GLYX 13NMDA receptor partial agonist; acts at the glycine site CAS# 117928-94-6 |
- PDK1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1843
CAS No.:1001409-50-2
- Nemorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC4151
CAS No.:108852-90-0
- Siramesine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5134
CAS No.:224177-60-0
- Oleuropein
Catalog No.:BCN5246
CAS No.:32619-42-4
- Fluorouracil (Adrucil)
Catalog No.:BCC2135
CAS No.:51-21-8
- Deguelin
Catalog No.:BCN4804
CAS No.:522-17-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

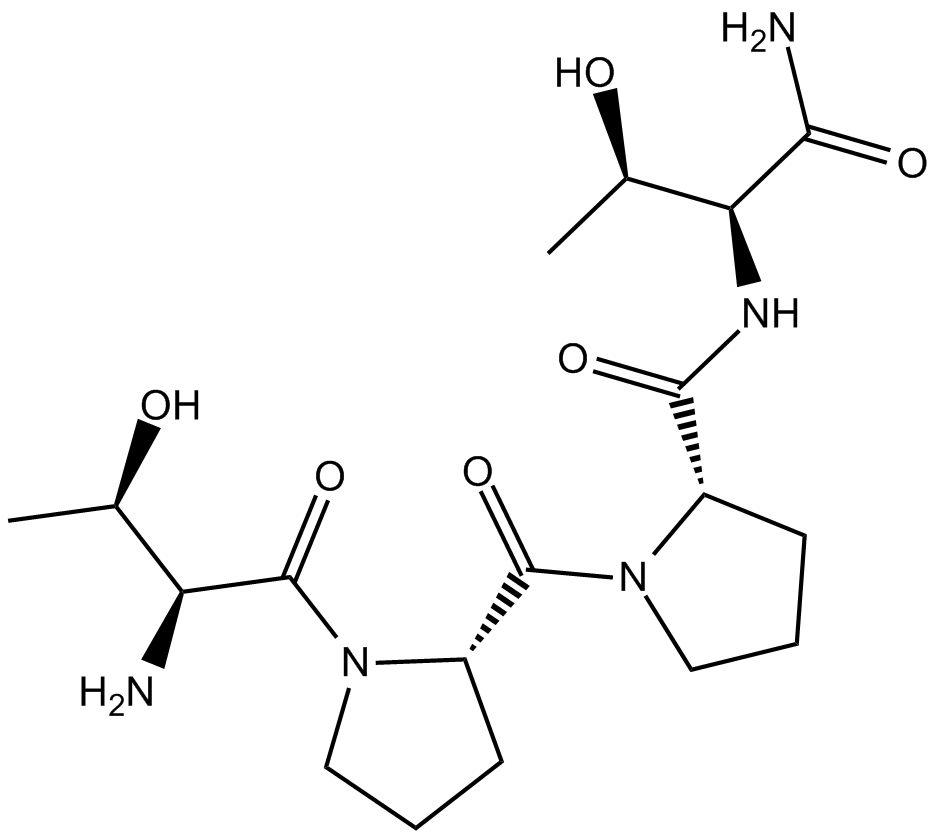
| Cas No. | 117928-94-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 14539800 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H31N5O6 | M.Wt | 413.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GLYX-13; Thr-Pro-Pro-Thr-NH2 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (77.39 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Sequence | TPPT (Modifications: Thr-4 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-1-[(2S)-1-[(2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]-N-[(2S,3R)-1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GIBQQARAXHVEGD-BSOLPCOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H31N5O6/c1-9(24)13(19)18(29)23-8-4-6-12(23)17(28)22-7-3-5-11(22)16(27)21-14(10(2)25)15(20)26/h9-14,24-25H,3-8,19H2,1-2H3,(H2,20,26)(H,21,27)/t9-,10-,11+,12+,13+,14+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NMDA receptor partial agonist that acts at the glycine site. Simultaneously acts as a promoter of the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) and as a suppressor of long-term depression (LTD). Exhibits nootropic, neuroprotective and antinociceptive activity, and enhances learning, memory and cognition in vivo. Brain penetrant. |

GLYX 13 Dilution Calculator

GLYX 13 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Rapastinel (GLYX-13) is an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) modulator that has characteristics of a glycine site partial agonist. Target: NMDA Rapastinel is a robust cognitive enhancer and facilitates hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic transmission in slices.
References:
[1]. Burgdorf J, et al. The long-lasting antidepressant effects of rapastinel (GLYX-13) are associated with a metaplasticity process in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 12;308:202-11.
- Boc-N-Me-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2611
CAS No.:117903-25-0
- Forsythoside H
Catalog No.:BCN6431
CAS No.:1178974-85-0
- 7,4'-Dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN3582
CAS No.:1178893-64-5
- Fmoc-Thr(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3550
CAS No.:117872-75-0
- L-CCG-lll
Catalog No.:BCC6608
CAS No.:117857-95-1
- L-CCG-l
Catalog No.:BCC6609
CAS No.:117857-93-9
- Loreclezole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7009
CAS No.:117857-45-1
- Ac-Asp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2880
CAS No.:117833-18-8
- Enterostatin
Catalog No.:BCC6050
CAS No.:117830-79-2
- 3,3',4',5,6,7,8-heptamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8203
CAS No.:1178-24-1
- NSC 23766
Catalog No.:BCC1149
CAS No.:1177865-17-6
- AP-III-a4
Catalog No.:BCC5292
CAS No.:1177827-73-4
- Luzindole
Catalog No.:BCC6826
CAS No.:117946-91-5
- Rabeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC5228
CAS No.:117976-89-3
- Rabeprazole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5227
CAS No.:117976-90-6
- Guanosine
Catalog No.:BCN2962
CAS No.:118-00-3
- Hydrastine
Catalog No.:BCC8187
CAS No.:118-08-1
- Cinchonine
Catalog No.:BCN2464
CAS No.:118-10-5
- Syringin
Catalog No.:BCN6059
CAS No.:118-34-3
- Trimethylgallic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3424
CAS No.:118-41-2
- Maltol
Catalog No.:BCN4819
CAS No.:118-71-8
- Ortho-Hydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3827
CAS No.:118-93-4
- Acetylepipodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN6056
CAS No.:1180-35-4
- Limonin
Catalog No.:BCN6057
CAS No.:1180-71-8
Anxiolytic effects of GLYX-13 in animal models of posttraumatic stress disorder-like behavior.[Pubmed:27147594]
J Psychopharmacol. 2016 Sep;30(9):913-21.
In the present study, we investigated the effectiveness of GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor glycine site functional partial agonist, to alleviate the enhanced anxiety and fear response in both a mouse and rat model of stress-induced behavioral changes that might be relevant to posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Studies over the last decades have suggested that the hyperactivity of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is one of the most consistent findings in stress-related disease. Herein, we used these animal models to further investigate the effect of GLYX-13 on the stress hormone levels and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. We found that exposure to foot shock induced long-lasting behavioral deficiencies in mice, including freezing and anxiety-like behaviors, that were significantly ameliorated by the long-term administration of GLYX-13 (5 or 10 mg/kg). Our enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results showed that long-term administration of GLYX-13 at behaviorally effective doses (5 or 10 mg/kg) significantly decreased the elevated serum levels of both corticosterone and its upstream stress hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone in rats subjected to the TDS procedure. These results suggest that GLYX-13 exerts a therapeutic effect on PTSD-like stress responding that is accompanied by (or associated with) modulation of the HPA axis, including inhibition of stress hormone levels and upregulation of hippocampal GR expression.
The Development of Rapastinel (Formerly GLYX-13); A Rapid Acting and Long Lasting Antidepressant.[Pubmed:26997507]
Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(1):47-56.
BACKGROUND: Rapastinel (GLYX-13) is a NMDA receptor modulator with glycine-site partial agonist properties. It is a robust cognitive enhancer and shows rapid and long-lasting antidepressant properties in both animal models and in humans. METHODS: Rapastinel was derived from a monoclonal antibody, B6B21, is a tetrapeptide (threonine-proline-proline-threonine-amide) obtained from amino acid sequence information obtained from sequencing one of the hypervariable regions of the light chain of B6B21. The in-vivo and in-vitro pharmacology of rapastinel was examined. RESULTS: Rapastinel was found to be a robust cognitive enhancer in a variety of learning and memory paradigms and shows marked antidepressant-like properties in multiple models including the forced swim (Porsolt), learned helplessness and chronic unpredictable stress. Rapastinel's rapid-acting antidepressant properties appear to be mediated by its ability to activate NMDA receptors leading to enhancement in synaptic plasticity processes associated with learning and memory. This is further substantiated by the increase in mature dendritic spines found 24 hrs after rapastinel treatment in both the rat dentate gyrus and layer five of the medial prefrontal cortex. Moreover, ex vivo LTP studies showed that the effects of rapastinel persisted at least two weeks post-dosing. CONCLUSION: These data suggest that rapastinel has significant effects on metaplasticity processes that may help explain the long lasting antidepressant effects of rapastinel seen in the human clinical trial results.
GLYX-13 Produces Rapid Antidepressant Responses with Key Synaptic and Behavioral Effects Distinct from Ketamine.[Pubmed:27634355]
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 May;42(6):1231-1242.
GLYX-13 is a putative NMDA receptor modulator with glycine-site partial agonist properties that produces rapid antidepressant effects, but without the psychotomimetic side effects of ketamine. Studies were conducted to examine the molecular, cellular, and behavioral actions of GLYX-13 to further characterize the mechanisms underlying the antidepressant actions of this agent. The results demonstrate that a single dose of GLYX-13 rapidly activates the mTORC1 pathway in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), and that infusion of the selective mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin into the medial PFC (mPFC) blocks the antidepressant behavioral actions of GLYX-13, indicating a requirement for mTORC1 similar to ketamine. The results also demonstrate that GLYX-13 rapidly increases the number and function of spine synapses in the apical dendritic tuft of layer V pyramidal neurons in the mPFC. Notably, GLYX-13 significantly increased the synaptic responses to hypocretin, a measure of thalamocortical synapses, compared with its effects on 5-HT responses, a measure of cortical-cortical responses mediated by the 5-HT2A receptor. Behavioral studies further demonstrate that GLYX-13 does not influence 5-HT2 receptor induced head twitch response or impulsivity in a serial reaction time task (SRTT), whereas ketamine increased responses in both tests. In contrast, both GLYX-13 and ketamine increased attention in the SRTT task, which is linked to hypocretin-thalamocortical responses. The differences in the 5-HT2 receptor synaptic and behavioral responses may be related to the lack of psychotomimetic side effects of GLYX-13 compared with ketamine, whereas regulation of the hypocretin responses may contribute to the therapeutic benefits of both rapid acting antidepressants.
The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulator GLYX-13 enhances learning and memory, in young adult and learning impaired aging rats.[Pubmed:19446371]
Neurobiol Aging. 2011 Apr;32(4):698-706.
NMDA receptor (NMDAR) activity has been strongly implicated in both in vitro and in vivo learning models and the decline in cognitive function associated with aging and is linked to a decrease in NMDAR functional expression. GLYX-13 is a tetrapeptide (Thr-Pro-Pro-Thr) which acts as a NMDAR receptor partial agonist at the glycine site. GLYX-13 was administered to young adult (3 months old) and aged (27-32 months old) Fischer 344 X Brown Norway F1 rats (FBNF1), and behavioral learning tested in trace eye blink conditioning (tEBC), a movable platform version of the Morris water maze (MWM), and alternating t-maze tasks. GLYX-13 (1mg/kg, i.v.) enhanced learning in both young adult and aging animals for MWM and alternating t-maze, and increased tEBC in aging rats. We previously showed optimal enhancement of tEBC in young adult rats given GLYX-13 at the same dose. Of these learning tasks, the MWM showed the most robust age related deficit in learning. In the MWM, GLYX-13 enhancement of learning was greater in the old compared to the young adult animals. Examination of the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampal slices showed that aged rats showed marked, selective impairment in the magnitude of LTP evoked by a sub-maximal tetanus, and that GLYX-13 significantly enhanced the magnitude of LTP in slices from both young adult and aged rats without affecting LTD. These data, combined with the observation that the GLYX-13 enhancement of learning was greater in old than in young adult animals, suggest that GLYX-13 may be a promising treatment for deficits in cognitive function associated with aging.
Antinociceptive action of GLYX-13: an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor glycine site partial agonist.[Pubmed:18580579]
Neuroreport. 2008 Jul 2;19(10):1059-61.
Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-mediated neurotransmission has been demonstrated to provide antinociceptive actions in a number of animal models of tonic and neuropathic pain. However, both competitive and noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists are ataxic at analgesic doses. Partial agonists and antagonists of the NMDA-associated glycine site have demonstrated antinociceptive actions at doses that are not ataxic. In this study, we present data showing that GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor, glycine-site, partial agonist, also is antinociceptive in the rat formalin model of tonic pain and in the rat constriction nerve injury model of neuropathic pain at doses not inducing ataxia.
A NMDA receptor glycine site partial agonist, GLYX-13, simultaneously enhances LTP and reduces LTD at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampus.[Pubmed:18796308]
Neuropharmacology. 2008 Dec;55(7):1238-50.
N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors (NMDARs) are a key route for Ca2+ influx into neurons important to both activity-dependent synaptic plasticity and, when uncontrolled, triggering events that cause neuronal degeneration and death. Among regulatory binding sites on the NMDAR complex is a glycine binding site, distinct from the glutamate binding site, which must be co-activated for NMDAR channel opening. We developed a novel glycine site partial agonist, GLYX-13, which is both nootropic and neuroprotective in vivo. Here, we assessed the effects of GLYX-13 on long-term synaptic plasticity and NMDAR transmission at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampal slices in vitro. GLYX-13 simultaneously enhanced the magnitude of long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic transmission, while reducing long-term depression (LTD). GLYX-13 reduced NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons evoked by low frequency Schaffer collateral stimulation, but enhanced NMDAR currents during high frequency bursts of activity, and these actions were occluded by a saturating concentration of the glycine site agonist d-serine. Direct two-photon imaging of Schaffer collateral burst-evoked increases in [Ca2+] in individual dendritic spines revealed that GLYX-13 selectively enhanced burst-induced NMDAR-dependent spine Ca2+ influx. Examining the rate of MK-801 block of synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDAR-gated channels revealed that GLYX-13 selectively enhanced activation of burst-driven extrasynaptic NMDARs, with an action that was blocked by the NR2B-selective NMDAR antagonist ifenprodil. Our data suggest that GLYX-13 may have unique therapeutic potential as a learning and memory enhancer because of its ability to simultaneously enhance LTP and suppress LTD.
GLYX-13: a monoclonal antibody-derived peptide that acts as an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulator.[Pubmed:16051282]
Neuropharmacology. 2005 Dec;49(7):1077-87.
We previously created a monoclonal antibody (MAb), B6B21, that acts as a partial agonist at the glycine site of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor [Moskal, J.R., Schaffner, A.E., 1986. Monoclonal antibodies to the dentate gyrus: immunocytochemical characterization and flow cytometric analysis of hippocampal neurons bearing a unique cell-surface antigen. J. Neurosci. 6, 2045-2053.]. The hypervariable region of the light chain of B6B21 was cloned and sequenced. Peptides were then synthesized based on this sequence information and screened using rat hippocampal membrane preparations to measure [(3)H]MK-801 binding in the presence of 7-chlorokynurenic acid, a glycine site-specific competitive inhibitor of NMDA receptor [Moskal, J.R., Yamamoto, H., Colley, P.A., 2001. The use of antibody engineering to create novel drugs that target N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Curr. Drug Targets 2, 331-345.]. Peptides that were able to increase [(3)H]MK-801 binding in a dose-dependent manner under these conditions were named Glyxins. Here we report that GLYX-13, a tetrapeptide (TPPT-amide), was found to readily cross the blood-brain barrier and modulate the NMDA receptor in a glycine-like fashion when examined pharmacologically and electrophysiologically. When GLYX-13 was administered to rats at 0.5-1.0mg/kg i.v., a significant enhancement in learning was observed using a hippocampus-dependent trace eye blink conditioning paradigm. These data indicate that the Glyxins are a new class of NMDA receptor modulators that may have therapeutic potential. Based on the broad agonist range in vitro and the potent cognitive-enhancing properties in a valid in vivo model of learning, GLYX-13 is a new drug candidate with potential for the treatment of cognitive disorders.


