L-CCG-lllPotent, competitive glutamate uptake inhibitor CAS# 117857-95-1 |
- Qingyangshengenin A
Catalog No.:BCN8126
CAS No.:106644-33-1
- Demethylzeylasteral
Catalog No.:BCN2282
CAS No.:107316-88-1
- Asarinin
Catalog No.:BCN2769
CAS No.:133-05-1
- Magnoflorine Iodide
Catalog No.:BCN2911
CAS No.:4277-43-4
- Magnoflorine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2405
CAS No.:6681-18-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 117857-95-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5310958 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C6H9NO4 | M.Wt | 159.14 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (2<em>S</em>,3<em>S</em>,4<em>R</em>)-CCG | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. NaOH | ||
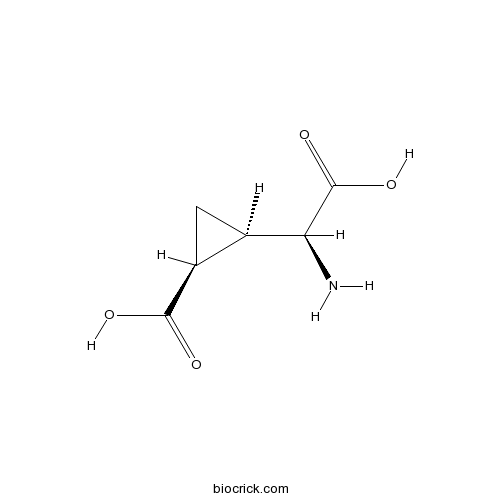
| Chemical Name | (1S,2R)-2-[(S)-amino(carboxy)methyl]cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C1C(=O)O)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GZOVEPYOCJWRFC-UZBSEBFBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H9NO4/c7-4(6(10)11)2-1-3(2)5(8)9/h2-4H,1,7H2,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)/t2-,3+,4+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and competitive inhibitor of both glial and neuronal uptake of glutamate, aspartate and cysteate. |

L-CCG-lll Dilution Calculator

L-CCG-lll Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.2838 mL | 31.4189 mL | 62.8378 mL | 125.6755 mL | 157.0944 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2568 mL | 6.2838 mL | 12.5676 mL | 25.1351 mL | 31.4189 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6284 mL | 3.1419 mL | 6.2838 mL | 12.5676 mL | 15.7094 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1257 mL | 0.6284 mL | 1.2568 mL | 2.5135 mL | 3.1419 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0628 mL | 0.3142 mL | 0.6284 mL | 1.2568 mL | 1.5709 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- L-CCG-l
Catalog No.:BCC6609
CAS No.:117857-93-9
- Loreclezole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7009
CAS No.:117857-45-1
- Ac-Asp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2880
CAS No.:117833-18-8
- Enterostatin
Catalog No.:BCC6050
CAS No.:117830-79-2
- 3,3',4',5,6,7,8-heptamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8203
CAS No.:1178-24-1
- NSC 23766
Catalog No.:BCC1149
CAS No.:1177865-17-6
- AP-III-a4
Catalog No.:BCC5292
CAS No.:1177827-73-4
- Desmethyl-YM 298198
Catalog No.:BCC7365
CAS No.:1177767-57-5
- Decumbenine C
Catalog No.:BCC8314
CAS No.:117772-89-1
- Azithromycin Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4631
CAS No.:117772-70-0
- CGH 2466 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7338
CAS No.:1177618-54-0
- SMANT hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6254
CAS No.:1177600-74-6
- Fmoc-Thr(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3550
CAS No.:117872-75-0
- 7,4'-Dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN3582
CAS No.:1178893-64-5
- Forsythoside H
Catalog No.:BCN6431
CAS No.:1178974-85-0
- Boc-N-Me-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2611
CAS No.:117903-25-0
- GLYX 13
Catalog No.:BCC6013
CAS No.:117928-94-6
- Luzindole
Catalog No.:BCC6826
CAS No.:117946-91-5
- Rabeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC5228
CAS No.:117976-89-3
- Rabeprazole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5227
CAS No.:117976-90-6
- Guanosine
Catalog No.:BCN2962
CAS No.:118-00-3
- Hydrastine
Catalog No.:BCC8187
CAS No.:118-08-1
- Cinchonine
Catalog No.:BCN2464
CAS No.:118-10-5
- Syringin
Catalog No.:BCN6059
CAS No.:118-34-3
Inhibition by folded isomers of L-2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine of glutamate uptake via the human glutamate transporter hGluT-1.[Pubmed:7621914]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):387-90.
The effects of isomers of 2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (CCG) on uptake of L-glutamate were investigated in COS-7 cells that expressed a cloned human glutamate transporter (hGluT-1). The (2S, 3S, 4R)-isomer (L-CCG-III) and the (2S, 3R, 4S)-isomer (L-CCG-IV) markedly inhibited glutamate uptake with a 50% inhibitory concentration of 290 nM and 1.1 microM, respectively. The (2S, 3S, 4S)-isomer (L-CCG-I) and the (2S, 3R, 4R)-isomer (L-CCG-II) did not inhibit glutamate uptake at concentrations of < or = 10 microM. Thus, hGluT-1 showed a markedly higher affinity for L-CCG-III and L-CCG-IV with a folded conformation of the glutamate skeleton, than for L-CCG-I or L-CCG-II with an extended conformation.
(2S,3S,4R)-2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine, a potent and competitive inhibitor of both glial and neuronal uptake of glutamate.[Pubmed:7901789]
Neuropharmacology. 1993 Sep;32(9):833-7.
The effects of several diastereoisomers of L-2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (CCG) on L-glutamate uptake were compared among three different preparations, glial plasmalemmal vesicles (GPV), synaptosomes and cultured astrocytes from rat hippocampus. The (2S,3S,4R)-isomer (L-CCG-III) inhibited a Na(+)-dependent high-affinity L-glutamate uptake in GPV and synaptosomes in a dose dependent manner at a micromolar range. The potency was quite similar to that of L-threo-beta-hydroxyaspartate in both subcellular fractions and much higher than L-aspartate-beta-hydroxamate, which were known as potent inhibitors of glutamate uptake. The (2S,3R,4S)-isomer (L-CCG-IV) also inhibited the glutamate uptake in GPV and synaptosomes, but it was about 100 times less active than L-CCG-III. The (2S,3S,4S)- and (2S,3R,4R)-isomers (L-CCG-I and L-CCG-II, respectively) hardly showed any inhibitory action on the glutamate uptake. Dixon plot analysis of the initial uptake rate revealed that the inhibition was in a competitive manner and the value of the inhibition constant (Ki) was about 1 microM in both GPV and synaptosomes. L-CCG-III effectively inhibited the glutamate uptake by cultured hippocampal astrocytes as well. These results suggested that L-CCG-III inhibited the glutamate uptake in both neurones and glial cells of the mammalian central nervous system in a similar manner.
2-(Carboxycyclopropyl)glycines: binding, neurotoxicity and induction of intracellular free Ca2+ increase.[Pubmed:1319341]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):195-202.
The excitatory actions of the eight stereoisomers of 2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (CCG), conformationally rigid glutamate analogues, were analyzed for the glutamate receptor subtypes by means of binding assays with rat brain membranes. All CCG isomers inhibited the binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazine-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid ([3H]CPP) to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The (2S,3R,4S) isomer (L-CCG-IV) was the most potent agonist for the NMDA receptor and its binding potency was 17- and 790-fold higher than that of L-glutamate and NMDA, respectively. The (2S,3S,4R) isomer (L-CCG-III) showed a potent inhibitory activity for [3H]D-aspartate uptake. Further, L-CCG-IV caused a marked increase of intracellular free Ca2+ concentration [( Ca2+]i) and potent neurotoxicity in the single rat cerebral cortical neurons in vitro, and both were blocked effectively by the NMDA antagonists. Significant correlations were observed between neurotoxicity and the increase of [Ca2+]i and [3H]CPP binding affinity to the NMDA receptor.
Potent NMDA-like actions and potentiation of glutamate responses by conformational variants of a glutamate analogue in the rat spinal cord.[Pubmed:2692753]
Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1213-24.
1. Neuropharmacological actions of all possible-state isomers of alpha-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (CCG), conformationally restricted analogues of glutamate, were examined for electrophysiological effects in the isolated spinal cord of the newborn rat. 2. Eight CCG stereoisomers demonstrated a large variety of depolarizing activities. Among them, the (2R, 3S, 4S) isomers of CCG (D-CCG-II) showed the most potent depolarizing activity, followed by the (2S, 3R, 4S) isomer (L-CCG-IV). 3. The depolarization evoked by L-CCG-IV, D-CCG-II and other D-CCG isomers was effectively depressed by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists. D-CCG-II was about 5 times more potent than NMDA in causing a depolarization. 4. The (2S, 3S, 4S) isomer of CCG (L-CCG-I) was more potent than L-glutamate in causing a depolarization of spinal motoneurones. The depolarization was slightly depressed by NMDA antagonists, but residual amplitudes of responses to L-CCG-I in the presence of NMDA antagonists We almost insensitive to 6,7-dinitro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX) or 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX), suggesting that L-CCG-I might be a novel potent agonist. 5. After application of the (2S, 3S, 4R) isomer of CCG (L-CCG-III), responses to L-glutamate, D- and L-aspartate were markedly enhanced. The enhancement lasted for a period of several hours without a further application of L-CCG-III. 6. L-CCG-III also caused a depolarization, but it seemed unlikely that the potentiation of the glutamate response was directly related to the depolarization evoked by L-CCG-III. 7. The potentiation might be due to inhibition of uptake processes, but L-CCG-III was superior to L-(-)-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate, a potent uptake inhibitor of L-glutamate and L-aspartate, in enhancing the response to L-glutamate in terms of amplitude and duration of responses. 8. CCG isomers should provide useful pharmacological tools for analysis of glutamate neurotransmitter systems.


