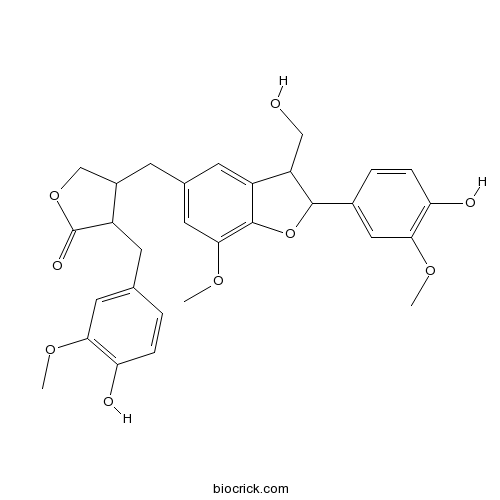
| Formula | C30H32O9 | M.Wt | 536.58 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[[2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-7-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl]methyl]-3-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]oxolan-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)CC2C(COC2=O)CC3=CC(=C4C(=C3)C(C(O4)C5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)OC)CO)OC)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PYLYQTVVQXPBIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H32O9/c1-35-25-11-16(4-6-23(25)32)9-20-19(15-38-30(20)34)8-17-10-21-22(14-31)28(39-29(21)27(12-17)37-3)18-5-7-24(33)26(13-18)36-2/h4-7,10-13,19-20,22,28,31-33H,8-9,14-15H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Lappaol A has antioxidant and antiaging properties, it may promote the C. elegans longevity and stress resistance through a JNK-1-DAF-16 cascade. 2. Lappaol A has potential chemosensitizing activity, it may be candidates for developing novel adjuvant anticancer agents. |
| Targets | JNK | P-gp |

Lappaol A Dilution Calculator

Lappaol A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8637 mL | 9.3183 mL | 18.6366 mL | 37.2731 mL | 46.5914 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3727 mL | 1.8637 mL | 3.7273 mL | 7.4546 mL | 9.3183 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1864 mL | 0.9318 mL | 1.8637 mL | 3.7273 mL | 4.6591 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0373 mL | 0.1864 mL | 0.3727 mL | 0.7455 mL | 0.9318 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0186 mL | 0.0932 mL | 0.1864 mL | 0.3727 mL | 0.4659 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Arjunglucoside I
Catalog No.:BCN8259
CAS No.:62319-70-4
- Ki20227
Catalog No.:BCC1678
CAS No.:623142-96-1
- 5-Hydroxy-2-pyrrolidinone
Catalog No.:BCN4155
CAS No.:62312-55-4
- Rutaevin 7-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7991
CAS No.:62306-81-4
- H-Tyr(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3133
CAS No.:6230-11-1
- H-Gly-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2950
CAS No.:623-33-6
- 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4154
CAS No.:623-05-2
- Desmopressin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1526
CAS No.:62288-83-9
- (-)-p-Bromotetramisole Oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5449
CAS No.:62284-79-1
- Ponceau S Staining Solution
Catalog No.:BCC8032
CAS No.:6226-79-5
- JLK 6
Catalog No.:BCC2343
CAS No.:62252-26-0
- 1-Hydroxy-9-medroxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3103
CAS No.:622408-85-9
- H-Glu(OtBu)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2935
CAS No.:6234-01-1
- Oxyntomodulin
Catalog No.:BCC5874
CAS No.:62340-29-8
- Isotschimgin
Catalog No.:BCN4156
CAS No.:62356-47-2
- Arjunglucoside II
Catalog No.:BCN6395
CAS No.:62369-72-6
- Kadsuric acid
Catalog No.:BCN4157
CAS No.:62393-88-8
- Alboctalol
Catalog No.:BCN4158
CAS No.:62394-00-7
- Cinnzeylanol
Catalog No.:BCN4159
CAS No.:62394-04-1
- Methyl levulinate
Catalog No.:BCN4160
CAS No.:624-45-3
- Dimethyl Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4776
CAS No.:624-49-7
- Ursonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4161
CAS No.:6246-46-4
- p-Vinylphenyl O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1393
CAS No.:62470-46-6
- MK-0812
Catalog No.:BCC1755
CAS No.:624733-88-6
Natural lignans from Arctium lappa modulate P-glycoprotein efflux function in multidrug resistant cancer cells.[Pubmed:25765837]
Phytomedicine. 2015 Feb 15;22(2):301-7.
Arctium lappa is a well-known traditional medicinal plant in China (TCM) and Europe that has been used for thousands of years to treat arthritis, baldness or cancer. The plant produces lignans as secondary metabolites which have a wide range of bioactivities. Yet, their ability to reverse multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells has not been explored. In this study, we isolated six lignans from A. lappa seeds, namely arctigenin, matairesinol, arctiin, (iso)Lappaol A, lappaol C, and lappaol F. The MDR reversal potential of the isolated lignans and the underlying mechanism of action were studied using two MDR cancer cell lines, CaCo2 and CEM/ADR 5000 which overexpress P-gp and other ABC transporters. In two-drug combinations of lignans with the cytotoxic doxorubicin, all lignans exhibited synergistic effects in CaCo2 cells and matairesinol, arctiin, lappaol C and lappaol F display synergistic activity in CEM/ADR 5000 cells. Additionally, in three-drug combinations of lignans with the saponin digitonin and doxorubicin MDR reversal activity was even stronger enhanced. The lignans can increase the retention of the P-gp substrate rhodamine 123 in CEM/ADR 5000 cells, indicating that lignans can inhibit the activity of P-gp. Our study provides a first insight into the potential chemosensitizing activity of a series of natural lignans, which might be candidates for developing novel adjuvant anticancer agents.
Natural lignans from Arctium lappa as antiaging agents in Caenorhabditis elegans.[Pubmed:26141518]
Phytochemistry. 2015 Sep;117:340-350.
Arctium lappa is a well-known traditional medicinal plant in China (TCM) and Europe that has been used for thousands of years to treat arthritis, baldness or cancer. The plant produces lignans as secondary metabolites, which have a wide range of bioactivities. Yet, their antiaging potential has not been explored. In this study, we isolated six lignans from A. lappa seeds, namely arctigenin, matairesinol, arctiin, (iso)Lappaol A, lappaol C, and lappaol F. The antioxidant and antiaging properties of the isolated lignans were studied using Caenorhabditis elegans as a relevant animal model. All lignans at concentrations of 10 and 100 muM significantly extended the mean life span of C. elegans. The strongest effect was observed with matairesinol, which at a concentration of 100 muM extended the life span of worms by 25%. Additionally, we observed that five lignans are strong free radical-scavengers in vitro and in vivo and all lignans can improve survival of C. elegans under oxidative stress. Furthermore, the lignans can induce the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor DAF-16 and up-regulate its expression, suggesting that a possible underlying mechanism of the observed longevity-promoting activity of lignans depends on DAF-16 mediated signaling pathway. All lignans up-regulated the expression of jnk-1, indicating that lignans may promote the C. elegans longevity and stress resistance through a JNK-1-DAF-16 cascade. Our study reports new antiaging activities of lignans, which might be candidates for developing antiaging agents.
Sesquiterpenes, lignans and other constituents from Saussurea macrota.[Pubmed:15638090]
Pharmazie. 2004 Dec;59(12):972-6.
From the methanol extract of the whole plant of Saussurea macrota Franch, 21 compounds were isolated. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and X-ray crystallography. Two of them are new: 3alpha-hydroxy-11alphaH-guaia-4(15),10(14)-diene-12,6alpha-olide (1) and 7'-hydroxyiso-Lappaol A (11). Compound 2 is reported as a natural compound for the first time. In addition, the compounds 12 and 13 showed significant antitumor activity against Bel-7402 and HO-8910 cells. Some of the compounds exhibited weak antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli.
Americanin, a bioactive dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, from the seeds of Centaurea americana.[Pubmed:16996096]
Phytochemistry. 2006 Nov;67(21):2370-5.
The reversed-phase preparative HPLC analysis of the methanol (MeOH) extract of the seeds of Centaurea americana afforded a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, 3''-O-caffeoyl arctiin (named americanin), together with five known lignans, arctiin, arctigenin, matairesinol, matairesinoside and Lappaol A, and two known phytoecdysteroids, 20-hydroxyecdysone and makisterone A. While the structures of the known compounds were determined by direct comparison of the spectral data with published data, the structure of americanin was elucidated by UV, MS and a combination of 1D and 2D NMR spectral analyses. The antioxidant properties and toxicity of the extracts and the isolated compounds were determined by the DPPH and the brine shrimp lethality assays, respectively.
Anti-austeric activity of phenolic constituents of seeds of Arctium lappa.[Pubmed:23738454]
Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Apr;8(4):463-6.
From seeds of Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) we obtained arctigenin (1), arctiin (2), chlorogenic acid (3), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (4), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6), matairesinol (11), isoLappaol A (12), lappaol F (14), and lappaol B (15), together with 1:1 mixtures of isolappaol C (7) and lappaol C (8), arctignan E (9) and arctignan D (10), and 12 and Lappaol A (13), while 3,3',4'-tri-O-demethylarctigenin (16), 3,3'-di-O-demethyl-4'-dehydroxyarctigenin (17), and 3-O-demethylarctigenin (18) were obtained by anaerobic microbiological metabolism of 1. Then, we evaluated the in vitro preferential cytotoxic activity of these pure compounds and 1:1 mixtures, together with enterodiol (19) and enterolactone (20), against human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells in nutrient-deprived medium (NDM). Among them, 1 and 18 showed potent activity, with PC50 values of 1.75 and 4.38 microM, respectively, while 11, 15, and 17 showed mild activity with PC50 values of 31.1, 30.9, and 38.7 microM, respectively. By comparing their structures and PC50 values, the following structural moieties could be concluded to be important for the preferential cytotoxicity of 1: 1) the 3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl group at the 2-position on the gamma-butyrolactone ring, 2) the less polar substituent at the 3-position on the gamma-butyrolactone ring, and 3) the gamma-butyrolactone ring.


