Ursonic acidCAS# 6246-46-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6246-46-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6454401 | Appearance | Powder |
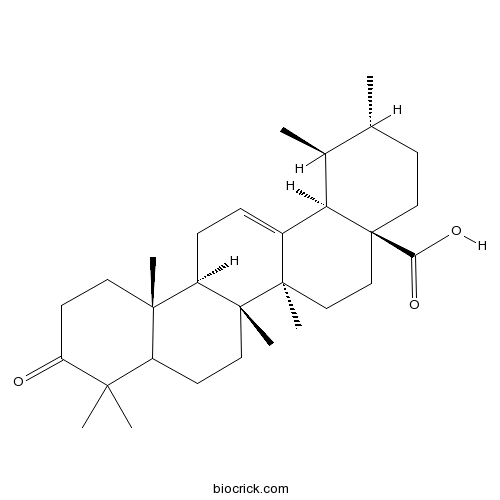
| Formula | C30H46O3 | M.Wt | 454.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 3-Ketoursolic acid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 10 mg/mL (21.99 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | (1S,2R,4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,12aR,14bR)-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-10-oxo-1,2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CCC(=O)C5(C)C)C)C)C2C1C)C)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MUCRYNWJQNHDJH-LWIALTINSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H46O3/c1-18-10-15-30(25(32)33)17-16-28(6)20(24(30)19(18)2)8-9-22-27(5)13-12-23(31)26(3,4)21(27)11-14-29(22,28)7/h8,18-19,21-22,24H,9-17H2,1-7H3,(H,32,33)/t18-,19+,21?,22-,24-,27+,28-,29-,30+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ursolic acid, a naturally occurring triterpenoid, induces the apoptosis of human cancer cells through multiple signaling pathways. Ursonic acid has antiviral activity against Herpes simplex virus types I and II in vitro; it also could be used in preparation of depression treatment medicine. |
| Targets | HIV |
| In vitro | Virtual Screening of Indonesian Herbal Database as HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor.[Pubmed: 24616554]Bioinformation. 2014 Feb 19;10(2):52-5.
HIV-1 (Human immunodeficiency virus type 1)׳s infection is considered as one of most harmful disease known by human, the survivability rate of the host reduced significantly when it developed into AIDS. HIV drug resistance is one of the main problems of its treatment and several drug designs have been done to find new leads compound as the cure.
|
| Cell Research | Cytotoxic triterpenes from the aerial roots of Ficus microcarpa.[Pubmed: 15694457 ]Phytochemistry. 2005 Feb;66(4):495-501.Six triterpenes, 3beta-acetoxy-12,19-dioxo-13(18)-oleanene (1), 3beta-acetoxy-19(29)-taraxasten-20alpha-ol (2), 3beta-acetoxy-21alpha,22alpha-epoxytaraxastan-20alpha-ol (3), 3,22-dioxo-20-taraxastene (4), 3beta-acetoxy-11alpha,12alpha-epoxy-16-oxo-14-taraxerene (5), 3beta-acetoxy-25-methoxylanosta-8,23-diene (6) along with nine known triterpenes, 3beta-acetoxy-11alpha,12alpha-epoxy-14-taraxerene (7), 3beta-acetoxy-25-hydroxylanosta-8,23-diene (8), oleanonic acid (9), acetylbetulinic acid (10), betulonic acid (11), acetylursolic acid (12), Ursonic acid (13), ursolic acid (14), and 3-oxofriedelan-28-oic acid (15) were isolated from the aerial roots of Ficus microcarpa, and their structures elucidated by spectroscopic methods. |
| Structure Identification | Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(7):628-32.Two new labdane diterpenoids from the rhizomes of Isodon yuennanensis.[Pubmed: 25420949]
|

Ursonic acid Dilution Calculator

Ursonic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1993 mL | 10.9963 mL | 21.9925 mL | 43.985 mL | 54.9813 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4399 mL | 2.1993 mL | 4.3985 mL | 8.797 mL | 10.9963 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2199 mL | 1.0996 mL | 2.1993 mL | 4.3985 mL | 5.4981 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.2199 mL | 0.4399 mL | 0.8797 mL | 1.0996 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.022 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.2199 mL | 0.4399 mL | 0.5498 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ursolic acid, a naturally occurring triterpenoid, induces the apoptosis of human cancer cells through multiple signaling pathways. In vitro: Ursolic acid is important in the induction of apoptosis via AKT/NF-κB signaling suppression in T24 human bladder cancer cells and this occurs in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, Akt and NF-κB are potential targets for bladder cancer therapy and ursolic acid may serve as a naturally-occurring candidate drug for the prevention and treatment of bladder cancer.[1] Ursolic acid induce apoptosis via inhibition of NF-κB induced BCl-2 mediated anti-apoptotic pathway leading to activation of p53 induced and caspase-3 mediated pro-apoptotic pathways.[2] In vivo: UA significantly suppressed prostate tumor growth in nude mice without any significant decrease in body weight. The systemic bioavailability of UA in serum samples obtained from nude mice. UA was detected in all serum samples 24 h after last injection. Systemic bioavailability of UA was in nanogram range and metabolites of UA were not detected in the samples. These results indicate that UA is well absorbed in the mouse peritoneum and supports the role of UA as a potent compound for chemoprevention and therapy of prostate cancer. [3]
References:
[1]. Gai, L., Cai, N., Wang, L., Xu, X. & Kong, X. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis via Akt/NF-kappaB signaling suppression in T24 human bladder cancer cells. Molecular medicine reports 7, 1673-1677, doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1364 (2013).
[2]. Manu, K. A. & Kuttan, G. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis by activating p53 and caspase-3 gene expressions and suppressing NF-kappaB mediated activation of bcl-2 in B16F-10 melanoma cells. International immunopharmacology 8, 974-981, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2008.02.013 (2008).
[3]. Shanmugam, M. K. et al. Ursolic acid inhibits multiple cell survival pathways leading to suppression of growth of prostate cancer xenograft in nude mice. Journal of molecular medicine 89, 713-727, doi:10.1007/s00109-011-0746-2 (2011).
- Dimethyl Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4776
CAS No.:624-49-7
- Methyl levulinate
Catalog No.:BCN4160
CAS No.:624-45-3
- Cinnzeylanol
Catalog No.:BCN4159
CAS No.:62394-04-1
- Alboctalol
Catalog No.:BCN4158
CAS No.:62394-00-7
- Kadsuric acid
Catalog No.:BCN4157
CAS No.:62393-88-8
- Arjunglucoside II
Catalog No.:BCN6395
CAS No.:62369-72-6
- Isotschimgin
Catalog No.:BCN4156
CAS No.:62356-47-2
- Oxyntomodulin
Catalog No.:BCC5874
CAS No.:62340-29-8
- H-Glu(OtBu)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2935
CAS No.:6234-01-1
- Lappaol A
Catalog No.:BCN8280
CAS No.:62333-08-8
- Arjunglucoside I
Catalog No.:BCN8259
CAS No.:62319-70-4
- Ki20227
Catalog No.:BCC1678
CAS No.:623142-96-1
- p-Vinylphenyl O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1393
CAS No.:62470-46-6
- MK-0812
Catalog No.:BCC1755
CAS No.:624733-88-6
- 3-O-Acetyloleanderolide
Catalog No.:BCN4162
CAS No.:62498-83-3
- 23-O-Acetylshengmanol 3-O-beta-D-xyloside
Catalog No.:BCN7947
CAS No.:62498-88-8
- Gastrodin
Catalog No.:BCN6306
CAS No.:62499-27-8
- Parishin A
Catalog No.:BCN3811
CAS No.:62499-28-9
- Isodihydrofutoquinol B
Catalog No.:BCN6690
CAS No.:62499-71-2
- 4-Amino-4-methyl-2-pentanone
Catalog No.:BCN1772
CAS No.:625-04-7
- 3-Hydroxybutyric acid
Catalog No.:BCN2212
CAS No.:625-71-8
- Viniferol D
Catalog No.:BCN4164
CAS No.:625096-18-6
- Riociguat
Catalog No.:BCC1899
CAS No.:625115-55-1
- Ethyl p-hydroxyphenyllactate
Catalog No.:BCN6654
CAS No.:62517-34-4
Two new labdane diterpenoids from the rhizomes of Isodon yuennanensis.[Pubmed:25420949]
Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(7):628-32.
Two new labdane diterpenoids, s-trans-8(17),12E,14-labdatrien-20-oic acid (1), s-trans-12E,14-labdadien-20,8beta-olide (2), along with 10 known compounds, hinokiol (3), Ursonic acid (4), 2alpha,3alpha-dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (5), 2alpha,3beta,23-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (6), ethyl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate (7), ethyl rosmarinate (8), (Z,E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl caffeic ester (9), tridecanoic acid (10), beta-sitosterol (11) and daucosterol (12), were isolated from the 70% acetone extract of the rhizomes of Isodon yuennanensis. Their structures were elucidated based on the analyses of extensive spectroscopic data and physicochemical properties.
Cytotoxic triterpenes from the aerial roots of Ficus microcarpa.[Pubmed:15694457]
Phytochemistry. 2005 Feb;66(4):495-501.
Six triterpenes, 3beta-acetoxy-12,19-dioxo-13(18)-oleanene (1), 3beta-acetoxy-19(29)-taraxasten-20alpha-ol (2), 3beta-acetoxy-21alpha,22alpha-epoxytaraxastan-20alpha-ol (3), 3,22-dioxo-20-taraxastene (4), 3beta-acetoxy-11alpha,12alpha-epoxy-16-oxo-14-taraxerene (5), 3beta-acetoxy-25-methoxylanosta-8,23-diene (6) along with nine known triterpenes, 3beta-acetoxy-11alpha,12alpha-epoxy-14-taraxerene (7), 3beta-acetoxy-25-hydroxylanosta-8,23-diene (8), oleanonic acid (9), acetylbetulinic acid (10), betulonic acid (11), acetylursolic acid (12), Ursonic acid (13), ursolic acid (14), and 3-oxofriedelan-28-oic acid (15) were isolated from the aerial roots of Ficus microcarpa, and their structures elucidated by spectroscopic methods. The in vitro cytotoxic efficacy of these triterpenes was investigated using three human cancer cell lines, namely, HONE-1 nasopharyngeal carcinoma, KB oral epidermoid carcinoma, and HT29 colorectal carcinoma cells. Compound 8 and pentacyclic triterpenes 9-15 possessing a carboxylic acid functionality at C-28 showed significant cytotoxic activities against the aforementioned cell lines and gave IC50 values in the range 4.0-9.4 microM.
Virtual Screening of Indonesian Herbal Database as HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor.[Pubmed:24616554]
Bioinformation. 2014 Feb 19;10(2):52-5.
HIV-1 (Human immunodeficiency virus type 1)s infection is considered as one of most harmful disease known by human, the survivability rate of the host reduced significantly when it developed into AIDS. HIV drug resistance is one of the main problems of its treatment and several drug designs have been done to find new leads compound as the cure. In this study, in silico virtual screening approach was used to find lead molecules from the library or database of natural compounds as HIV-1 protease inhibitor. Virtual screening against Indonesian Herbal Database with AutoDock was performed on HIV-1 protease. From the virtual screening, top ten compounds obtained were 8-Hydroxyapigenin 8-(2",4"-disulfatoglucuronide), Isoscutellarein 4'-methyl ether, Amaranthin, Torvanol A, Ursonic acid, 5-Carboxypyranocyanidin 3-O-(6"-O-malonyl-beta-glucopyranoside), Oleoside, Jacoumaric acid, Platanic acid and 5-Carboxypyranocyanidin 3-O-beta-glucopyranoside.


