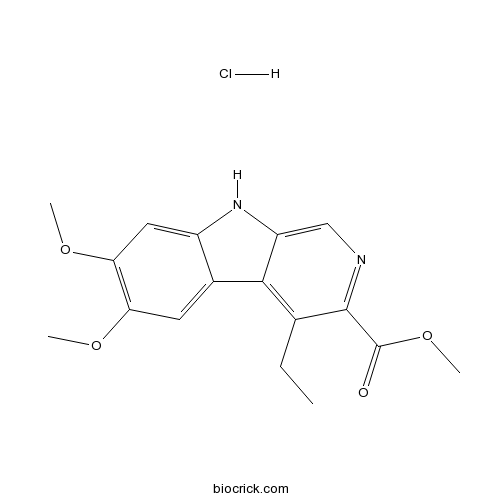
DMCM hydrochlorideBenzodiazepine inverse agonist CAS# 1215833-62-7 |
- 7-Chlorokynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7757
CAS No.:1263094-00-3
- TFB-TBOA
Catalog No.:BCC5919
CAS No.:480439-73-4
- Dihydrokainic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6556
CAS No.:52497-36-6
- L-(-)-threo-3-Hydroxyaspartic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6565
CAS No.:7298-99-9
- WAY 213613
Catalog No.:BCC7442
CAS No.:868359-05-1
- LDN 212320
Catalog No.:BCC6361
CAS No.:894002-50-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1215833-62-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 45261899 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H19ClN2O4 | M.Wt | 350.8 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 25 mg/mL (71.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 10 mg/mL (28.51 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl 4-ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=C2C3=CC(=C(C=C3NC2=CN=C1C(=O)OC)OC)OC.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FHCRBVQGMZUJKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18N2O4.ClH/c1-5-9-15-10-6-13(21-2)14(22-3)7-11(10)19-12(15)8-18-16(9)17(20)23-4;/h6-8,19H,5H2,1-4H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Benzodiazepine inverse agonist that displays anxiogenic and potent convulsant activity. |

DMCM hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

DMCM hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8506 mL | 14.2531 mL | 28.5063 mL | 57.0125 mL | 71.2657 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5701 mL | 2.8506 mL | 5.7013 mL | 11.4025 mL | 14.2531 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2851 mL | 1.4253 mL | 2.8506 mL | 5.7013 mL | 7.1266 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.057 mL | 0.2851 mL | 0.5701 mL | 1.1403 mL | 1.4253 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0285 mL | 0.1425 mL | 0.2851 mL | 0.5701 mL | 0.7127 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
DMCM (hydrochloride) is Benzodiazepine inverse agonist that displays anxiogenic and potent convulsant activity. The reference for administration is ranging 0.4 from 0.8 mg/kg . DMCM (hydrochloride) was shown to bind to GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors in the rat brain with high affinity. DMCM (hydrochloride) can inhibit pain and learning in rats.
References:
[1]. Sieve AN et al. Pain and negative affect: evidence the inverse benzodiazepine agonist DMCM inhibits pain and learning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 2001 Jan 1, 153(2):180-90.
- Gatifloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4224
CAS No.:121577-32-0
- NBI 27914 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7124
CAS No.:1215766-76-9
- CP-809101 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1499
CAS No.:1215721-40-6
- RS 100329 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5741
CAS No.:1215654-26-4
- SB 242084
Catalog No.:BCC5949
CAS No.:1215566-78-1
- CFM 1571 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5924
CAS No.:1215548-30-3
- RG2833
Catalog No.:BCC1893
CAS No.:1215493-56-3
- GR 144053 trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6998
CAS No.:1215333-48-4
- SR 58611A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7833
CAS No.:121524-09-2
- Salvianolic acid B; Lithospermic acid B; Danfensuan B
Catalog No.:BCC8249
CAS No.:121521-90-2
- PF-04991532
Catalog No.:BCC8094
CAS No.:1215197-37-7
- 5-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8742
CAS No.:1215-59-4
- Valspodar
Catalog No.:BCC2027
CAS No.:121584-18-7
- 6-Demethoxy-9'-deoxycleomiscosin A
Catalog No.:BCN7298
CAS No.:121587-18-6
- 6-Demethoxycleomiscosin A
Catalog No.:BCN7299
CAS No.:121587-20-0
- YM 298198 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7366
CAS No.:1216398-09-2
- SB 258585 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7216
CAS No.:1216468-02-8
- Kaempferol-3-O-(2',6'-di-O-trans-p-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1603
CAS No.:121651-61-4
- BX 513 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5940
CAS No.:1216540-18-9
- ZK 93423 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7227
CAS No.:1216574-52-5
- 2-Cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-quinolyl-3-methanol
Catalog No.:BCC8574
CAS No.:121660-11-5
- 2-Cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinoline-3-carboxaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8573
CAS No.:121660-37-5
- Trap 101
Catalog No.:BCC7390
CAS No.:1216621-00-9
- SCH 79797 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7125
CAS No.:1216720-69-2
Behavioral differences between subgroups of rats with high and low threshold to clonic convulsions induced by DMCM, a benzodiazepine inverse agonist.[Pubmed:16297441]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005 Nov;82(3):417-26.
In epileptic patients, there is a high incidence of psychiatric comorbidities, such as anxiety. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ionotropic receptor GABA(A)/benzodiazepine allosteric site is involved in both epilepsy and anxiety. This involvement is based on the fact that benzodiazepine allosteric site agonists are anticonvulsant and anxiolytic drugs; on the other hand, benzodiazepine inverse agonists are potent convulsant and anxiogenic drugs. The aim of this work was to determine if subgroups of rats selected according to their susceptibility to clonic convulsions induced by a convulsant dose 50% (CD50) of DMCM, a benzodiazepine inverse agonist, would differ in behavioral tests commonly used to measure anxiety (elevated plus-maze, open field) and depression (forced swimming test). In the first experiment, subgroups of adult male Wistar rats were selected after a single dose of DMCM and in the second experiment they were selected after two injections of DMCM given after an interval of 1 week. Those rats presenting full clonic convulsions were termed Low Threshold rats to DMCM-induced clonic convulsions (LTR) and those not having clonic convulsions High Threshold rats to DMCM-induced clonic convulsions (HTR). In both experiments, only those rats presenting full clonic convulsions induced by DMCM and those not showing any signs of motor disturbances were used in the behavioral tests. The results showed that the LTR subgroup selected after two injections of a CD50 of DMCM spent a significantly lower time in the open arms of the elevated plus-maze and in the off the walls area of the open field; moreover, this group also presented a higher number of rearings in the open field. There were no significant differences between HTR and LTR subgroups in the forced swimming test. LTR and HTR subgroups selected after only one injection of DMCM did not differ in the three behavioral tests. To verify if the behavioral differences between HTR and LTR subgroups of rats selected after two injections of DMCM were due to the clonic convulsion, another experiment was carried out in which subgroups of rats susceptible and nonsusceptible to clonic convulsions induced by a CD50 of picrotoxin, a GABA(A) receptor channel blocker, were selected and submitted to the elevated plus-maze and open field tests. The results obtained did not show any significant differences between these two subgroups in the elevated plus-maze and open field tests. In another approach to determine the relation between fear/anxiety and susceptibility to clonic convulsions, subgroups of rats were selected in the elevated plus-maze as more or less fearful/anxious. The CD50 for clonic convulsions induced by DMCM was determined for each of these two subgroups. The results showed a significantly lower CD50 for the more fearful/anxious subgroup, which means a higher susceptibility to clonic convulsions induced by DMCM. The present findings show a relation between susceptibility to clonic convulsions and fear/anxiety and vice versa which may be due to differences in the assembly of GABA(A)/allosteric benzodiazepine site receptors in regions of the brain.
DMCM: a potent convulsive benzodiazepine receptor ligand.[Pubmed:6317396]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 14;94(1-2):117-24.
DMCM (methyl 6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate) is a very potent convulsant with high affinity for specific benzodiazepine binding sites. A number of compounds were compared for their ability to prevent seizures induced by DMCM and pentylenetetrazol. DMCM seizures were antagonized by benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor antagonists, such as Ro 15-1788, CGS 8216 and several beta-carboline-3-carboxylates, which all fail to inhibit pentylenetetrazol seizures. The benzodiazepines diazepam, clonazepam and lorazepam as well as valproate, ethosuximid, phenobarbital, primidone, diphenylhydantoin and carbamazepine antagonized both DMCM and pentylenetetrazol. Muscimol and gamma-vinyl-GABA did not inhibit DMCM seizures whereas THIP showed a weak and selective effect against DMCM. Valproate showed a relatively potent (60 mg/kg i.p.) and competitive antagonism of short duration. Baclofen antagonized DMCM at 3 mg/kg. Valproate and baclofen were at least 5 times more potent against DMCM-induced than against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. DMCM most probably induces the seizures by selective impairment of the functions mediated by the GABA/BZ receptor-chloride channel complex (inverse agonism) and therefore differs from GABA receptor blockers.


