NicorandilPotassium channel activator CAS# 65141-46-0 |
- Sulfo-NHS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3576
CAS No.:119616-38-5
- Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3578
CAS No.:127062-22-0
- NHS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3577
CAS No.:35013-72-0
- Biotin Hydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC3582
CAS No.:66640-86-6
- NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3579
CAS No.:72040-63-2
- Iodoacetyl-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3584
CAS No.:93285-75-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 65141-46-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 47528 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H9N3O4 | M.Wt | 211.17 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (156.27 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
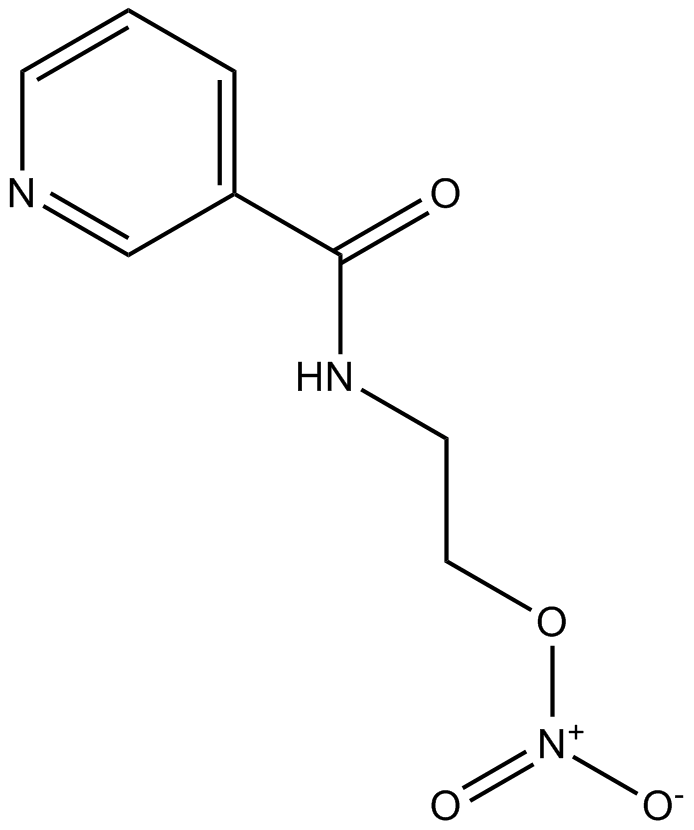
| Chemical Name | 2-(pyridine-3-carbonylamino)ethyl nitrate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)NCCO[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LBHIOVVIQHSOQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H9N3O4/c12-8(7-2-1-3-9-6-7)10-4-5-15-11(13)14/h1-3,6H,4-5H2,(H,10,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Kir6 (KATP) channel opener and NO donor; antianginal agent. Preferentially activates SUR2B- versus SUR2A-containing Kir6 channels (EC50 values are 10 and > 500 μM respectively) and causes 1.6-fold increase in cardiac eNOS expression. Displays coronary and peripheral vasodilatory properties, reduces both pre- and after-load, and increases coronary blood flow. Also displays cardioprotective effects, possibly through ischemic preconditioning. |

Nicorandil Dilution Calculator

Nicorandil Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.7355 mL | 23.6776 mL | 47.3552 mL | 94.7104 mL | 118.388 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9471 mL | 4.7355 mL | 9.471 mL | 18.9421 mL | 23.6776 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4736 mL | 2.3678 mL | 4.7355 mL | 9.471 mL | 11.8388 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0947 mL | 0.4736 mL | 0.9471 mL | 1.8942 mL | 2.3678 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0474 mL | 0.2368 mL | 0.4736 mL | 0.9471 mL | 1.1839 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Nicorandil is potassium channel activator.Nicorandil is a vasodilatory drug used to treat angina. Nicorandil stimulates guanylate cyclase to increase formation of cyclic GMP (cGMP). cGMP activates protein kinase G (PKG) which phosphorylates and inhibits G
- N-Methylcorydaldine
Catalog No.:BCN3300
CAS No.:6514-05-2
- NGR peptide
Catalog No.:BCC4418
CAS No.:651328-78-8
- Nanchangmycin
Catalog No.:BCC4970
CAS No.:65101-87-3
- Sulfameter
Catalog No.:BCC4855
CAS No.:651-06-9
- L-152,804
Catalog No.:BCC7041
CAS No.:6508-43-6
- 6-Amino-2-methylquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8759
CAS No.:65079-19-8
- Nimorazole
Catalog No.:BCC5253
CAS No.:6506-37-2
- Boc-His(Tos)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2605
CAS No.:65057-34-3
- VGX-1027
Catalog No.:BCC5203
CAS No.:6501-72-0
- 3,8-Dihydroxy-2,4,6-trimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1387
CAS No.:65008-17-5
- 1,5,6-Trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7347
CAS No.:65008-02-8
- Orotic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4162
CAS No.:65-86-1
- Elastase Inhibitor, SPCK
Catalog No.:BCC1226
CAS No.:65144-34-5
- 7-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6539
CAS No.:6515-36-2
- 4'-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6548
CAS No.:6515-37-3
- (16R)-Dihydrositsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN4195
CAS No.:6519-26-2
- (16R)-E-Isositsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN4000
CAS No.:6519-27-3
- Avermectin B1a
Catalog No.:BCC1382
CAS No.:65195-55-3
- Avermectin B1b
Catalog No.:BCC1383
CAS No.:65195-56-4
- Isosorbide
Catalog No.:BCC4667
CAS No.:652-67-5
- Gossypin
Catalog No.:BCN7987
CAS No.:652-78-8
- N-Glyceryltaurine
Catalog No.:BCN1753
CAS No.:65222-42-6
- Dehydrocrenatidine
Catalog No.:BCN4196
CAS No.:65236-62-6
- Cucurbitacin B 2-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3119
CAS No.:65247-27-0
The clinical effect of nicorandil on perioperative myocardial protection in patients undergoing elective PCI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.[Pubmed:28322321]
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 21;7:45117.
Many scholars have studied the effect of Nicorandil on perioperative myocardial protection in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), but results are inconsistent. Therefore, we performed this meta-analysis. Finally, 16 articles, including 1616 patients, were included into this meta-analysis. Meta-analysis results showed that: (1) Nicorandil can reduce the level of CK-MB after PCI, including at 6 hours, 12 hours, 18 hours and 24 hours. (2) Nicorandil can reduce the level of TnT after PCI, including at 6 hours, 12 hours, 18 hours and 24 hours. (3) Nicorandil can reduce the incidence of adverse reactions after PCI. (4) Nicorandil cannot reduce the level of MVP after PCI, including at 12 hours and 24 hours. (5) Subgroup analysis showed that Nicorandil can reduce CK-MB and TnT level at 24 hours after PCI for Chinese's population (P < 0.05), but can not reduce CK-MB and TnT level at 24 hours after PCI for non Chinese's population (P > 0.05). Our meta-analysis indicate that Nicorandil can reduce myocardial injury and reduce the incidence of adverse reaction caused by PCI for Chinese's population, but is not obvious for non Chinese's population. However, this conclusion still needs to be confirmed in the future.
[Comparative Assessment of Antianginal Efficacy and Safety of Nicorandil at the Background of Therapy With -Adrenoblockers in Ischemic Heart Disease Patients With Stable Angina].[Pubmed:28290892]
Kardiologiia. 2016 Oct;56(10):30-34.
AIM: to demonstrate impact of addition of Nicorandil to standard treatment in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (IHD) on clinical manifestations of the disease and safety of conducted therapy. MATERIAL AND METHODS: We included in this double-blind placebo controlled study with parallel groups 120 patients with verified IHD and stable effort angina. During the entire study all patients received metoprolol (100 mg/day). Patients of main group were given Nicorandil (10 mg twice a day for 2 weeks and 20 mg twice a day thereafter); patients of control group were given placebo. Study duration was 6 weeks. RESULTS: Addition of Nicorandil was associated with significant reduction of number of anginal attacks both compared with control period and addition of placebo. Consumption of short acting nitrates significantly decreased on both Nicorandil doses compared with control period. Adverse events were registered in 10 of 61 and 7 of 59 patients (16.4 and 11.9%) taking Nicorandil and placebo, respectively (n.s.). Three patients withdrew from the study because of headache. CONCLUSION: Addition of Nicorandil to standard therapy in patients with chronic IHD and stable effort angina promoted significant reduction of number of angina attacks. Good tolerability of Nicorandil was also demonstrated.
[Influence of the Potassium Channels Activator Nicorandil to the Quality of Life in Patients With Ishemic Heart Disease and Stable Angina Pectoris].[Pubmed:28290843]
Kardiologiia. 2016 Jun;56(6):26-31.
The aim of the study to assess the influence of medicamentous therapy to the quality of life of ischemic heart disease patients with stable angina pectoris by activator potassium channels Nicorandil in comparison with traditional therapy by isosorbide dinitrate. The study included 84 ischemic heart disease patients. Authors consider quality of life as an estimated category of state of the subject in an illness situation. The dynamic of physical and psychological components of quality of life are compared in ischemic heart disease patients under the treatment by Nicorandil and isosorbide dinitrate. Indicators of quality of life, defined on the basis of a questionnaires of SAQ and GHQ supplementing an illness picture, are an multiple-factor criterion of an assessment of a condition of this category of patients. The benefits of Nicorandil in influence on quality of life indicators were revealed in the study.
Potassium channel openers in myocardial ischaemia: therapeutic potential of nicorandil.[Pubmed:11693460]
Drugs. 2001;61(12):1705-10.
Potassium channel openers or agonists represent a novel new class of compounds in the treatment of a range of cardiovascular disorders, particularly angina pectoris and hypertension. Nicorandil is the only clinically available potassium channel opener with antianginal effects, and with comparable efficacy and tolerability to existing antianginal therapy. It confers benefits through a dual action: opening the mitochondrial KATP channels leading to preconditioning of the myocardium and a nitrate-like effect. Myocardial preconditioning is important in reducing infarct size, severity of stunning and cardiac arrhythmias. These effects make Nicorandil a unique antianginal compound that reduces both pre- and after-load and improves coronary blood flow. Comparative and noncomparative studies support the use of Nicorandil as monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal therapy for stable angina pectoris. However, large studies are required to confirm its role in the treatment of acute coronary syndromes despite the favourable results from small studies.
Nicorandil enhances cardiac endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression via activation of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K channel in rat.[Pubmed:11483869]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;38(2):200-10.
In the heart, nitric oxide activates an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive K (K(ATP)) channel that is constructed of two subunits, i.e., an ATP-binding cassette protein sulfonylurea receptor (SUR2) and a pore-forming inward rectifier (Kir6.1 or 6.2). However, whether this K(ATP) channel affects nitric oxide activation is unknown. Our aim was to assess whether pharmacologic activation of the K(ATP) channel by Nicorandil contributes to endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) levels. A total of 21 7-week old male Sprague-Dawley rats were used. Seven were treated by intraperitoneal injection of Nicorandil at 3 mg/kg/d; seven were treated with intraperitoneal Nicorandil at 3 mg/kg/d after glibenclamide at 12 mg/kg/d twice a day p.o.; and seven were left untreated (controls). At 24 h after treatment, blood pressure and heart rate were measured, and eNOS, SUR2, Kir6.1, and Kir6.2 mRNA levels and eNOS protein levels in the left ventricle were determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot analysis. Nicorandil caused tachycardia without a change in blood pressure, whereas glibenclamide had no effect on the Nicorandil-induced change in heart rate or on blood pressure. RT-PCR revealed that Nicorandil increased the eNOS and SUR2 mRNA levels by 2.2- and 2.0-fold, respectively, (p < 0.01 versus control), and that these increases were completely inhibited by glibenclamide. A significant correlation was observed between eNOS and SUR2 mRNA levels in all experimental rats (r = 0.760, p < 0.001). However, Kir6.1 or 6.2 mRNA level was constant. Western blot analysis revealed that Nicorandil caused a 1.6-fold increase in eNOS protein levels (p < 0.01 versus control). This increase was completely inhibited by glibenclamide. In conclusion, up-regulation of eNOS mRNA and protein levels by Nicorandil, and inhibition of this upregulation by glibenclamide, were demonstrated in normotensive conscious rat hearts. Nicorandil appears to enhance cardiac eNOS expression via activation of a K(ATP) channel.
SUR2 subtype (A and B)-dependent differential activation of the cloned ATP-sensitive K+ channels by pinacidil and nicorandil.[Pubmed:9692785]
Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jul;124(5):985-91.
1. The classical ATP sensitive K+ (K(ATP)) channels are composed of a sulphonylurea receptor (SUR) and an inward rectifying K+ channel subunit (BIR/Kir6.2). They are the targets of vasorelaxant agents called K+ channel openers, such as pinacidil and Nicorandil. 2. In order to examine the tissue selectivity of pinacidil and Nicorandil, in vitro, we compared the effects of these agents on cardiac type (SUR2A/Kir6.2) and vascular smooth muscle type (SUR2B/Kir6.2) of the K(ATP) channels heterologously expressed in HEK293T cells, a human embryonic kidney cell line, by using the patch-clamp method. 3. In the cell-attached recordings (145 mM K+ in the pipette), pinacidil and Nicorandil activated a weakly inwardly-rectifying, glibenclamide-sensitive 80 pS K+ channel in both the transfected cells. 4. In the whole-cell configuration, pinacidil showed a similar potency in activating the SUR2B/Kir6.2 and SUR2A/Kir6.2 channels (EC50 of approximately 2 and approximately 10 microM, respectively). On the other hand, Nicorandil activated the SUR2B/Kir6.2 channel > 100 times more potently than the SUR2A/Kir6.2 (EC50 of approximately 10 microM and > 500 microM, respectively). 5. Thus, Nicorandil, but not pinacidil, preferentially activates the K(ATP) channels containing SUR2B. Because SUR2A and SUR2B are diverse only in 42 amino acids at their C-terminal ends, it is strongly suggested that this short part of SUR2B may play a critical role in the action of Nicorandil on the vascular type classical K(ATP) channel.


