Sanggenol ACAS# 174423-30-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 174423-30-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15233693 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H28O6 | M.Wt | 424.5 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
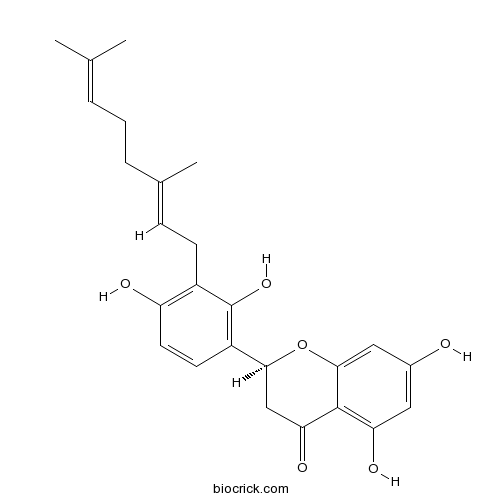
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[3-[(2E)-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dienyl]-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCCC(=CCC1=C(C=CC(=C1O)C2CC(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QNPMSYLDWCXEOI-CEMXSPGASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H28O6/c1-14(2)5-4-6-15(3)7-8-17-19(27)10-9-18(25(17)30)22-13-21(29)24-20(28)11-16(26)12-23(24)31-22/h5,7,9-12,22,26-28,30H,4,6,8,13H2,1-3H3/b15-7+/t22-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Sanggenol A shows neuroprotective activity on glutamate-induced cell death in HT22 cells, with EC50 values of 34.03 ± 7.71 uM. 2. Sanggenol A inhibits influenza A viral and pneumococcal neuraminidase (NA), it also disrupts the synergism between influenza A virus and pneumococcal NA in vitro, hence functioning as dual-acting anti-infectives. |
| Targets | Influenza virus |

Sanggenol A Dilution Calculator

Sanggenol A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3557 mL | 11.7786 mL | 23.5571 mL | 47.1143 mL | 58.8928 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4711 mL | 2.3557 mL | 4.7114 mL | 9.4229 mL | 11.7786 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2356 mL | 1.1779 mL | 2.3557 mL | 4.7114 mL | 5.8893 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0471 mL | 0.2356 mL | 0.4711 mL | 0.9423 mL | 1.1779 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0236 mL | 0.1178 mL | 0.2356 mL | 0.4711 mL | 0.5889 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Amiloride HCl dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5068
CAS No.:17440-83-4
- Riluzole
Catalog No.:BCC3849
CAS No.:1744-22-5
- Tsugaric acid A
Catalog No.:BCN2980
CAS No.:174391-64-1
- Picropodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN2585
CAS No.:17434-18-3
- Astragaloside
Catalog No.:BCN5959
CAS No.:17429-69-5
- Caohuoside E
Catalog No.:BCN8198
CAS No.:174286-23-8
- Epimedin K
Catalog No.:BCN8201
CAS No.:174286-13-6
- Apigenin 7-O-(2G-rhamnosyl)gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN1524
CAS No.:174284-20-9
- Pancixanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7379
CAS No.:174232-30-5
- Methyl 3-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionate
Catalog No.:BCN1525
CAS No.:17422-90-1
- 3-Chloro-4-hydroxypiperidin-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3992
CAS No.:174204-83-2
- Aristolochic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN2902
CAS No.:17413-38-6
- Tipranavir
Catalog No.:BCC2002
CAS No.:174484-41-4
- alpha-Spinasterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1120
CAS No.:1745-36-4
- 2-Allylphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8518
CAS No.:1745-81-9
- SDZ 220-581
Catalog No.:BCC1939
CAS No.:174575-17-8
- SDZ 220-040
Catalog No.:BCC6992
CAS No.:174575-40-7
- SB 218795
Catalog No.:BCC7037
CAS No.:174635-53-1
- SB-222200
Catalog No.:BCC1926
CAS No.:174635-69-9
- Talnetant
Catalog No.:BCC1981
CAS No.:174636-32-9
- Phalloidin
Catalog No.:BCC7945
CAS No.:17466-45-4
- AN-2690
Catalog No.:BCC1360
CAS No.:174671-46-6
- CH 275
Catalog No.:BCC5913
CAS No.:174688-78-9
- 2-Amino-6-methoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8542
CAS No.:1747-60-0
New isoprenylated flavonoid from Morus alba.[Pubmed:20815207]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Jun;35(12):1560-5.
Sanggenol P (1), a new isoprenylated flavonoid, together with nine known ones, cyclomorusin (2), morusin (3), mulberrofuran G (4), Sanggenol A (5), sanggenol L (6), sanggenol N (7), cyclomulberrin (8), cyclocommunol (9) and ursolic acid (10) was isolated from Morus alba L. Sanggenol P (1) was characterized based on extensive IR, UV, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic analysis. Compounds 5, 6, 7 and 9 were obtained from this plant for the first time.
Isoprenylated flavonoids from the root bark of Morus alba and their hepatoprotective and neuroprotective activities.[Pubmed:25981820]
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Nov;38(11):2066-75.
A new isoprenylated flavonoid, 2S-5,7,2',4'-tetrahydroxy-3',5'-di-(gamma,gamma-dimethylallyl)flavanone, sanggenol Q (1), along with seven known isoprenylated flavonoids, Sanggenol A (2), sanggenol L (3), kuwanon T (4), cyclomorusin (5), sanggenon F (6), sanggenol O (7), and sanggenon N (8), three known Diels-Alder type adducts, sanggenon G (9), mulberrofuran G (10), and mulberrofuran C (11), and a known benzofuran, moracin E (12), were isolated from the root bark of Morus alba using silica gel, ODS, and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography. Chemical structures were determined based on spectroscopic data analyses including NMR, MS, CD, and IR. For the first time, compounds 1 and 7 were isolated from the root bark of M. alba. All compounds were evaluated for hepatoprotective activity on t-BHP-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and neuroprotective activity on glutamate-induced cell death in HT22 cells. Compounds 1, 4, 8, 10, and 11 showed protective effects on t-BHP-induced oxidative stress with EC50 values of 6.94 +/- 0.38, 30.32 +/- 6.82, 23.45 +/- 4.72, 15.31 +/- 2.21, and 0.41 +/- 0.48 muM, respectively, and compounds 1, 2, 10, 11, and 12 showed protective effects on glutamate-induced cell death with EC50 values of 5.54 +/- 0.86, 34.03 +/- 7.71, 19.71 +/- 0.71, 16.50 +/- 7.82, and 1.02 +/- 0.13 muM, respectively.
Discovery of prenylated flavonoids with dual activity against influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.[Pubmed:27257160]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 3;6:27156.
Influenza virus neuraminidase (NA) is the primary target for influenza therapeutics. Severe complications are often related to secondary pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci), which also express NAs. Recently, a NA-mediated lethal synergism between influenza A viruses and pneumococci was described. Therefore, dual inhibitors of both viral and bacterial NAs are expected to be advantageous for the treatment of influenza. We investigated the traditional Chinese herbal drug sang bai pi (mulberry root bark) as source for anti-infectives. Two prenylated flavonoid derivatives, sanggenon G (4) and Sanggenol A (5) inhibited influenza A viral and pneumococcal NAs and, in contrast to the approved NA inhibitor oseltamivir, also planktonic growth and biofilm formation of pneumococci. Evaluation of 27 congeners of 5 revealed a correlation between the degree of prenylation and bioactivity. Abyssinone-V 4'-methyl ether (27) inhibited pneumococcal NA with IC50 = 2.18 muM, pneumococcal growth with MIC = 5.63 muM, and biofilm formation with MBIC = 4.21 muM, without harming lung epithelial cells. Compounds 5 and 27 also disrupt the synergism between influenza A virus and pneumococcal NA in vitro, hence functioning as dual-acting anti-infectives. The results warrant further studies on whether the observed disruption of this synergism is transferable to in vivo systems.


