OvatodiolideCAS# 3484-37-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

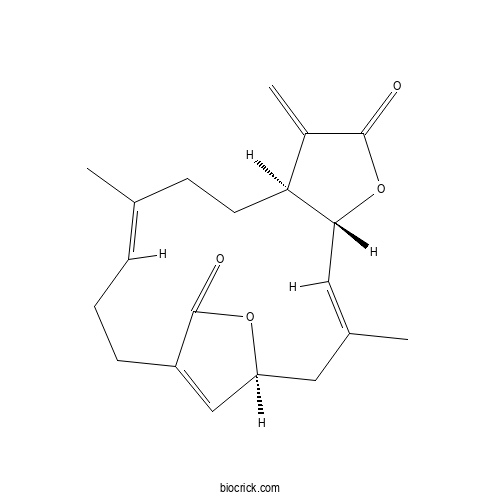
| Cas No. | 3484-37-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 38347030.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24O4 | M.Wt | 328.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1S,3E,5R,9S,12E)-3,12-dimethyl-8-methylidene-6,18-dioxatricyclo[14.2.1.05,9]nonadeca-3,12,16(19)-triene-7,17-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CCCC2=CC(CC(=CC3C(CC1)C(=C)C(=O)O3)C)OC2=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KTYZKXFERQUCPX-SIKGVNBJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24O4/c1-12-5-4-6-15-11-16(23-20(15)22)9-13(2)10-18-17(8-7-12)14(3)19(21)24-18/h5,10-11,16-18H,3-4,6-9H2,1-2H3/b12-5+,13-10+/t16-,17-,18+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ovatodiolide Dilution Calculator

Ovatodiolide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.045 mL | 15.2249 mL | 30.4497 mL | 60.8995 mL | 76.1244 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.609 mL | 3.045 mL | 6.0899 mL | 12.1799 mL | 15.2249 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3045 mL | 1.5225 mL | 3.045 mL | 6.0899 mL | 7.6124 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.609 mL | 1.218 mL | 1.5225 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0304 mL | 0.1522 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.609 mL | 0.7612 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Anisomelic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1000
CAS No.:59632-76-7
- Apigenin triacetate
Catalog No.:BCX0999
CAS No.:3316-46-9
- Homodihydrocapsaicin II
Catalog No.:BCX0998
CAS No.:71239-21-9
- Neopuerarin B
Catalog No.:BCX0997
CAS No.:1150314-39-8
- Hericene D
Catalog No.:BCX0996
CAS No.:1343477-87-1
- Maltononaose
Catalog No.:BCX0995
CAS No.:6471-60-9
- Maltodecaose
Catalog No.:BCX0994
CAS No.:6082-21-9
- 1,3-Disinapoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCX0993
CAS No.:1423128-15-7
- S-Isogambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0992
CAS No.:942623-57-6
- Forbesione
Catalog No.:BCX0991
CAS No.:180961-63-1
- (9Z,11E)-13-Oxo-9,11-octadecadienoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCX0990
CAS No.:54739-30-9
- 5-Methoxyisosakuranin
Catalog No.:BCX0989
CAS No.:59942-61-9
- Neohesperidose
Catalog No.:BCX1002
CAS No.:17074-02-1
- α-Glucosyl Hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCX1003
CAS No.:161713-86-6
- Hericene B
Catalog No.:BCX1004
CAS No.:157207-55-1
- Hericene A
Catalog No.:BCX1005
CAS No.:157207-54-0
- Euphorbetin
Catalog No.:BCX1006
CAS No.:35897-99-5
- Alitame hydrate
Catalog No.:BCX1007
CAS No.:99016-42-9
- Isomaltooctaose
Catalog No.:BCX1008
CAS No.:35867-37-9
- Isomaltoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX1009
CAS No.:6513-12-8
- Isomaltohexaose
Catalog No.:BCX1010
CAS No.:6175-02-6
- Isomaltopentaose
Catalog No.:BCX1011
CAS No.:6082-32-2
- Isomaltotetraose
Catalog No.:BCX1012
CAS No.:35997-20-7
- 6'-Hydroxy-3,4,2',3',4'-pentamethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCX1013
CAS No.:114021-62-4
Ovatodiolide induces autophagy-mediated cell death through the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.[Pubmed:38000454]
Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Jan 5;387:110819.
Ovatodiolide is a macrocyclic diterpenoid compound with various biological activities that displays considerable anticancer potential in different tumor models. However, the underlying mechanism for this antineoplastic activity remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the anticancer effect and possible molecular mechanism of Ovatodiolide in human chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Ovatodiolide suppressed cell colony formation and induced apoptosis in the K562 and KU812 cells. We also observed that Ovatodiolide enhanced the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), activated Nrf2 signaling, and inhibited mTOR phosphorylation. Autophagic flux was shown to be enhanced after treatment with Ovatodiolide in K562 cells. Furthermore, autophagy inhibition alleviated Ovatodiolide-induced cell apoptosis, whereas autophagy promotion aggravated apoptosis in CML cells. These results demonstrated that Ovatodiolide activates autophagy-mediated cell death in CML cells. Additionally, Ovatodiolide transcriptionally activated the expression of p62, and the p62 levels were negatively regulated by autophagy. Moreover, p62-Keap1-Nrf2 signaling was confirmed to be involved in Ovatodiolide-induced cell death. Accordingly, LC3B knockdown augmented the Ovatodiolide-induced p62 expression, increased the p62-Keap1 interaction, and enhanced the translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus. In contrast, p62 inhibition abolished the effects that were induced through Ovatodiolide treatment. Nrf2 inhibition with ML385 diminished the protective effect of autophagy inhibition in CML cells. Collectively, our results indicate that Ovatodiolide induces oxidative stress and provokes autophagy, which effectively decreases the expression of p62 and weakens the protective effect of Nrf2 signaling activation, thus contributing to apoptosis in CML cells.
Anisomeles indica Extracts and Their Constituents Suppress the Protein Expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 In Vivo and In Vitro.[Pubmed:37894745]
Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 11;24(20):15062.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), stemming from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has had a profound global impact. This highly contagious pneumonia remains a significant ongoing threat. Uncertainties persist about the virus's effects on human health, underscoring the need for treatments and prevention. Current research highlights angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) as key targets against SARS-CoV-2. The virus relies on ACE2 to enter cells and TMPRSS2 to activate its spike protein. Inhibiting ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression can help prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infections. Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze, a medicinal plant in traditional Chinese medicine, shows various promising pharmacological properties. In this study, ethanolic extracts of A. indica were examined both in vivo (250 and 500 muM) and in vitro (500 muM). Through Western blotting analysis, a significant reduction in the expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 proteins was observed in HepG2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma) cells and HEK 293T (human embryonic kidney) cell lines without inducing cellular damage. The principal constituents of A. indica, namely, Ovatodiolide (5 and 10 muM), anisomlic acid (5 and 10 muM), and apigenin (12.5 and 25 muM), were also found to produce the same effect. Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis of mouse liver, kidney, and lung tissues demonstrated a decrease in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 protein expression levels. Consequently, this article suggests that A. indica and its constituents have the potential to reduce ACE2 and TMPRSS2 protein expression levels, thus aiding in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress.[Pubmed:37764856]
Nutrients. 2023 Sep 20;15(18):4074.
A high-fat diet (HFD) is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Many pure compounds have been demonstrated to be effective in treating cardiovascular diseases. In this study, we investigated the alleviating effects of oral Ovatodiolide and antcin K (OAK) supplements on HFD-induced cardiovascular dysfunction in apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-knockout mice. Cardiovascular dysfunction was induced in ApoE-knockout mice by feeding them an HFD for 12 weeks. The degree of cardiovascular dysfunction was assessed through echocardiography, hematological and biochemical analyses, and immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical staining. The HFD-fed mice exhibited cardiovascular dysfunction-abnormal blood biochemical index. The arterial wall tissue exhibited the marked deposition of lipids, upregulated expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and CD36 receptors, and downregulated expression of the ABCA1 receptor. Macrophages isolated from the peritoneal cavity of the mice exhibited increased levels of lipid accumulation, reactive oxygen species, and CD11b expression but reduced mitochondrial membrane potential. The expression of superoxide dismutase 2 was downregulated and that of tumor necrosis factor-alpha was upregulated in the myocardial tissue. Oral OAK supplements twice a day for 12 weeks significantly mitigated HFD-induced cardiovascular dysfunction in the experimental mice. Oral OAK supplements appear to be a promising strategy for treating HFD-induced cardiovascular dysfunction. The underlying mechanisms may involve the reduction of lipid accumulation in the artery and oxidative stress and inflammation in the cardiovascular tissue.
N-methylpiperazine-diepoxyovatodiolide ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis via suppressing TGF-beta/Smad and JAK/STAT signaling pathway.[Pubmed:37268199]
Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Sep 1;382:110589.
Peritoneal fibrosis (PF) is the main cause of peritoneal ultrafiltration failure in patients undergoing long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is the key pathogenesis of PF. However, currently, no specific treatments are available to suppress PF. N-methylpiperazine-diepoxyOvatodiolide (NMPDOva) is a newly synthesized compound that involves a chemical modification of Ovatodiolide. In this study, we aimed to explore the antifibrotic effects of NMPDOva in PD-related PF and underlying mechanisms. A mouse model of PD-related PF was established via daily intraperitoneal injection of 4.25% glucose PD fluid. In vitro studies were performed using the transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1)-stimulated HMrSV5 cell line. Pathological changes were observed, and fibrotic markers were significantly elevated in the peritoneal membrane in mice model of PD-related PF. However, NMPDOva treatment significantly alleviated PD-related PF by decreasing the extracellular matrix accumulation. NMPDOva treatment decreased the expression of fibronectin, collagen Ⅰ, and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) in mice with PD-related PF. Moreover, NMPDOva could alleviate TGF-beta1-induced EMT in HMrSV5 cells, inhibited phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Smad2/3, and increased the expression of Smad7. Meanwhile, NMPDOva inhibited phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3. Collectively, these results indicated that NMPDOva prevents PD-related PF by inhibiting the TGF-beta1/Smad and JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Therefore, because of these antifibrotic effects, NMPDOva may be a promising therapeutic agent for PD-related PF.
Ovatodiolide inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through suppression of the TGF-beta/TbetaRs signaling pathway.[Pubmed:36906971]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114481.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection continues to pose threats to public health. The clinical manifestations of lung pathology in COVID-19 patients include sustained inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis. The macrocyclic diterpenoid Ovatodiolide (OVA) has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-allergic, and analgesic activities. Here, we investigated the pharmacological mechanism of OVA in suppressing SARS-CoV-2 infection and pulmonary fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Our results revealed that OVA was an effective SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitor and showed remarkable inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 infection. On the other hand, OVA ameliorated pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin (BLM)-induced mice, reducing inflammatory cell infiltration and collagen deposition in the lung. OVA decreased the levels of pulmonary hydroxyproline and myeloperoxidase, as well as lung and serum TNF-a, IL-1beta, IL-6, and TGF-beta in BLM-induced pulmonary fibrotic mice. Meanwhile, OVA reduced the migration and fibroblast-to-myofibroblast conversion of TGF-beta1-induced fibrotic human lung fibroblasts. Consistently, OVA downregulated TGF-beta/TbetaRs signaling. In computational analysis, OVA resembles the chemical structures of the kinase inhibitors TbetaRI and TbetaRII and was shown to interact with the key pharmacophores and putative ATP-binding domains of TbetaRI and TbetaRII, showing the potential of OVA as an inhibitor of TbetaRI and TbetaRII kinase. In conclusion, the dual function of OVA highlights its potential for not only fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection but also managing injury-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Gastroprotective Effect of Anisomeles indica on Aspirin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice.[Pubmed:36552535]
Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;11(12):2327.
Gastric ulcers are commonly seen in the upper gastrointestinal tract and may be related to the Helicobacter pylori infection and the use of aspirin, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Typically, proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are used to treat gastric ulcers; however, adverse effects have emerged following long-term treatment. Natural medicines are used as alternative therapeutic agents in the treatment of gastric ulcers, with few side effects. Despite various reports on the anti-H. pylori and anti-gastric cancer activities of Anisomeles indica, its gastroprotective effect on ulcers remains undetermined. This study investigated the protective effect of A. indica on aspirin-induced gastric ulcers in murine models. Our results show that three fractions of ethanol-extracted A. indica inhibited aspirin-induced gastric injury. Among these, A. indica Fraction 1 was observed to enrich Ovatodiolide, which effectively diminished gastric acidity and alleviated aspirin-induced inflammation in the stomach. Our results provide evidence that A. indica could be developed as an effective therapeutic agent for gastroprotective purposes.
Ovatodiolide and antrocin synergistically inhibit the stemness and metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma via impairing ribosome biogenesis and modulating ERK/Akt-mTOR signaling axis.[Pubmed:36265255]
Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154478.
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and PI3K signaling confers resistance against sorafenib, a mainstay treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Antrocin and Ovatodiolide constitute as the most potent secondary metabolites isolated from Antrodia camphorata and Anisomeles indica, respectively. Both natural compounds have recently gained a lot of attention due to their putative inhibition of MAPK and PI3K signaling in various solid cancers. However, whether their combination is effective in HCC remains unknown. Here, we investigated their effect, alone or in various combinations, on MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways in HCC cells. An array of in vitro study were used to investigate anticancer and stemness effects to treat HCC, such as cytotoxicity, drug combination index, migration, invasion, colony formation, and tumor sphere formation. Drug effect in vivo was evaluated using mouse xenograft models. In this study, antrocin and Ovatodiolide synergistically inhibited the SNU387, Hep3B, Mahlavu, and Huh7 cell lines. Sequential combination treatment of Huh7 and Mahlavu with Ovatodiolide followed by antrocin resulted stronger cytotoxic effect than did treatment with antrocin followed by Ovatodiolide, their simultaneous administration, antrocin alone, or Ovatodiolide alone. In the Huh7 and Mahlavu cell lines, Ovatodiolide-->antrocin significantly suppressed colony formation and proliferation as well as markedly downregulated ERK1/2, Akt, and mTOR expression. Inhibition of ERK1/2 and Akt/mTOR signaling by Ovatodiolide-->antrocin suppressed ribosomal biogenesis, autophagy, and cancer stem cell-like phenotypes and promoted apoptosis in Huh7 and Mahlavu cells. The sorafenib-resistant clone of Huh7 was effectively inhibited by synergistic combination of both compound in vitro. Eventually, the Ovatodiolide-->antrocin combination synergistically suppressed the growth of HCC xenografts. Taken together, our findings suggested that Ovatodiolide-->antrocin combination may represent potential therapeutic approach for patients with advanced HCC.
Innovative Purification Method of Ovatodiolide from Anisomeles indica to Induce Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:35163851]
Molecules. 2022 Jan 18;27(3):587.
Ovatodiolide (Ova), found in the plant Anisomeles indica (AI), has been reported to have an anti-proliferation effect in various cancer cells. However, little information is available regarding the anti-cancer effect of Ova in human gastric cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the inhibitory effects and the mechanisms of action responsible for these effects on human AGS cell lines from a newly developed purification technique for Ova from AI extract. Extract obtained at the optimum condition of 95% ethanol extraction of AI was sequentially partitioned by using different polarity solvents. Enriched content of Ova (35.9% purity) from the n-hexane fraction was then applied to the purification by using centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) in a two-phase solvent system consisting of n-hexane:ethyl acetate:methanol:water (1.0:1.0:1.0:1.0, v/v/v/v) to reach purity over >95.0%. In evaluation of the anti-proliferation effect on AGS cells, Ova induced cell apoptosis with IC(50) values of 13.02 and 6.18 muM at 24 and 48 h, respectively, and arrested the cells at the G2/M phase. Quantification of Bax/Bcl2 mRNA expressions using qPCR showed a 2.5-fold increase in the Ova (5 muM)-treated cells at 48 h than in the control group. Specific protein expression data warrant further research to further confirm the proposed Ova-induced apoptotic pathway in AGS cells.
Identification of a Novel Theranostic Signature of Metabolic and Immune-Inflammatory Dysregulation in Myocardial Infarction, and the Potential Therapeutic Properties of Ovatodiolide, a Diterpenoid Derivative.[Pubmed:35163208]
Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 24;23(3):1281.
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a multifactorial global disease, recognized as one of the leading causes of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Timely and correct diagnoses and effective treatments could significantly reduce incidence of complications and improve patient prognoses. In this study, seven unconventional differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (MAN2A2, TNFRSF12A, SPP1, CSNK1D, PLAUR, PFKFB3, and CXCL16, collectively termed the MTSCPPC signature) were identified through integrating DEGs from six MI microarray datasets. The pathological and theranostic roles of the MTSCPPC signature in MI were subsequently analyzed. We evaluated interactions of the MTSCPPC signature with Ovatodiolide, a bioactive compound isolated from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze, using in silico molecular docking tools and compared it to specific inhibitors of the members of the MTSCPPC signature. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of the public databases revealed high expression levels of the MTSCPPC signature in immune cells of adult human hearts during an MI event. The MTSCPPC signature was significantly associated with the cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions, chemokine signaling, immune and inflammatory responses, and metabolic dysregulation in MI. Analysis of a micro (mi)RNA regulatory network of the MTSCPPC signature suggested post-transcriptional activation and the roles of miRNAs in the pathology of MI. Our molecular docking analysis suggested a higher potential for Ovatodiolide to target MAN2A2, CSNK1D, and TNFRSF12A. Collectively, the results derived from the present study further advance our understanding of the complex regulatory mechanisms of MI and provide a potential MI theranostic signature with Ovatodiolide as a therapeutic candidate.
Ovatodiolide protects ischemia-reperfusion-induced neuronal injury via microglial neuroinflammation via mediating SIRT1/NF-kappaB pathway.[Pubmed:34968641]
Brain Res Bull. 2022 Mar;180:97-107.
BACKGROUND: Ovatodiolide (OVA), a bioactive substance extracted from the bioactive component of Anisomeles indica, is reported to be endowed with anti-inflammatory properties. Nonetheless, its function in ischemia-reperfusion (I/R)-induced neurological deficits and microglial inflammation remains unclear. METHOD: A middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was set up in SD rats, which were then dealt with varying doses of OVA. The rats' neurological functions were estimated at diverse periods postoperatively. The dry and wet method, triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, and Nissl's staining were conducted to measure brain edema, cerebral infarction area and neuronal damage, respectively. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to detect neuronal apoptosis and microglial activation, and the profiles of inflammatory factors in the cerebral tissues were estimated by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). In-vitro assays were implemented on HT22 neuronal cells and BV2 microglia to elaborate the effect of OVA against oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-mediated effects. RESULTS: OVA relieved HT22 cell apoptosis and eased inflammation in BV2 microglia, which were induced by OGD. OVA mitigated NF-kappaB phosphorylation in BV2 cells, whereas boosted SIRT1 expression. However, inhibiting SIRT1 abolished the anti-inflammatory effects of OVA in BV2 microglia under OGD stimulation. The condition medium (CM) of OGD-treated BV2 cells enhanced HT22 cell apoptosis and damage. OVA treatment in BV2 cells relieved BV2-mediated injury on HT22 cells, which was reversed by SIRT1 inhibitor. In-vivo results revealed that OVA dose-dependently attenuated I/R rats' neurological deficits, reduced brain edema, cerebral infarction area, neuronal apoptosis and microglial overactivation. Additionally, OVA inactivated the NF-kappaB pathway and up-regulated SIRT1 in the I/R rat model. CONCLUSION: OVA prevented rats from brain I/R damage by hampering neuronal apoptosis and microglial inflammation via the SIRT1-NF-kappaB pathway. DATA AVAILABILITY: The data sets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Genotoxicity and 28-day repeated dose oral toxicity study of ovatodiolide in rats.[Pubmed:34722163]
Toxicol Rep. 2021 Oct 11;8:1783-1791.
Ovatodiolide is a bioactive cembrane-type diterpenoid isolated from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze. It has been proven that Ovatodiolide is anti-inflammatory, anti-tumorigenic, anti-melanogenic and attenuates asthma by regulating signaling pathways. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety of Ovatodiolide by conducting genotoxicity tests and 28-day oral toxicity tests in rats. Genotoxicity assays were conducted by using a bacterial reverse mutation test and mammalian chromosomal aberration test to assess whether Ovatodiolide causes reverse mutations and mutagenicity with or without metabolism activation. For the in vivo mammalian erythrocyte micronucleus test, mice were administered a single dose of 0, 250, 500 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. Ovatodiolide by single gavage. In the acute oral toxicity test, rats were given a single dose of Ovatodiolide 1000 mg/kg b.w. by single gavage. In the 28-day oral toxicity test, groups were divided into a control, Ovatodiolide 10, 25 and 50 mg/kg b.w. The results showed that there was no mutagenicity in the bacterial reverse mutation test or the mammalian chromosomal aberration test with or without S9 fraction. Ovatodiolide did not produce an increase in micronucleated reticulocytes in the micronucleus test. The results revealed that the acute oral toxicity of Ovatodiolide is over 1000 mg/kg b.w. in rats. Moreover, 10, 25 and 50 mg/kg b.w. of Ovatodiolide did not cause a significant effect in rats. According to the results of the genotoxicity and oral toxicity studies in rats, Ovatodiolide did not produce any adverse effects, and the tested doses can serve as clinical references.
MicroRNAs regulating SOX2 in cancer progression and therapy response.[Pubmed:34583803]
Expert Rev Mol Med. 2021 Sep 29;23:e13.
The proliferation, metastasis and therapy response of tumour cells are tightly regulated by interaction among various signalling networks. The microRNAs (miRNAs) can bind to 3'-UTR of mRNA and down-regulate expression of target gene. The miRNAs target various molecular pathways in regulating biological events such as apoptosis, differentiation, angiogenesis and migration. The aberrant expression of miRNAs occurs in cancers and they have both tumour-suppressor and tumour-promoting functions. On the contrary, SOX proteins are capable of binding to DNA and regulating gene expression. SOX2 is a well-known member of SOX family that its overexpression in different cancers to ensure progression and stemness. The present review focuses on modulatory impact of miRNAs on SOX2 in affecting growth, migration and therapy response of cancers. The lncRNAs and circRNAs can function as upstream mediators of miRNA/SOX2 axis in cancers. In addition, NF-kappaB, TNF-alpha and SOX17 are among other molecular pathways regulating miRNA/SOX2 axis in cancer. Noteworthy, anti-cancer compounds including bufalin and Ovatodiolide are suggested to regulate miRNA/SOX2 axis in cancers. The translation of current findings to clinical course can pave the way to effective treatment of cancer patients and improve their prognosis.
Retraction Note to: Anticancer effects of ovatodiolide on human prostate cancer cells involves cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and blocking of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.[Pubmed:34565048]
J BUON. 2021 Jul-Aug;26(4):1692.
Retraction of "Anticancer effects of Ovatodiolide on human prostate cancer cells involves cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and blocking of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway", by Dongsheng Jia, Jianbo Zheng, Junli Yu, Ning Zhao, Shengxing Lu, Dongfang Hao. JBUON 2020;25(5):2412-2417; PMID: 33277863 Following the publication of the above article, readers drew to our attention that part of the data was unreliable: Figures of this article appeared in other articles (by totally different authors). The authors were requested to provide the raw data and were also asked for an explanation to account for these concerns, but the Editorial Office did not receive any reply. Given above, we decided to retract this article. Authors were informed of the retraction. We thank the readers for bringing this matter to our attention. We apologize for any inconvenience it may cause.
Identification of Cancer Hub Gene Signatures Associated with Immune-Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Ovatodiolide as a Potential Cancer Immunotherapeutic Agent.[Pubmed:34359748]
Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;13(15):3847.
Despite the significant advancement in therapeutic strategies, breast, colorectal, gastric, lung, liver, and prostate cancers remain the most prevalent cancers in terms of incidence and mortality worldwide. The major causes ascribed to these burdens are lack of early diagnosis, high metastatic tendency, and drug resistance. Therefore, exploring reliable early diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers universal to most cancer types is a clinical emergency. Consequently, in the present study, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the publicly available microarray datasets of six cancer types (liver, lung colorectal, gastric, prostate, and breast cancers), termed hub cancers, were analyzed to identify the universal DEGs, termed hub genes. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and KEGG mapping of the hub genes suggested their crucial involvement in the tumorigenic properties, including distant metastases, treatment failure, and survival prognosis. Notably, our results suggested high frequencies of genetic and epigenetic alterations of the DEGs in association with tumor staging, immune evasion, poor prognosis, and therapy resistance. Translationally, we intended to identify a drug candidate with the potential for targeting the hub genes. Using a molecular docking platform, we estimated that Ovatodiolide, a bioactive anti-cancer phytochemical, has high binding affinities to the binding pockets of the hub genes. Collectively, our results suggested that the hub genes were associated with establishing an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment favorable for disease progression and promising biomarkers for the early diagnosis and prognosis in multiple cancer types and could serve as potential druggable targets for Ovatodiolide.
Targeting FGL2, a molecular drug target for glioblastoma, with natural compounds through virtual screening method.[Pubmed:33821685]
Future Med Chem. 2021 May;13(9):805-816.
Background: Fibroleukin-2 protein (FGL2) causes redevelopment of brain tumors. Inhibition of these proteins has shown to improve glioblastoma prognosis and treatment efficacy. Aim: The current study gathered recently exploited natural compounds that suppress glioblastoma proliferation in vitro, tested against FGL2 protein. Method: Twenty-five compounds were explored through a virtual screening platform. Results: Three natural compounds (betanine, hesperetin and Ovatodiolide) hit the active site of FGL2. Furthermore, the influence of these compounds was also assessed using in silico gene expression, and ADMET tools showed downregulation of some genes, which caused rapid tumor development while possessing a moderate acute toxicity and pharmacokinetic profile. Conclusion: Our study presents three compounds that are good candidates for evaluation in FGL2 mutated glioblastoma animal models.


