MesnaChemotherapy adjuvant;potential antioxidant CAS# 19767-45-4 |
- Cefoselis
Catalog No.:BCC4092
CAS No.:122841-10-5
- Cefoselis Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4769
CAS No.:122841-12-7
- Balofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4892
CAS No.:127294-70-6
- Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5089
CAS No.:149676-40-4
- Toltrazuril
Catalog No.:BCC4870
CAS No.:69004-03-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19767-45-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23662354 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C2H5NaO3S2 | M.Wt | 164.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate; Mesnum | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (304.54 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
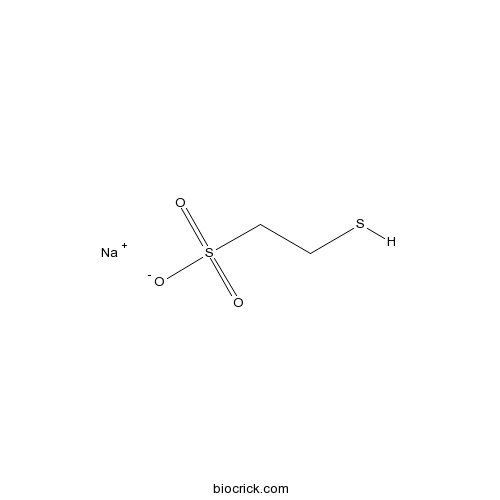
| Chemical Name | sodium;2-sulfanylethanesulfonate | ||
| SMILES | C(CS(=O)(=O)[O-])S.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XOGTZOOQQBDUSI-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C2H6O3S2.Na/c3-7(4,5)2-1-6;/h6H,1-2H2,(H,3,4,5);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 2-mercaptoethane sulfonate (Mesna), is a synthetic small molecule, widely used as a systemic protective agent against chemotherapy toxicity, but is primarily used to reduce hemorrhagic cystitis induced by cyclophosphamide.
IC50 Value: 182 mM (decreased superoxide anion production stimulated with PMA (tetradecanoylphorbol acetate) in PMN in-vitro); 70mM (inhibited H2O2 production) [3]
Target:
in vitro: MESNA had no effect on the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the indicated processes in both the types of the doxorubicin sensitive cells. The combined use of doxorubicin and phosphamide or cyclophosphane the use of MESNA for lowering the urotoxic action of oxazophosphorines had no effect on the biological efficacy of doxorubicin [4].
in vivo: AMH-positive follicles were significantly decreased after cisplatin administration, which was significantly reversed when mesna was co-administered with cisplatin. The end product of lipid peroxidation, malondialdehyde (MDA), was significantly increased, but the anti-oxidative enzymatic activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) were significantly decreased in cisplatin groups when compared with NS group. In contrast, after co-administration of cisplatin with mesna, MDA was significantly decreased whereas the activity of SOD and the concentration of GSH were increased. Moreover, mesna did not decrease the anti-tumor property of cisplatin in HePG2 cell lines [2]. After head trauma, tissue malondialdehyde levels increased; these levels were significantly decreased by MESNA administration. Caspase-3 levels were increased after trauma, but no effect of MESNA was determined in caspase-3 activity [1].
Clinical trial: Effects of Mesna on Homocysteine in Kidney Failure . Phase2 References: | |||||

Mesna Dilution Calculator

Mesna Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0909 mL | 30.4544 mL | 60.9088 mL | 121.8175 mL | 152.2719 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2182 mL | 6.0909 mL | 12.1818 mL | 24.3635 mL | 30.4544 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6091 mL | 3.0454 mL | 6.0909 mL | 12.1818 mL | 15.2272 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1218 mL | 0.6091 mL | 1.2182 mL | 2.4364 mL | 3.0454 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.6091 mL | 1.2182 mL | 1.5227 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Mesna reacts with acrolein and other urotoxic metabolites of oxazaphosphorines (cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide) to form stable, non-urotoxic compounds. Mesna does not have any antitumor activity.
- Tigecycline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4228
CAS No.:197654-04-9
- Fmoc-N-Me-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3353
CAS No.:197632-77-2
- Fmoc-D-β-HomoTrp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2624
CAS No.:197632-75-1
- Fmoc-β-HomoTrp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2625
CAS No.:197632-75-0
- Calystegine B5
Catalog No.:BCN1883
CAS No.:197565-91-6
- Calystegine A7
Catalog No.:BCN1885
CAS No.:197565-90-5
- TRAM 39
Catalog No.:BCC8038
CAS No.:197525-99-8
- 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8580
CAS No.:1975-51-5
- Boc-Cys(Acm)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3374
CAS No.:19746-37-3
- Latisxanthone C
Catalog No.:BCN7346
CAS No.:197447-32-8
- Isocudraniaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7426
CAS No.:197447-26-0
- (2RS)-Lotaustralin
Catalog No.:BCN7848
CAS No.:1973415-50-7
- Loxapine
Catalog No.:BCC4026
CAS No.:1977-10-2
- Ajugatakasins A
Catalog No.:BCN3661
CAS No.:197723-20-9
- Peimisine
Catalog No.:BCN4992
CAS No.:19773-24-1
- Amiodarone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4377
CAS No.:19774-82-4
- Daphmacrine
Catalog No.:BCN4868
CAS No.:19775-48-5
- Bonducellpin C
Catalog No.:BCN7647
CAS No.:197781-84-3
- Bonducellpin D
Catalog No.:BCN7544
CAS No.:197781-85-4
- 7-O-Acetylbonducellpin C
Catalog No.:BCN7558
CAS No.:197781-86-5
- TFLLR-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3948
CAS No.:197794-83-5
- SN 003
Catalog No.:BCC7633
CAS No.:197801-88-0
- Stachartin A
Catalog No.:BCN6974
CAS No.:1978388-54-3
- Stachartin B
Catalog No.:BCN6973
CAS No.:1978388-55-4
Effect of Submucosal Mesna Application on Mucoperichondrial Elevation in Septoplasty.[Pubmed:27997451]
J Craniofac Surg. 2017 Jan;28(1):e94-e96.
OBJECTIVE: It was revealed that the thiol compound named Mesna chemically softens the connective tissue with submucosal injection, and facilitates the endoscopic submucosal dissection. The authors aimed to investigate the effect of Mesna injection on mucoperichondrial elevation during septoplasty operation. METHODS: This study was planned as a patient-control study and performed. Fifty-six patients who had septoplasty operation were divided into 2 groups that are submucosal Mesna (group 1) and submucosal saline (group 2) applied ones. In both groups, the measurement was initiated by a timer during the start of septal incision and elevation processes. After bilateral subperichondrial and subperiostal elevation were finished, timer was stopped and time was recorded. After that, mucosal integrity was reviewed and mucosal damage status was recorded. The difficulty of mucoperichondrial elevation for the surgeon was recorded for each patient. RESULTS: Twenty-five (44.7%) of the patients who participated in our study were females while 31 (55.3%) were males. The average elevation periods were 201.4 +/- 74.3 seconds in group 1 and 260.2 +/- 84.1 seconds in group 2. In Mesna applied patients, elevation period was statistically and significantly shorter (P = 0.009). Impairment in mucosal integrity was observed as 33.3% in group 1 and 58.8% in group 2. In Mesna applied patients, significantly less impairment in mucosal integrity was observed (P = 0.031). The average mucoperichondrial elevation difficulty for the surgeon is observed as 4.83 +/- 2.47 in group 1 and 6.5 +/- 1.9 in group 2. Mesna applied patients were defined as significantly easier patients for the surgeon (P = 0.006). CONCLUSION: Submucosal Mesna application is an approach that provides a convenient, fast, and effective mucoperichondrial elevation in septoplasty and protects the mucosal integrity.
Single dose intratympanic mesna application inhibits propylene glycol induced cholesteatoma formation.[Pubmed:27995828]
J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Mar;131(3):215-220.
OBJECTIVE: Mesna (i.e. sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate; C2H5NaO3S2) has been used in otological surgery such as cholesteatoma dissection and tympanic membrane lateralisation in atelectatic ears. However, this study aimed to investigate its effect on cholesteatoma formation. METHODS: A total of 20 Wistar rats were divided into two groups of 10 animals. The right and left ears of control animals were treated with saline (saline control group; n = 10 ears) and propylene glycol plus saline (propylene glycol control group; n = 10 ears), respectively. In the Mesna group, both ears were treated with propylene glycol plus Mesna (n = 20 ears). On days 1, 8 and 15, the saline control group had intratympanic injections of 0.2 ml saline and the propylene glycol control and Mesna groups had intratympanic injections of 0.2 ml 100 per cent propylene glycol. On day 22, the propylene glycol control group had a single intratympanic injection of 0.2 ml saline and the Mesna group had a single intratympanic injection of 10 per cent Mesna. Animals were killed 12 weeks after the last injection and the temporal bones were sent for histopathological evaluation. RESULTS: The cholesteatoma formation rate was 88 per cent in the propylene glycol control group, but was significantly lower in the Mesna group (p = 0.01). There were no significant differences in granulation tissue formation (p = 0.498), cyst formation in the bulla (p = 0.381), fibrosis (p = 0.072) and epithelial hyperplasia (p = 0.081) among experimental groups. CONCLUSION: Intratympanic propylene glycol administration is an effective method of promoting experimental cholesteatoma formation. Administration of a single dose of intratympanic Mesna inhibited cholesteatoma formation in an animal model.


