beta-Lipoic acidCAS# 6992-30-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6992-30-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5319044 | Appearance | Powder |
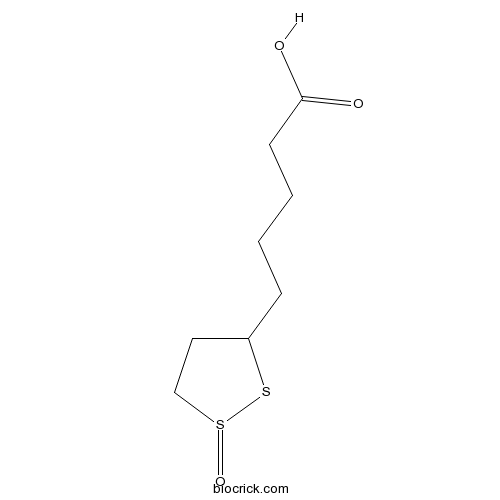
| Formula | C8H14O3S2 | M.Wt | 222.32 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Protogen-B;5-(1-oxodithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-(1-oxodithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CS(=O)SC1CCCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HRIQWEOKIFSCBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H14O3S2/c9-8(10)4-2-1-3-7-5-6-13(11)12-7/h7H,1-6H2,(H,9,10) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

beta-Lipoic acid Dilution Calculator

beta-Lipoic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.498 mL | 22.4901 mL | 44.9802 mL | 89.9604 mL | 112.4505 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8996 mL | 4.498 mL | 8.996 mL | 17.9921 mL | 22.4901 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4498 mL | 2.249 mL | 4.498 mL | 8.996 mL | 11.2451 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.09 mL | 0.4498 mL | 0.8996 mL | 1.7992 mL | 2.249 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.045 mL | 0.2249 mL | 0.4498 mL | 0.8996 mL | 1.1245 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Merucathine
Catalog No.:BCN1782
CAS No.:107673-74-5
- Bulleyaconitine A
Catalog No.:BCN1210
CAS No.:107668-79-1
- Merucathinone
Catalog No.:BCN1783
CAS No.:107638-80-2
- Erycibelline
Catalog No.:BCN1876
CAS No.:107633-95-4
- Dehydroformouregine
Catalog No.:BCN4054
CAS No.:107633-69-2
- PF 998425
Catalog No.:BCC7811
CAS No.:1076225-27-8
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN2561
CAS No.:1076-38-6
- 4-Demethyl-3,9-dihydroeucomin
Catalog No.:BCN5876
CAS No.:107585-77-3
- 3'-Hydroxy-3,9-dihydroeucomin
Catalog No.:BCN5875
CAS No.:107585-75-1
- Anwulignan
Catalog No.:BCN5362
CAS No.:107534-93-0
- Omadacycline tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC5136
CAS No.:1075240-43-5
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC7258
CAS No.:107444-51-9
- MDL 11,939
Catalog No.:BCC6822
CAS No.:107703-78-6
- Epleremone
Catalog No.:BCC3776
CAS No.:107724-20-9
- Methyl 7beta,15-dihydroxydehydroabietate
Catalog No.:BCN7270
CAS No.:107752-10-3
- Zafirlukast
Catalog No.:BCC4881
CAS No.:107753-78-6
- A 61603 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6912
CAS No.:107756-30-9
- Coccinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5877
CAS No.:107783-45-9
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzenepropanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8500
CAS No.:1078-61-1
- PF 04418948
Catalog No.:BCC6299
CAS No.:1078166-57-0
- Exemestane
Catalog No.:BCC1061
CAS No.:107868-30-4
- Quinovin
Catalog No.:BCN5878
CAS No.:107870-05-3
- Dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7707
CAS No.:107870-88-2
- Japonicones D
Catalog No.:BCN3614
CAS No.:1078711-42-8
Lipoic acid favors thiolsulfinate formation after hypochlorous acid scavenging: a study with lipoic acid derivatives.[Pubmed:8031117]
Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Jul;312(1):114-20.
Lipoic acid, the oxidized form of 6,8-dimercapto-octanoic acid has a strained cyclic disulfide in a 1,2-dithiolane ring. Recently its antioxidant activity gained attention. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is an oxidant produced by neutrophils. A prominent effect of HOCl is the inactivation of alpha-1-antiproteinase. Due to this inactivation, the ability of alpha-1-antiproteinase to inhibit elastase is lost. The resulting higher activity of elastase is held responsible for tissue damage in lung emphysema. We studied the HOCl scavenging capability of three metabolites of lipoic acid: tetranor-, bisnor-, and beta-Lipoic acid. To obtain some insight on the molecular basis of HOCl scavenging 1,2-dithiane-4,5-diol, cystine, lipoic acid methyl ester, and lipoamide were also included in the study. The extent of alpha-1-antiproteinase inactivation by HOCl in the presence of scavenger was taken as a parameter to quantify the scavenging activity. It was found that lipoic acid, tetranor- and bisnorlipoic acid, lipoic acid methyl ester, and lipoamide all showed the same activity toward HOCl. beta-Lipoic acid, 1,2-dithiane-4,5-diol and cystine were less active. The products of lipoic acid after reaction with HOCl were studied using GC/MS. Indications for thiolsulfinate formation were found by comparing these products with the GC/MS profile of beta-Lipoic acid. Thiolsulfinate formation may also be suggested in the reaction of tetranor- and bisnorlipoic acid and lipoic acid methyl ester with HOCl. The present results show an antioxidant activity of the metabolites tetranor- and bisnorlipoic acid. The 1,2-dithiolane ring may enhance the reactivity toward HOCl compared to less strained disulfides, resulting in the formation a thiolsulfinate.


