SN 003CAS# 197801-88-0 |
- 3,3'-Diindolylmethane
Catalog No.:BCC1306
CAS No.:1968-05-4
- BAM7
Catalog No.:BCC1397
CAS No.:331244-89-4
- Bendamustine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1153
CAS No.:3543-75-7
- Betulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5524
CAS No.:472-15-1
- Brassinolide
Catalog No.:BCC1438
CAS No.:72962-43-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

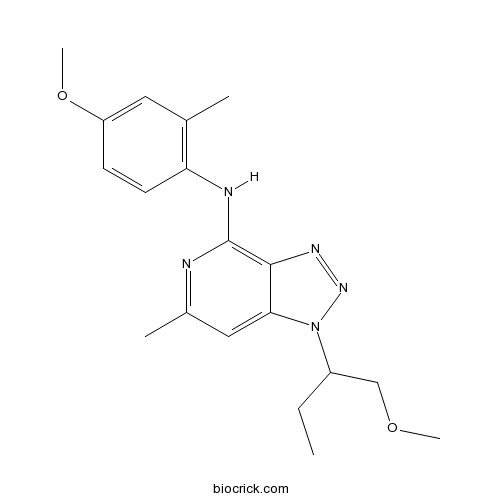
| Cas No. | 197801-88-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10291750 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H25N5O2 | M.Wt | 355.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(1-methoxybutan-2-yl)-N-(4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl)-6-methyltriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | CCC(COC)N1C2=CC(=NC(=C2N=N1)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)OC)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FZMBHAQCHCEGNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H25N5O2/c1-6-14(11-25-4)24-17-10-13(3)20-19(18(17)22-23-24)21-16-8-7-15(26-5)9-12(16)2/h7-10,14H,6,11H2,1-5H3,(H,20,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Reversible corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1 (CRF1) antagonist (Ki values are 3.4 and 7.9 nM at rat and human CRF1 respectively) that displays >1000-fold selectivity over CRF2 receptors. Suppresses CRF-induced ACTH release in vitro (IC50 = 241 nM) and is brain penetrant. |

SN 003 Dilution Calculator

SN 003 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8135 mL | 14.0675 mL | 28.1349 mL | 56.2699 mL | 70.3373 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5627 mL | 2.8135 mL | 5.627 mL | 11.254 mL | 14.0675 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2813 mL | 1.4067 mL | 2.8135 mL | 5.627 mL | 7.0337 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0563 mL | 0.2813 mL | 0.5627 mL | 1.1254 mL | 1.4067 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1407 mL | 0.2813 mL | 0.5627 mL | 0.7034 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- TFLLR-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3948
CAS No.:197794-83-5
- 7-O-Acetylbonducellpin C
Catalog No.:BCN7558
CAS No.:197781-86-5
- Bonducellpin D
Catalog No.:BCN7544
CAS No.:197781-85-4
- Bonducellpin C
Catalog No.:BCN7647
CAS No.:197781-84-3
- Daphmacrine
Catalog No.:BCN4868
CAS No.:19775-48-5
- Amiodarone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4377
CAS No.:19774-82-4
- Peimisine
Catalog No.:BCN4992
CAS No.:19773-24-1
- Ajugatakasins A
Catalog No.:BCN3661
CAS No.:197723-20-9
- Loxapine
Catalog No.:BCC4026
CAS No.:1977-10-2
- Mesna
Catalog No.:BCC3811
CAS No.:19767-45-4
- Tigecycline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4228
CAS No.:197654-04-9
- Fmoc-N-Me-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3353
CAS No.:197632-77-2
- Stachartin A
Catalog No.:BCN6974
CAS No.:1978388-54-3
- Stachartin B
Catalog No.:BCN6973
CAS No.:1978388-55-4
- Stachartin C
Catalog No.:BCN6972
CAS No.:1978388-56-5
- Stachartin D
Catalog No.:BCN6971
CAS No.:1978388-57-6
- Stachartin E
Catalog No.:BCN6970
CAS No.:1978388-58-7
- GW311616 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5394
CAS No.:197890-44-1
- AM 404
Catalog No.:BCC6945
CAS No.:198022-70-7
- GW311616
Catalog No.:BCC5393
CAS No.:198062-54-3
- Triptobenzene K
Catalog No.:BCN8055
CAS No.:198129-88-3
- Gap 27
Catalog No.:BCC1033
CAS No.:198284-64-9
- Medicagol
Catalog No.:BCN8430
CAS No.:1983-72-8
- Myricetin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8144
CAS No.:19833-12-6
PET Imaging of CRF1 with [11C]R121920 and [11C]DMP696: is the target of sufficient density?[Pubmed:17499724]
Nucl Med Biol. 2007 May;34(4):353-61.
AIM: Overstimulation of the CRF type 1 receptor (CRF1) is implicated in anxiety and depressive disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate the in vivo binding characteristics of [11C]R121920 and [11C]DMP696 in the nonhuman primate for application in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of CRF1. METHODS: PET imaging with the two novel CRF1 radioligands was performed in baboon. In vitro binding studies for CRF1 were performed in postmortem brain tissue of baboon and human to assess sufficiency of receptor density for PET. RESULTS: Both [11C]R121920 and [11C]DMP696 distributed rapidly and uniformly throughout the brain. Washout was comparable across brain regions, without differences in volume of distribution between regions reported to have high and low in vitro CRF1 binding. Membrane-enriched tissue homogenate assay using [(125)I]Tyr(0)-sauvagine and specific CRF1 antagonists CP154,526 and SN003 in human occipital cortex yielded maximal binding (Bmax) of 63.3 and 147.3 fmol/mg protein, respectively, and in human cerebellar cortex yielded Bmax of 103.6 and 64.6 fmol/mg protein, respectively. Dissociation constants (K(D)) were subnanomolar. In baboon, specific binding was not detectable in the same regions; therefore, Bmax and K(D) were not measurable. Autoradiographic results were consistent except there was also detectable CRF1-specific binding in baboon cerebellum. CONCLUSION: Neither [11C]R121920 nor [11C]DMP696 demonstrated quantifiable regional binding in vivo in baboon. In vitro results suggest CRF1 density in baboon may be insufficient for PET. Studies in man may generate more promising results due to the higher CRF1 density compared with baboon in cerebral cortex and cerebellum.
Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of [11C]SN003 as a PET ligand for CRF1 receptors.[Pubmed:16529935]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Jun 15;14(12):4029-34.
Synthesis and evaluation of [O-methyl-11C](4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl)[1-(1-methoxymethylpropyl)-6-methyl-1H-[1 ,2,3]triazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl]amine or [11C]SN003 ([11C]6), as a PET imaging agent for CRF1 receptors, in baboons is described. 4-[1-(1-Methoxymethylpropyl)-6-methyl-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-ylamino] -3-methylphenol (5), the precursor molecule for the radiolabeling, was synthesized from 2,4-dichloro-6-methyl-3-nitropyridine in seven steps with 20% overall yield. The total time required for the synthesis of [11C]SN003 is 30 min from EOB using [11C]methyl triflate in the presence of NaOH in acetone. The yield of the synthesis is 22% (EOS) with >99% chemical and radiochemical purities and a specific activity of >2000 Ci/mmol. PET studies in baboon show that [11C]6 penetrates the BBB and accumulates in brain. No detectable specific binding was observed, likely due to the rapid metabolism or low density of CRF1 receptors in primate brain.


