Trimethylgallic acidCAS# 118-41-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 118-41-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 8357 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H12O5 | M.Wt | 212.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
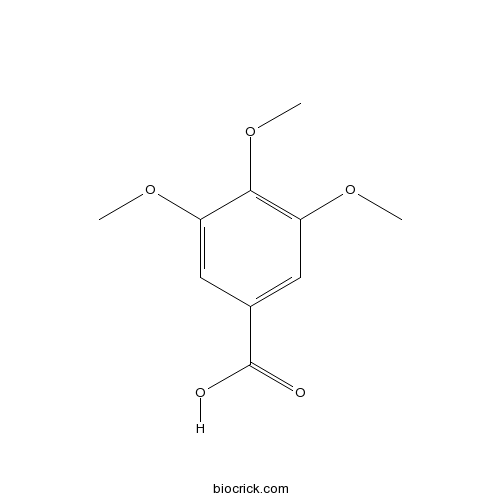
| Chemical Name | 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SJSOFNCYXJUNBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12O5/c1-13-7-4-6(10(11)12)5-8(14-2)9(7)15-3/h4-5H,1-3H3,(H,11,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Trimethylgallic acid esters are potent antioxidants and inhibitor of cytokine production, can ameliorate chronic stress-induced various behavioral and biochemical alterations in mice, showing protective effects against chronic stress; they also exert hepatoprotective effects in CCl4-induced rats, specifically by modulating oxidative-nitrosative stress and inflammation. |
| Targets | TNF-α |
| In vivo | Effect of trimethylgallic acid esters against chronic stress-induced anxiety-like behavior and oxidative stress in mice.[Pubmed: 24948061 ]Pharmacological Reports Pr, 2014, 66(4): 606-12.
Hepatoprotective effect of trimethylgallic acid esters against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats.[Pubmed: 26742325]Indian J. Exp. Biol., 2015, 53(12):803-9.Gallic acid and its derivatives are potential therapeutic agents for treating various oxidative stress mediated disorders. |

Trimethylgallic acid Dilution Calculator

Trimethylgallic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.7125 mL | 23.5627 mL | 47.1254 mL | 94.2507 mL | 117.8134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9425 mL | 4.7125 mL | 9.4251 mL | 18.8501 mL | 23.5627 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4713 mL | 2.3563 mL | 4.7125 mL | 9.4251 mL | 11.7813 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0943 mL | 0.4713 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.885 mL | 2.3563 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0471 mL | 0.2356 mL | 0.4713 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.1781 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Syringin
Catalog No.:BCN6059
CAS No.:118-34-3
- Cinchonine
Catalog No.:BCN2464
CAS No.:118-10-5
- Hydrastine
Catalog No.:BCC8187
CAS No.:118-08-1
- Guanosine
Catalog No.:BCN2962
CAS No.:118-00-3
- Rabeprazole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5227
CAS No.:117976-90-6
- Rabeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC5228
CAS No.:117976-89-3
- Luzindole
Catalog No.:BCC6826
CAS No.:117946-91-5
- GLYX 13
Catalog No.:BCC6013
CAS No.:117928-94-6
- Boc-N-Me-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2611
CAS No.:117903-25-0
- Forsythoside H
Catalog No.:BCN6431
CAS No.:1178974-85-0
- 7,4'-Dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN3582
CAS No.:1178893-64-5
- Fmoc-Thr(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3550
CAS No.:117872-75-0
- Maltol
Catalog No.:BCN4819
CAS No.:118-71-8
- Ortho-Hydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3827
CAS No.:118-93-4
- Acetylepipodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN6056
CAS No.:1180-35-4
- Limonin
Catalog No.:BCN6057
CAS No.:1180-71-8
- Blumeatin
Catalog No.:BCN6055
CAS No.:118024-26-3
- PHM 27 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5869
CAS No.:118025-43-7
- Eriodictyol-6-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8026
CAS No.:118040-45-2
- 4-O-Methylgrifolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7287
CAS No.:118040-60-1
- 7-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)chroman
Catalog No.:BCN3578
CAS No.:1180504-64-6
- PS 48
Catalog No.:BCC7859
CAS No.:1180676-32-7
- Dihydroprehelminthosporol
Catalog No.:BCN7288
CAS No.:118069-95-7
- Zoledronic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC1067
CAS No.:118072-93-8
Effect of trimethylgallic acid esters against chronic stress-induced anxiety-like behavior and oxidative stress in mice.[Pubmed:24948061]
Pharmacol Rep. 2014 Aug;66(4):606-12.
BACKGROUND: Many studies have shown that the levels of oxidative stress (increased lipid peroxidation, decreased glutathione levels and endogenous antioxidant enzyme activities) and proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-alpha) are increased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Gallic acid and other phenolic compounds are potent antioxidants and inhibitor of cytokine production. The present study was designed to investigate the effect of newly synthesized conjugated esters of Trimethylgallic acid in an experimental model of chronic stress. METHODS: The animals were forced to swim individually for a period of 6min every day for 15 days to induce chronic stress. The locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, and memory retention were evaluated in chronically stressed animals, followed by biochemical estimations and neuroinflammatory surge in the brain. RESULTS: Chronic treatment with Trimethylgallic acid esters for 15 days significantly reversed the chronic stress-induced behavioral (impaired locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, and decreased percentage of memory retention), biochemical (increased lipid peroxidation and nitrite levels; decreased glutathione levels, superoxide dismutase and catalase activities), and inflammation surge (serum TNF-alpha) in stressed mice. CONCLUSIONS: The study revealed that Trimethylgallic acid esters could ameliorate chronic stress-induced various behavioral and biochemical alterations in mice, showing protective effects against chronic stress.
Hepatoprotective effect of trimethylgallic acid esters against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats.[Pubmed:26742325]
Indian J Exp Biol. 2015 Dec;53(12):803-9.
Gallic acid and its derivatives are potential therapeutic agents for treating various oxidative stress mediated disorders. In the present study, we investigated the hepatoprotective effects of newly synthesized conjugated Trimethylgallic acid (TMGA) esters against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Animals were pre-treated with TMGA esters at their respective doses for 7 days against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. The histopathological changes were evaluated to find out degenerative fatty changes including vacuole formation, inflammation and tissue necrosis. Various biomarkers of oxidative stress (lipid peroxidation, glutathione levels, and endogenous antioxidant enzyme activities), liver enzymes (AST and ALT), triacylglycerol and cholesterol were evaluated. Pre-treatment with TMGA esters (MRG, MGG, MSG, and MUG at the dose of 28.71, 30.03, 31.35, 33.62 mg/kg/day), respectively reversed the CCl4-induced liver injury scores (reduced vacuole formation, inflammation and necrosis), biochemical parameters of plasma (increased AST, ALT, TG, and cholesterol), antioxidant enzymes (increased lipid peroxidation and nitrite levels; decreased glutathione levels, superoxide dismutase and catalase activities) in liver tissues and inflammatory surge (serum TNF-alpha) significantly. The study revealed that TMGA esters exerted hepatoprotective effects in CCl4-induced rats, specifically by modulating oxidative-nitrosative stress and inflammation.


