Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide (human, rat)Potent insulinotropic peptide CAS# 107444-51-9 |
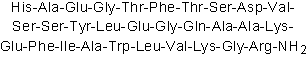
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 107444-51-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16133831 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C149H226N40O45 | M.Wt | 3297.67 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GLP-1 (7-36) amide | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | HAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIAWLVKGR (Modifications: Arg-30 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CNC=N6)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DTHNMHAUYICORS-KTKZVXAJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C149H226N40O45/c1-17-76(10)119(146(232)167-80(14)126(212)175-104(60-86-63-159-91-36-25-24-35-89(86)91)136(222)177-100(56-73(4)5)137(223)186-117(74(6)7)144(230)174-93(37-26-28-52-150)128(214)160-65-110(197)168-92(122(154)208)39-30-54-158-149(155)156)188-138(224)102(57-83-31-20-18-21-32-83)178-133(219)98(47-51-115(204)205)173-132(218)94(38-27-29-53-151)170-124(210)78(12)164-123(209)77(11)166-131(217)97(44-48-109(153)196)169-111(198)66-161-130(216)96(46-50-114(202)203)172-134(220)99(55-72(2)3)176-135(221)101(59-85-40-42-88(195)43-41-85)179-141(227)106(68-190)182-143(229)108(70-192)183-145(231)118(75(8)9)187-140(226)105(62-116(206)207)180-142(228)107(69-191)184-148(234)121(82(16)194)189-139(225)103(58-84-33-22-19-23-34-84)181-147(233)120(81(15)193)185-112(199)67-162-129(215)95(45-49-113(200)201)171-125(211)79(13)165-127(213)90(152)61-87-64-157-71-163-87/h18-25,31-36,40-43,63-64,71-82,90,92-108,117-121,159,190-195H,17,26-30,37-39,44-62,65-70,150-152H2,1-16H3,(H2,153,196)(H2,154,208)(H,157,163)(H,160,214)(H,161,216)(H,162,215)(H,164,209)(H,165,213)(H,166,217)(H,167,232)(H,168,197)(H,169,198)(H,170,210)(H,171,211)(H,172,220)(H,173,218)(H,174,230)(H,175,212)(H,176,221)(H,177,222)(H,178,219)(H,179,227)(H,180,228)(H,181,233)(H,182,229)(H,183,231)(H,184,234)(H,185,199)(H,186,223)(H,187,226)(H,188,224)(H,189,225)(H,200,201)(H,202,203)(H,204,205)(H,206,207)(H4,155,156,158)/t76-,77-,78-,79-,80-,81+,82+,90-,92-,93-,94-,95-,96-,97-,98-,99-,100-,101-,102-,103-,104-,105-,106-,107-,108-,117-,118-,119-,120-,121-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide produced by post-translational processing of proglucagon in intestinal L-cells. Displays high affinity for GLP-1 receptors expressed in rat insulinoma-derived RINm5F cells (Kd = 204 pM). Stimulates insulin gene transcription and secretion in pancreatic β-cells. Displays antiapoptotic effects in hippocampal neurons and reduces food intake in fasted rats following central administration. |

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide (human, rat) Dilution Calculator

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide (human, rat) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Bisabola-2,10-diene-1,9-dione
Catalog No.:BCN7269
CAS No.:107439-25-8
- Ginkgolide J
Catalog No.:BCN5939
CAS No.:107438-79-9
- CD 1530
Catalog No.:BCC7406
CAS No.:107430-66-0
- Garcinone D
Catalog No.:BCN2526
CAS No.:107390-08-9
- Cleroindicin B
Catalog No.:BCN5874
CAS No.:107389-91-3
- LDC000067
Catalog No.:BCC5452
CAS No.:1073485-20-7
- Demethylzeylasteral
Catalog No.:BCN2282
CAS No.:107316-88-1
- Defactinib
Catalog No.:BCC5494
CAS No.:1073154-85-4
- SR-3677
Catalog No.:BCC4302
CAS No.:1072959-67-1
- MLN2238
Catalog No.:BCC2092
CAS No.:1072833-77-2
- Carasinol D
Catalog No.:BCN8228
CAS No.:1072797-66-0
- Baogongteng C
Catalog No.:BCN1873
CAS No.:107259-50-7
- Omadacycline tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC5136
CAS No.:1075240-43-5
- Anwulignan
Catalog No.:BCN5362
CAS No.:107534-93-0
- 3'-Hydroxy-3,9-dihydroeucomin
Catalog No.:BCN5875
CAS No.:107585-75-1
- 4-Demethyl-3,9-dihydroeucomin
Catalog No.:BCN5876
CAS No.:107585-77-3
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN2561
CAS No.:1076-38-6
- PF 998425
Catalog No.:BCC7811
CAS No.:1076225-27-8
- Dehydroformouregine
Catalog No.:BCN4054
CAS No.:107633-69-2
- Erycibelline
Catalog No.:BCN1876
CAS No.:107633-95-4
- Merucathinone
Catalog No.:BCN1783
CAS No.:107638-80-2
- Bulleyaconitine A
Catalog No.:BCN1210
CAS No.:107668-79-1
- Merucathine
Catalog No.:BCN1782
CAS No.:107673-74-5
- beta-Lipoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9198
CAS No.:6992-30-9
Protection and reversal of excitotoxic neuronal damage by glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendin-4.[Pubmed:12183643]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Sep;302(3):881-8.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36)-amide (GLP-1) is an endogenous insulinotropic peptide that is secreted from the L cells of the gastrointestinal tract in response to food. It has potent effects on glucose-dependent insulin secretion, insulin gene expression, and pancreatic islet cell formation. In type 2 diabetes, GLP-1, by continuous infusion, can normalize blood glucose and is presently being tested in clinical trials as a therapy for this disease. More recently, GLP-1 has been found to have central nervous system (CNS) effects and to stimulate neurite outgrowth in cultured cells. We now report that GLP-1, and its longer-acting analog exendin-4, can completely protect cultured rat hippocampal neurons against glutamate-induced apoptosis. Extrapolating these effects to a well defined rodent model of neurodegeneration, GLP-1 and exendin-4 greatly reduced ibotenic acid-induced depletion of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. These findings identify a novel neuroprotective/neurotrophic function of GLP-1 and suggest that such peptides may have potential for halting or reversing neurodegenerative processes in CNS disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, and in neuropathies associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Glucagon-like peptide-1: a major regulator of pancreatic beta-cell function.[Pubmed:11124853]
Eur J Endocrinol. 2000 Dec;143(6):717-25.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a gut hormone synthesized by post-translational processing in intestinal L-cells, and it is released in response to food ingestion. GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion during hyperglycemia, suppresses glucagon secretion, stimulates (pro)-insulin biosynthesis and decreases the rate of gastric emptying and acid secretion. GLP-1 has also been shown to have a pro-satiety effect. In addition, it has been demonstrated that a long-term infusion with GLP-1, or exendin-4, a long-acting analog of human GLP-1, increases beta-cell mass in rats. In conclusion, GLP-1 appears to regulate plasma glucose levels via various and independent mechanisms. GLP-1 is an excellent candidate option for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding.[Pubmed:8538742]
Nature. 1996 Jan 4;379(6560):69-72.
The sequence of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide (GLP-1) is completely conserved in all mammalian species studied, implying that it plays a critical physiological role. We have shown that GLP-1 and its specific receptors are present in the hypothalamus. No physiological role for central GLP-1 has been established. We report here that intracerebroventricular (ICV) GLP-1 powerfully inhibits feeding in fasted rats. ICV injection of the specific GLP-1-receptor antagonist, exendin (9-39), blocked the inhibitory effect of GLP-1 on food intake. Exendin (9-39) alone had no influence on fast-induced feeding but more than doubled food intake in satiated rats, and augmented the feeding response to the appetite stimulant, neuropeptide Y. Induction of c-fos is a marker of neuronal activation. Following ICV GLP-1 injection, c-fos appeared exclusively in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and central nucleus of the amygdala, and this was inhibited by prior administration of exendin (9-39). Both of these regions of the brain are of primary importance in the regulation of feeding. These findings suggest that central GLP-1 is a new physiological mediator of satiety.
Receptors for glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36) amide on rat insulinoma-derived cells.[Pubmed:2832504]
J Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;116(3):357-62.
Specific binding of 125I-labelled glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide (GLP-1(7-36)amide) to rat insulinoma-derived RINm5F cells was dependent upon time and temperature and was proportional to cell concentration. Binding of radioactivity was inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner by GLP-1(7-36) amide consistent with the presence of a single class of binding site with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 204 +/- 8 pmol/l (mean +/- S.E.M.). Binding of the peptide resulted in a dose-dependent increase in cyclic AMP concentrations (half maximal response at 250 +/- 20 pmol/l). GLP-1(1-36)amide was approximately 200 times less potent than GLP-1(7-36)amide in inhibiting the binding of 125I-labelled GLP-1(7-36)amide to the cells (Kd of 45 +/- 6 nmol/l). Binding sites for GLP-1 (7-36)amide were not present on dispersed enterocytes from porcine small intestine.


