ScoparinCAS# 301-16-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 301-16-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 20055255 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H22O11 | M.Wt | 462.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
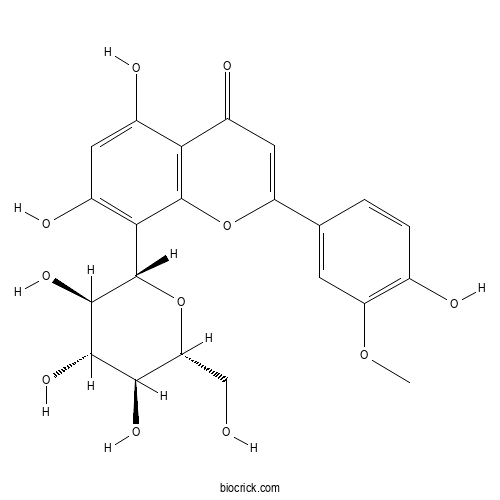
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(O2)C(=C(C=C3O)O)C4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YXHFXGHAELQJGK-PGPONNFDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22O11/c1-31-14-4-8(2-3-9(14)24)13-6-12(27)16-10(25)5-11(26)17(21(16)32-13)22-20(30)19(29)18(28)15(7-23)33-22/h2-6,15,18-20,22-26,28-30H,7H2,1H3/t15-,18-,19+,20-,22+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Scoparin Dilution Calculator

Scoparin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1626 mL | 10.8131 mL | 21.6263 mL | 43.2526 mL | 54.0657 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4325 mL | 2.1626 mL | 4.3253 mL | 8.6505 mL | 10.8131 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2163 mL | 1.0813 mL | 2.1626 mL | 4.3253 mL | 5.4066 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.8651 mL | 1.0813 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1081 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.5407 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tembetarine
Catalog No.:BCX0034
CAS No.:18446-73-6
- Apigenin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-8-C-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)]-beta-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0033
CAS No.:1646598-06-2
- Ganolucidic acid E
Catalog No.:BCX0032
CAS No.:114567-50-9
- Caffeoylcalleryanin
Catalog No.:BCX0031
CAS No.:20300-49-6
- Odontoside
Catalog No.:BCX0030
CAS No.:20300-50-9
- Catechin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0029
CAS No.:65597-47-9
- 5-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0028
CAS No.:32451-86-8
- Gossypetin 3-sophoroside-8-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0027
CAS No.:77306-93-5
- Alopecurone A
Catalog No.:BCX0026
CAS No.:162558-89-6
- Kidjolanin
Catalog No.:BCX0025
CAS No.:38395-01-6
- Hainanic acid B
Catalog No.:BCX0024
CAS No.:1637737-46-2
- 5-Hydroxy-4a,8-dimethyl-3-methylen-decahydroazuleno[6,5-b]furan-2(3H)-on
Catalog No.:BCX0023
CAS No.:114579-31-6
- (Z)-Ferulic acid 4-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0036
CAS No.:94942-20-8
- Methyl ganoderate A
Catalog No.:BCX0037
CAS No.:105742-78-7
- (3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)methyl 3-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-4-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCX0038
CAS No.:877461-90-0
- Bayin
Catalog No.:BCX0039
CAS No.:3681-96-7
- Ganoderic acid GS-2
Catalog No.:BCX0040
CAS No.:1206781-65-8
- Ephedrannin D1
Catalog No.:BCX0041
CAS No.:1592431-55-4
- Ganoderic acid beta
Catalog No.:BCX0042
CAS No.:217476-76-1
- Methyl ganoderate B
Catalog No.:BCX0043
CAS No.:81907-65-5
- Oblongaroside B
Catalog No.:BCX0044
CAS No.:1000889-11-1
- Symplocoside
Catalog No.:BCX0045
CAS No.:76502-76-6
- Mahuannin B
Catalog No.:BCX0046
CAS No.:82796-37-0
- Calleryanin
Catalog No.:BCX0047
CAS No.:20300-53-2
C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids in Sanguinello and Tarocco blood orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) juice: Identification and influence on antioxidant properties and acetylcholinesterase activity.[Pubmed:26593535]
Food Chem. 2016 Apr 1;196:619-27.
Sanguinello and Tarocco are the blood orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) cultivars most diffused worldwide. Reversed phase liquid chromatography coupled with MS-MS analysis showed that these two varieties have a similar chromatographic pattern, characterised by the presence of C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids. Of the two, Sanguinello was found to be far richer in flavonoids than Tarocco. In the juices, twelve individual components were identified for the first time, namely, four C-glycosyl flavones (lucenin-2, vicenin-2, stellarin-2, lucenin-2 4'-methyl ether and Scoparin), three flavonol derivatives (quercetin-3-O-(2-rhamnosyl)-rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-hexoside, quercetin 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-glycoside), an O-triglycosyl flavanone (narirutin 4'-O-glucoside) and a flavone O-glycosides (chrysoeriol 7-O-neoesperidoside). Moreover, the influence of the identified C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids on the antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase activity of these juices has been evaluated.
First evidence of C- and O-glycosyl flavone in blood orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) juice and their influence on antioxidant properties.[Pubmed:24295703]
Food Chem. 2014 Apr 15;149:244-52.
RP-LC-DAD-ESI-MS-MS separation/identification protocol has been employed for the identification and characterisation of nine C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids in Moro (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) juice grown in Southern Italy. For the first time we reported the presence of five C-glycosyl flavones (lucenin-2, vicenin-2, stellarin-2, lucenin-2 4'-methyl ether and Scoparin), a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl glycosyl flavonol (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl glycosyl quercetin) and a flavone O-glycosides (chrysoeriol 7-O-neoesperidoside). Moreover, the influence of the identified C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids on the total antioxidant activity of crude juice has been evaluated on the basis of its ability to scavenge DPPH*, OH* and ABTS*+ radicals and to reduce iron.
Flavonoid profile and radical-scavenging activity of Mediterranean sweet lemon (Citrus limetta Risso) juice.[Pubmed:30634246]
Food Chem. 2011 Nov 15;129(2):417-422.
The flavonoid composition of crude Citrus limetta Risso (limetta, Mediterranean sweet lemon) juice was elucidated by means of reverse-phase HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS analysis. In a single course, eight compounds (C- and O-glycosyl flavonoids) were identified, six of which were found for the first time in limetta juice: four C-glucosyl flavones, namely vicenin-2, lucenin-2 4'-methyl ether, orientin 4'-methyl ether and Scoparin; the O-glycosyl flavone, rhoifolin; and the O-glycosyl flavanone, eriocitrin. In addition, ABTS(+) and DPPH radical quenching and FRAP assays demonstrate that limetta juice possesses remarkable antioxidant activity.
Antimicrobial activity of wax and hexane extracts from Citrus spp. peels.[Pubmed:17923995]
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2007 Sep;102(6):681-5.
Antibacterial and antifungal properties of wax and hexane extracts of Citrus spp. peels were tested using bioautographic and microdilution techniques against three plant pathogenic fungi (Penicillium digitatum, Curvularia sp., and Colletotrichum sp.), two human pathogens (Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Microsporum canis), and two opportunistic bacteria (Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus). Two polymethoxylated flavonoids and a coumarin derivative, were isolated and identified from peel extracts, which presented antimicrobial activity especially against M. canis and T. mentagrophytes: 4',5,6,7,8-pentamethoxyflavone (tangeritin) and 3',4',5,6,7,8-hexamethoxyflavone (nobiletin) from C. reticulata; and 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin (also known as escoparone, scoparone or Scoparin) from C. limon.
Phytochemical and nutrient composition of the freeze-dried amazonian palm berry, Euterpe oleraceae mart. (acai).[Pubmed:17061839]
J Agric Food Chem. 2006 Nov 1;54(22):8598-603.
Euterpe oleraceae is a large palm tree indigenous to the Amazon River and its tributaries and estuaries in South America. Its fruit, known as acai, is of great economic value to native people. In this study, a standardized freeze-dried acai fruit pulp/skin powder was used for all analyses and tests. Among many findings, anthocyanins (ACNs), proanthocyanidins (PACs), and other flavonoids were found to be the major phytochemicals. Two ACNs, cyandin 3-glucoside and cyanidin 3-rutinoside were found to be predominant ACNs; three others were also found as minor ACNs. The total content of ACNs was measured as 3.1919 mg/g dry weight (DW). Polymers were found to be the major PACs. The concentration of total PACs was calculated as 12.89 mg/g DW. Other flavonoids, namely, homoorientin, orientin, isovitexin, Scoparin, and taxifolin deoxyhexose, along with several unknown flavonoids, were also detected. Resveratrol was found but at a very low concentration. In addition, components including fatty acids, amino acids, sterols, minerals, and other nutrients were analyzed and quantified. Total polyunsaturated fatty acid, total monounsaturated fatty acid, and total saturated fatty acids contributed to 11.1%, 60.2%, and 28.7% of total fatty acid. Oleic acid (53.9%) and palmitic acid (26.7%) were found to be the two dominant fatty acids. Nineteen amino acids were found; the total amino acid content was determined to be 7.59% of total weight. The total sterols accounted for 0.048% by weight of powder. The three sterols B-sitosterol, campesterol, and sigmasterol were identified. A complete nutrient analysis is also presented. Microbiological analysis was also performed.
Flavonoid glycosides in bergamot juice (Citrus bergamia Risso).[Pubmed:16719517]
J Agric Food Chem. 2006 May 31;54(11):3929-35.
A comprehensive profile of flavonoids in bergamot juice was obtained by a single DAD-ESI-LC-MS-MS course. Eight flavonoids were found for the first time, five of these are C-glucosides (lucenin-2, stellarin-2, isovitexin, Scoparin, and orientin 4'-methyl ether), and three are O-glycosides (rhoifolin 4'-O-glucoside, chrysoeriol 7-O-neohesperidoside-4'-O-glucoside, and chrysoeriol 7-O-neohesperidoside). A method is proposed to differentiate chrysoeriol and diosmetin derivatives, which are often indistinguishable by LC-MS-MS. In-depth knowledge of the flavonoid content is the starting point for bergamot juice exploitation in food industry applications.


