NGR peptideCAS# 651328-78-8 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

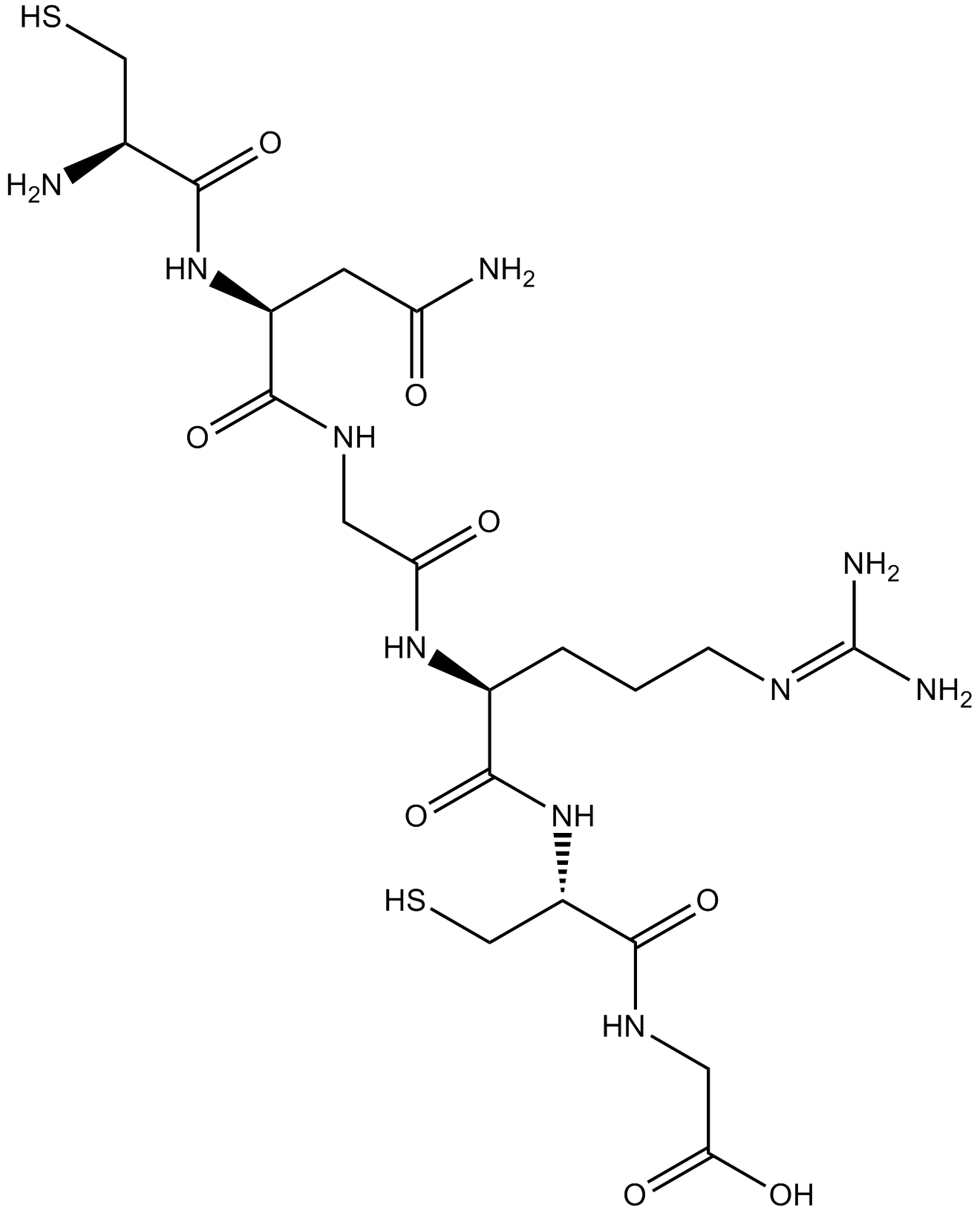
| Cas No. | 651328-78-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10348740 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H36N10O8S2 | M.Wt | 608.69 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >20.3mg/ml in DMSO or water | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(CC(C(=O)NC(CS)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CS)N)CN=C(N)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UAXAYRSMIDOXCU-BJDJZHNGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H36N10O8S2/c21-9(7-39)16(35)29-11(4-13(22)31)17(36)26-5-14(32)28-10(2-1-3-25-20(23)24)19(38)30-12(8-40)18(37)27-6-15(33)34/h9-12,39-40H,1-8,21H2,(H2,22,31)(H,26,36)(H,27,37)(H,28,32)(H,29,35)(H,30,38)(H,33,34)(H4,23,24,25)/t9-,10-,11-,12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

NGR peptide Dilution Calculator

NGR peptide Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NGR peptide
- Nanchangmycin
Catalog No.:BCC4970
CAS No.:65101-87-3
- Sulfameter
Catalog No.:BCC4855
CAS No.:651-06-9
- L-152,804
Catalog No.:BCC7041
CAS No.:6508-43-6
- 6-Amino-2-methylquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8759
CAS No.:65079-19-8
- Nimorazole
Catalog No.:BCC5253
CAS No.:6506-37-2
- Boc-His(Tos)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2605
CAS No.:65057-34-3
- VGX-1027
Catalog No.:BCC5203
CAS No.:6501-72-0
- 3,8-Dihydroxy-2,4,6-trimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1387
CAS No.:65008-17-5
- 1,5,6-Trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7347
CAS No.:65008-02-8
- Orotic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4162
CAS No.:65-86-1
- Benzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4201
CAS No.:65-85-0
- Ac-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2991
CAS No.:65-82-7
- N-Methylcorydaldine
Catalog No.:BCN3300
CAS No.:6514-05-2
- Nicorandil
Catalog No.:BCC5004
CAS No.:65141-46-0
- Elastase Inhibitor, SPCK
Catalog No.:BCC1226
CAS No.:65144-34-5
- 7-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6539
CAS No.:6515-36-2
- 4'-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6548
CAS No.:6515-37-3
- (16R)-Dihydrositsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN4195
CAS No.:6519-26-2
- (16R)-E-Isositsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN4000
CAS No.:6519-27-3
- Avermectin B1a
Catalog No.:BCC1382
CAS No.:65195-55-3
- Avermectin B1b
Catalog No.:BCC1383
CAS No.:65195-56-4
- Isosorbide
Catalog No.:BCC4667
CAS No.:652-67-5
- Gossypin
Catalog No.:BCN7987
CAS No.:652-78-8
- N-Glyceryltaurine
Catalog No.:BCN1753
CAS No.:65222-42-6
Efficacy of NGR peptide-modified PEGylated quantum dots for crossing the blood-brain barrier and targeted fluorescence imaging of glioma and tumor vasculature.[Pubmed:27682740]
Nanomedicine. 2017 Jan;13(1):83-93.
Delivery of imaging agents to brain glioma is challenging because the blood-brain barrier (BBB) functions as a physiological checkpoint guarding the central nervous system from circulating large molecules. Moreover, the ability of existing probes to target glioma has been insufficient and needs to be improved. In present study, PEG-based long circulation, CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs)-based nanoscale and fluorescence, asparagines-glycine-arginine peptides (NGR)-based specific CD13 recognition were integrated to design and synthesize a novel nanoprobe by conjugating biotinylated NGR peptides to avidin-PEG-coated QDs. Our data showed that the NGR-PEG-QDs were nanoscale with less than 100 nm and were stable in various pH (4.0~8.0). These nanomaterials with non-toxic concentrations could cross the BBB and target CD13-overexpressing glioma and tumor vasculature in vitro and in vivo, contributing to fluorescence imaging of this brain malignancy. These achievements allowed groundbreaking technological advances in targeted fluorescence imaging for the diagnosis and surgical removal of glioma, facilitating potential transformation toward clinical nanomedicine.
Succinimide Formation from an NGR-Containing Cyclic Peptide: Computational Evidence for Catalytic Roles of Phosphate Buffer and the Arginine Side Chain.[Pubmed:28212316]
Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 16;18(2). pii: ijms18020429.
The Asn-Gly-Arg (NGR) motif and its deamidation product isoAsp-Gly-Arg (isoDGR) have recently attracted considerable attention as tumor-targeting ligands. Because an NGR-containing peptide and the corresponding isoDGR-containing peptide target different receptors, the spontaneous NGR deamidation can be used in dual targeting strategies. It is well known that the Asn deamidation proceeds via a succinimide derivative. In the present study, we computationally investigated the mechanism of succinimide formation from a cyclic peptide, c[CH(2)CO-NGRC]-NH(2), which has recently been shown to undergo rapid deamidation in a phosphate buffer. An H(2)PO(4)(-) ion was explicitly included in the calculations. We employed the density functional theory using the B3LYP functional. While geometry optimizations were performed in the gas phase, hydration Gibbs energies were calculated by the SM8 (solvation model 8) continuum model. We have found a pathway leading to the five-membered ring tetrahedral intermediate in which both the H(2)PO(4)(-) ion and the Arg side chain act as catalyst. This intermediate, once protonated at the NH(2) group on the five-membered ring, was shown to easily undergo NH(3) elimination leading to the succinimide formation. This study is the first to propose a possible catalytic role for the Arg side chain in the NGR deamidation.
A photo-responsive peptide- and asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) peptide-mediated liposomal delivery system.[Pubmed:25693640]
Drug Deliv. 2016 Sep;23(7):2445-2456.
The conjugation of tunable peptides or materials with nanocarriers represents a promising approach for drug delivery to tumor cells. In this study, we report the development of a novel liposomal carrier system that exploits the cell surface binding synergism between photo-sensitive peptides (PSPs) and targeting ligands. The positive charges of the lysine residues on the cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) were temporarily caged by the photolabile-protective groups (PG), thereby forming a PSP. Furthermore, this PSP enhances specific uptake into cancer cells after rapidly uncaging the PG via near-infrared (NIR) light illumination. In the circulatory system, the cell penetrability of PSP was hindered. In contrast, the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) peptide moieties, selectively bind to CD13-positive tumors, were attached to the nanocarrier to facilitate the active accumulation of this liposomal carrier in tumor tissue. The dual-modified liposomes (PSP/NGR-L) were prepared by emulsification method, and the concentrations of DSPE-PEG2000-psCPP and DSPE-PEG5000-NGR in the liposomes were chosen to be 4% and 1% (molar ratio), respectively. The mean particle size of the PSP/NGR-L was about 95 nm, and the drug entrapment efficiency was more than 90%. Cellular uptake results demonstrated that the proposed PSP/NGR-L had an enhancement of cancer cell recognition and specific uptake. Furthermore, the PSP/NGR-L demonstrated a stronger antitumor efficacy in the HT-1080 tumor model in nude mice with the aid of NIR illumination.
Cell-penetrating peptide-doxorubicin conjugate loaded NGR-modified nanobubbles for ultrasound triggered drug delivery.[Pubmed:26176270]
J Drug Target. 2016;24(2):134-46.
A new drug-targeting system for CD13(+) tumors has been developed, based on ultrasound-sensitive nanobubbles (NBs) and cell-permeable peptides (CPPs). Here, the CPP-doxorubicin conjugate (CPP-DOX) was entrapped in the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) peptide modified NB (CPP-DOX/NGR-NB) and the penetration of CPP-DOX was temporally masked; local ultrasound stimulation could trigger the CPP-DOX release from NB and activate its penetration. The CPP-DOX/NGR-NBs had particle sizes of about 200 nm and drug entrapment efficiency larger than 90%. In vitro release results showed that over 85% of the encapsulated DOX or CPP-DOX would release from NBs in the presence of ultrasound, while less than 1.5% of that (30 min) without ultrasound. Cell experiments showed the higher cellular CPP-DOX uptake of CPP-DOX/NGR-NB among the various NB formulations in Human fibrosarcoma cells (HT-1080, CD13(+)). The CPP-DOX/NGR-NB with ultrasound treatment exhibited an increased cytotoxic activity than the one without ultrasound. In nude mice xenograft of HT-1080 cells, CPP-DOX/NGR-NB with ultrasound showed a higher tumor inhibition effect (3.1% of T/C%, day 24), longer median survival time (50 days) and excellent body safety compared with the normal DOX injection group. These results indicate that the constructed vesicle would be a promising drug delivery system for specific cancer treatment.


