NSC 23766Selective inhibitor of Rac1-GEF interaction. CAS# 1177865-17-6 |
- EHop-016
Catalog No.:BCC5022
CAS No.:1380432-32-5
- ZCL278
Catalog No.:BCC3665
CAS No.:587841-73-4
- EHT 1864
Catalog No.:BCC6075
CAS No.:754240-09-0
- AS 1892802
Catalog No.:BCC6335
CAS No.:928320-12-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1177865-17-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16759159 | Appearance | Powder |
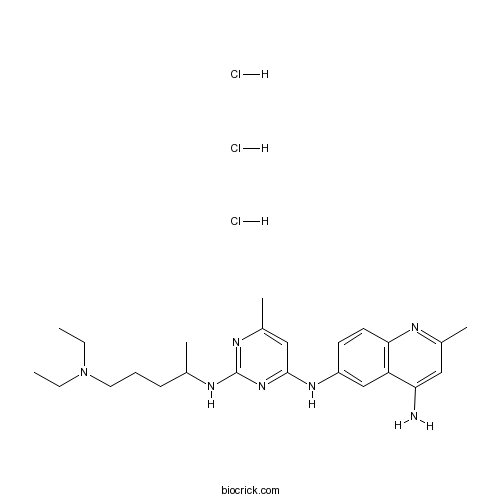
| Formula | C24H38Cl3N7 | M.Wt | 530.96 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (62.77 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : ≥ 32 mg/mL (60.27 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 6-N-[2-[5-(diethylamino)pentan-2-ylamino]-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl]-2-methylquinoline-4,6-diamine;trihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=NC(=CC(=N1)NC2=CC3=C(C=C2)N=C(C=C3N)C)C.Cl.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CPUHORIUXPQCHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H35N7.3ClH/c1-6-31(7-2)12-8-9-16(3)27-24-28-18(5)14-23(30-24)29-19-10-11-22-20(15-19)21(25)13-17(4)26-22;;;/h10-11,13-16H,6-9,12H2,1-5H3,(H2,25,26)(H2,27,28,29,30);3*1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of Rac1-GEF interaction. Prevents Rac1 activation by Rac-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) TrioN and Tiam1 (IC50 ~ 50 μM) without affecting Cdc42 or RhoA activation. Inhibits Rac1-mediated cell functions and is reported to reverse tumor cell phenotyes in prostate cancer cells. |

NSC 23766 Dilution Calculator

NSC 23766 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8834 mL | 9.4169 mL | 18.8338 mL | 37.6676 mL | 47.0845 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3767 mL | 1.8834 mL | 3.7668 mL | 7.5335 mL | 9.4169 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1883 mL | 0.9417 mL | 1.8834 mL | 3.7668 mL | 4.7085 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0377 mL | 0.1883 mL | 0.3767 mL | 0.7534 mL | 0.9417 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0188 mL | 0.0942 mL | 0.1883 mL | 0.3767 mL | 0.4708 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NSC-23766 is a specific inhibitor of Rac with IC50 of 50μM.
NSC-23766 blocks the activation of Rac 1 through binding the GEFs including Trio and Tiam 1 [1]. In human dermal microvascular endothelial cells, NSC-23766 decreased trans-endothelial electrical resistance and caused the intercellular gap formation. Inhibition of Rac 1 by NSC-23766 shortly reduced endothelial barrier functions as revealed by measurement of TER and the appearance of intracellular gaps [2]. In the mucous cell of the intestine, inhibition of Rac1 either by NSC-23766 protected cells from TNF-α-induced apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3, -8 and -9 activities. Inhibition of Rac1 significantly prevented TNF-α-induced activation of JNK1/2, but did not modulate TNF-α-induced ERK1/2, Akt and p38 MAPK activity [3].
References:
[1]. Gao Y, Dickerson JB, Guo F, Zheng J, Zheng Y. Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 May 18;101(20):7618-23.
[2]. Baumer Y, Spindler V, Werthmann RC, Bünemann M, Waschke J. Role of Rac 1 and cAMP in endothelial barrier stabilization and thrombin-induced barrier breakdown. J Cell Physiol. 2009 Sep;220(3):716-26.
[3]. Jin S1, Ray RM, Johnson LR. Rac1 mediates intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via JNK. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):G1137-47.
- AP-III-a4
Catalog No.:BCC5292
CAS No.:1177827-73-4
- Desmethyl-YM 298198
Catalog No.:BCC7365
CAS No.:1177767-57-5
- Decumbenine C
Catalog No.:BCC8314
CAS No.:117772-89-1
- Azithromycin Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4631
CAS No.:117772-70-0
- CGH 2466 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7338
CAS No.:1177618-54-0
- SMANT hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6254
CAS No.:1177600-74-6
- N20C hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7292
CAS No.:1177583-87-7
- Forsythoside I
Catalog No.:BCN6430
CAS No.:1177581-50-8
- Felbamate hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4160
CAS No.:1177501-39-1
- (R)-(+)-Blebbistatin
Catalog No.:BCC7195
CAS No.:1177356-70-5
- CKI 7 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5614
CAS No.:1177141-67-1
- Doramectin
Catalog No.:BCC1536
CAS No.:117704-25-3
- 3,3',4',5,6,7,8-heptamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8203
CAS No.:1178-24-1
- Enterostatin
Catalog No.:BCC6050
CAS No.:117830-79-2
- Ac-Asp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2880
CAS No.:117833-18-8
- Loreclezole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7009
CAS No.:117857-45-1
- L-CCG-l
Catalog No.:BCC6609
CAS No.:117857-93-9
- L-CCG-lll
Catalog No.:BCC6608
CAS No.:117857-95-1
- Fmoc-Thr(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3550
CAS No.:117872-75-0
- 7,4'-Dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN3582
CAS No.:1178893-64-5
- Forsythoside H
Catalog No.:BCN6431
CAS No.:1178974-85-0
- Boc-N-Me-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2611
CAS No.:117903-25-0
- GLYX 13
Catalog No.:BCC6013
CAS No.:117928-94-6
- Luzindole
Catalog No.:BCC6826
CAS No.:117946-91-5
VEGF alleviates ALS-CSF induced cytoplasmic accumulations of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS in NSC-34 cells.[Pubmed:28163215]
J Chem Neuroanat. 2017 Apr;81:48-52.
Cytoplasmic mislocalisation and aggregation of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS proteins in spinal motor neurons contribute to the pathogenesis of the highly fatal disorder amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). We investigated the neuroprotective effect of VEGF on expression of these proteins in the motor neuronal cell line NSC-34 modelled to reminisce sporadic form of ALS. We studied the expression of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS proteins after exposure to ALS-CSF and following VEGF supplementation by quantitative confocal microscopy and electron microscopy. ALS-CSF caused cytoplasmic overexpression of both the proteins and stress-granule formation in the cells. These alterations were alleviated by VEGF supplementation. The related ultrastructural changes like nuclear membrane dysmorphism and p-bodies associated changes were also reversed. However the protein expression did not completely translocate to the nucleus, as some cells continued to show to cytoplasmic mislocalisation. Thus, the present findings indicate that VEGF alleviates TDP43 and FUS pathology by complimenting its role in controlling apoptosis and reversing choline acetyl transferase expression. Hence, VEGF appears to target multiple pathogenic processes in the neurodegenerative cascade of ALS.
Important modifications by sugammadex, a modified gamma-cyclodextrin, of ion currents in differentiated NSC-34 neuronal cells.[Pubmed:28049438]
BMC Neurosci. 2017 Jan 3;18(1):6.
BACKGROUND: Sugammadex (SGX) is a modified gamma-cyclodextrin used for reversal of steroidal neuromuscular blocking agents during general anesthesia. Despite its application in clinical use, whether SGX treatment exerts any effects on membrane ion currents in neurons remains largely unclear. In this study, effects of SGX treatment on ion currents, particularly on delayed-rectifier K(+) current [I K(DR)], were extensively investigated in differentiated NSC-34 neuronal cells. RESULTS: After cells were exposed to SGX (30 muM), there was a reduction in the amplitude of I K(DR) followed by an apparent slowing in current activation in response to membrane depolarization. The challenge of cells with SGX produced a depolarized shift by 15 mV in the activation curve of I K(DR) accompanied by increased gating charge of this current. However, the inactivation curve of I K(DR) remained unchanged following SGX treatment, as compared with that in untreated cells. According to a minimal reaction scheme, the lengthening of activation time constant of I K(DR) caused by cell treatment with different SGX concentrations was quantitatively estimated with a dissociation constant of 17.5 muM, a value that is clinically achievable. Accumulative slowing in I K(DR) activation elicited by repetitive stimuli was enhanced in SGX-treated cells. SGX treatment did not alter the amplitude of voltage-gated Na(+) currents. In SGX-treated cells, dexamethasone (30 muM), a synthetic glucocorticoid, produced little or no effect on L-type Ca(2+) currents, although it effectively suppressed the amplitude of this current in untreated cells. CONCLUSIONS: The treatment of SGX may influence the amplitude and gating of I K(DR) and its actions could potentially contribute to functional activities of motor neurons if similar results were found in vivo.
Adult NSC diversity and plasticity: the role of the niche.[Pubmed:27978480]
Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Feb;42:68-74.
Adult somatic stem cells are generally defined as cells with the ability to differentiate into multiple different lineages and to self-renew during long periods of time. These features were long presumed to be represented in one single tissue-specific stem cell. Recent development of single-cell technologies reveals the existence of diversity in fate and activation state of somatic stem cells within the blood, skin and intestinal compartments [1] but also in the adult brain. Here we review how recent advances have expanded our view of neural stem cells (NSCs) as a diverse pool of cells and how the specialized microenvironment in which they reside acts to maintain this diversity. In addition, we discuss the plasticity of the system in the injured brain.
c-Jun Amino-Terminal Kinase is Involved in Valproic Acid-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic NSCs and Neurite Outgrowth of NSC-Derived Neurons.[Pubmed:28321599]
Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):1254-1266.
Valproic acid (VPA), an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug, can induce neuronal differentiation, promote neurite extension and exert a neuroprotective effect in central nervous system (CNS) injuries; however, comparatively little is known regarding its action on mouse embryonic neural stem cells (NSCs) and the underlying molecular mechanism. Recent studies suggested that c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is required for neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation during neuronal development. In the present study, we cultured mouse embryonic NSCs and treated the cells with 1 mM VPA for up to 7 days. The results indicate that VPA promotes the neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic NSCs and neurite outgrowth of NSC-derived neurons; moreover, VPA induces the phosphorylation of c-Jun by JNK. In contrast, the specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 decreased the VPA-stimulated increase in neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic NSCs and neurite outgrowth of NSC-derived neurons. Taken together, these results suggest that VPA promotes neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic NSCs and neurite outgrowth of NSC-derived neurons. Moreover, JNK activation is involved in the effects of VPA stimulation.


