PF-04991532Potent hepatoselective glucokinase activator CAS# 1215197-37-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1215197-37-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46181428 | Appearance | Off-white solid |
| Formula | C18H19F3N4O3 | M.Wt | 396.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | UNII-AJ212MS2O2; CHEMBL2165620; PF-04991532; AJ212MS2O2; SCHEMBL1711504; | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO,ethanol | ||
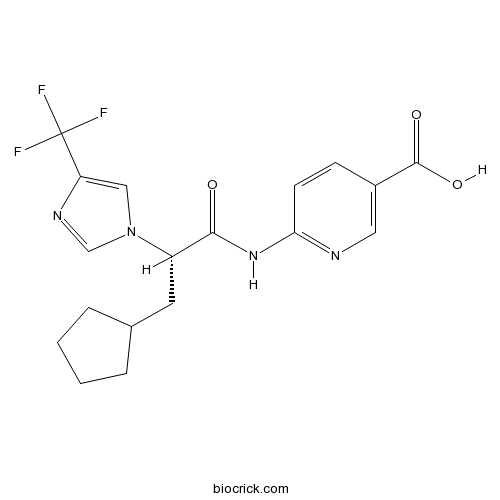
| Chemical Name | 6-[[(2S)-3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(trifluoromethyl)imidazol-1-yl]propanoyl]amino]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CCC(C1)CC(C(=O)NC2=NC=C(C=C2)C(=O)O)N3C=C(N=C3)C(F)(F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GKMLFBRLRVQVJO-ZDUSSCGKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19F3N4O3/c19-18(20,21)14-9-25(10-23-14)13(7-11-3-1-2-4-11)16(26)24-15-6-5-12(8-22-15)17(27)28/h5-6,8-11,13H,1-4,7H2,(H,27,28)(H,22,24,26)/t13-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent hepatoselective glucokinase activator (EC50 = 90 nM). Exhibits >50-fold liver to pancreas ratio of tissue distribution. Reduces fasting and postprandial glucose levels with no hypoglycemia in a rat diabetes model. |

PF-04991532 Dilution Calculator

PF-04991532 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.523 mL | 12.6148 mL | 25.2296 mL | 50.4592 mL | 63.074 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5046 mL | 2.523 mL | 5.0459 mL | 10.0918 mL | 12.6148 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2523 mL | 1.2615 mL | 2.523 mL | 5.0459 mL | 6.3074 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0505 mL | 0.2523 mL | 0.5046 mL | 1.0092 mL | 1.2615 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.1261 mL | 0.2523 mL | 0.5046 mL | 0.6307 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8742
CAS No.:1215-59-4
- Daclatasvir (BMS-790052)
Catalog No.:BCC2533
CAS No.:1214735-16-6
- Ajugapantin A
Catalog No.:BCN3663
CAS No.:121449-67-0
- WZ4003
Catalog No.:BCC4363
CAS No.:1214265-58-3
- WZ8040
Catalog No.:BCC1075
CAS No.:1214265-57-2
- WZ3146
Catalog No.:BCC4004
CAS No.:1214265-56-1
- POM 1
Catalog No.:BCC7454
CAS No.:12141-67-2
- N6-Benzyladenine
Catalog No.:BCC9076
CAS No.:1214-39-7
- Bernardioside A
Catalog No.:BCN7862
CAS No.:121368-52-3
- SR 33805 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7181
CAS No.:121346-33-6
- Fmoc-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3489
CAS No.:121343-82-6
- WZ4002
Catalog No.:BCC1074
CAS No.:1213269-23-8
- Salvianolic acid B; Lithospermic acid B; Danfensuan B
Catalog No.:BCC8249
CAS No.:121521-90-2
- SR 58611A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7833
CAS No.:121524-09-2
- GR 144053 trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6998
CAS No.:1215333-48-4
- RG2833
Catalog No.:BCC1893
CAS No.:1215493-56-3
- CFM 1571 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5924
CAS No.:1215548-30-3
- SB 242084
Catalog No.:BCC5949
CAS No.:1215566-78-1
- RS 100329 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5741
CAS No.:1215654-26-4
- CP-809101 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1499
CAS No.:1215721-40-6
- NBI 27914 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7124
CAS No.:1215766-76-9
- Gatifloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4224
CAS No.:121577-32-0
- DMCM hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7560
CAS No.:1215833-62-7
- Valspodar
Catalog No.:BCC2027
CAS No.:121584-18-7
Effect of Hepatic Organic Anion-Transporting Polypeptide 1B Inhibition and Chronic Kidney Disease on the Pharmacokinetics of a Liver-Targeted Glucokinase Activator: A Model-Based Evaluation.[Pubmed:30919935]
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Mar 28.
PF-04991532 ((S)-6-(3-Cyclopentyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl) propanamido) nicotinic acid) is a glucokinase activator designed to achieve hepato-selectivity via organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATP)s, so as to minimize systemic hypoglycemic effects. This study investigated the effect of OATP1B1/1B3 inhibition and renal impairment on PF-04991532 oral pharmacokinetics. Cyclosporine (600 mg single dose) increased mean area under the plasma curve (AUC) of PF-04991532 by approximately threefold in healthy subjects. In a renal impairment study, PF-04991532 AUC values were ~ 2.3-fold greater in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe kidney dysfunction, compared with healthy subjects. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model parameterizing hepatic and renal transporter-mediated disposition based on in vitro inputs, and verified using first-in-human data, indicated the key role of OATP-mediated hepatic uptake in the systematic and target-tissue exposure of PF-04991532. Mechanistic evaluation of the clinical data suggest reduced hepatic OATPs (~ 35%) and renal organic anion transporter (OAT)3 (80-90%) function with renal impairment. This study illustrates the adequacy and utility of the PBPK approach in assessing the impact of drug interactions and kidney dysfunction on transporter-mediated disposition.
Metabolism and excretion of (S)-6-(3-cyclopentyl-2-(4-trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propanamido)nicotinic acid (PF-04991532), a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, in humans: confirmation of the MIST potential noted in first-in-Human metabolite scouting studies.[Pubmed:30747552]
Xenobiotica. 2019 Feb 12:1-11.
1. The absorption, metabolism, and excretion of a single oral 450-mg dose of [(14)C]-(S)-6-(3-cyclopentyl-2-(4-trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propanamido)n icotinic acid (PF-04991532), a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, was investigated in humans. Mass balance was achieved with approximately 94.6% of the administered dose recovered in urine and feces. The total administered radioactivity excreted in feces and urine was 70.6% and 24.1%, respectively. Unchanged PF-04991532 collectively accounted for approximately 47.2% of the dose excreted in feces and urine, suggestive of moderate metabolic elimination in humans. 2. The biotransformation pathways involved acyl glucuronidation (M1), amide bond hydrolysis (M3), and CYP3A4-mediated oxidative metabolism on the cyclopentyl ring in PF-04991532 yielding monohydroxylated isomers (M2a-d). Unchanged PF-04991532 was the major circulating component (64.4% of total radioactivity) whereas M2a-d collectively represented 28.9% of the total plasma radioactivity. 3. Metabolites M2a-d were not detected systemically in rats and dogs, the preclinical species for the toxicological evaluation of PF-04991532. In contrast, cynomologus monkeys dosed orally with unlabeled PF-04991532 revealed M2a-d in circulation, whose UV abundance was comparable to the profile in humans. This observation suggested that monkeys could potentially serve as a non-rodent alternative for studying the toxicity of PF-04991532 and its metabolites M2a-d. 4. The present results are in excellent agreement with our previously generated metabolite scouting data, which provided preliminary evidence for the disproportionate metabolism of PF-04991532 in humans.
Comparison of the circulating metabolite profile of PF-04991532, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, across preclinical species and humans: potential implications in metabolites in safety testing assessment.[Pubmed:25384899]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Feb;43(2):190-8.
A previous report from our laboratory disclosed the identification of PF-04991532 [(S)-6-(3-cyclopentyl-2-(4-trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propanamido)nicotini c acid] as a hepatoselective glucokinase activator for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lack of in vitro metabolic turnover in microsomes and hepatocytes from preclinical species and humans suggested that metabolism would be inconsequential as a clearance mechanism of PF-04991532 in vivo. Qualitative examination of human circulating metabolites using plasma samples from a 14-day multiple ascending dose clinical study, however, revealed a glucuronide (M1) and monohydroxylation products (M2a and M2b/M2c) whose abundances (based on UV integration) were greater than 10% of the total drug-related material. Based on this preliminary observation, mass balance/excretion studies were triggered in animals, which revealed that the majority of circulating radioactivity following the oral administration of [(1)(4)C]PF-04991532 was attributed to an unchanged parent (>70% in rats and dogs). In contrast with the human circulatory metabolite profile, the monohydroxylated metabolites were not detected in circulation in either rats or dogs. Available mass spectral evidence suggested that M2a and M2b/M2c were diastereomers derived from cyclopentyl ring oxidation in PF-04991532. Because cyclopentyl ring hydroxylation on the C-2 and C-3 positions can generate eight possible diastereomers, it was possible that additional diastereomers may have also formed and would need to be resolved from the M2a and M2b/M2c peaks observed in the current chromatography conditions. In conclusion, the human metabolite scouting study in tandem with the animal mass balance study allowed early identification of PF-04991532 oxidative metabolites, which were not predicted by in vitro methods and may require additional scrutiny in the development phase of PF-04991532.
The hepatoselective glucokinase activator PF-04991532 ameliorates hyperglycemia without causing hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats.[Pubmed:24858947]
PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e97139.
Hyperglycemia resulting from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the main cause of diabetic complications such as retinopathy and neuropathy. A reduction in hyperglycemia has been shown to prevent these associated complications supporting the importance of glucose control. Glucokinase converts glucose to glucose-6-phosphate and determines glucose flux into the beta-cells and hepatocytes. Since activation of glucokinase in beta-cells is associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia, we hypothesized that selectively activating hepatic glucokinase would reduce fasting and postprandial glucose with minimal risk of hypoglycemia. Previous studies have shown that hepatic glucokinase overexpression is able to restore glucose homeostasis in diabetic models; however, these overexpression experiments have also revealed that excessive increases in hepatic glucokinase activity may also cause hepatosteatosis. Herein we sought to evaluate whether liver specific pharmacological activation of hepatic glucokinase is an effective strategy to reduce hyperglycemia without causing adverse hepatic lipids changes. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, PF-04991532, in Goto-Kakizaki rats. In these studies, PF-04991532 reduced plasma glucose concentrations independent of changes in insulin concentrations in a dose-dependent manner both acutely and after 28 days of sub-chronic treatment. During a hyperglycemic clamp in Goto-Kakizaki rats, the glucose infusion rate was increased approximately 5-fold with PF-04991532. This increase in glucose infusion can be partially attributed to the 60% reduction in endogenous glucose production. While PF-04991532 induced dose-dependent increases in plasma triglyceride concentrations it had no effect on hepatic triglyceride concentrations in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Interestingly, PF-04991532 decreased intracellular AMP concentrations and increased hepatic futile cycling. These data suggest that hepatoselective glucokinase activation may offer glycemic control without inducing hepatic steatosis supporting the evaluation of tissue specific activators in clinical trials.


