Sennoside ACAS# 81-27-6 |
- Sennoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1003
CAS No.:128-57-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 81-27-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73111 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C42H38O20 | M.Wt | 862.74 |
| Type of Compound | Anthraquinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (144.89 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
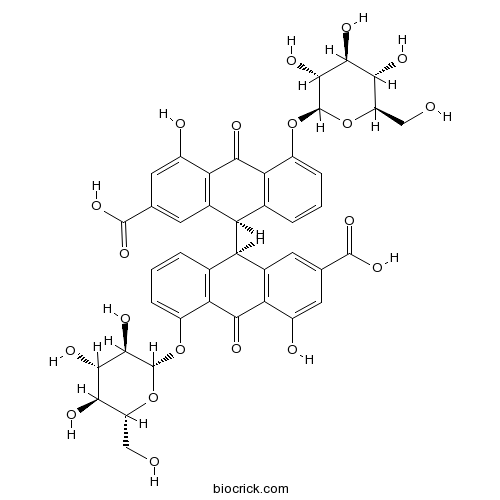
| Chemical Name | (9R)-9-[(9R)-2-carboxy-4-hydroxy-10-oxo-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-9H-anthracen-9-yl]-4-hydroxy-10-oxo-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-9H-anthracene-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C(=C1)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)C(=O)C4=C(C2C5C6=C(C(=CC=C6)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O)C(=O)C8=C5C=C(C=C8O)C(=O)O)C=C(C=C4O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IPQVTOJGNYVQEO-KGFNBKMBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C42H38O20/c43-11-23-31(47)35(51)37(53)41(61-23)59-21-5-1-3-15-25(17-7-13(39(55)56)9-19(45)27(17)33(49)29(15)21)26-16-4-2-6-22(60-42-38(54)36(52)32(48)24(12-44)62-42)30(16)34(50)28-18(26)8-14(40(57)58)10-20(28)46/h1-10,23-26,31-32,35-38,41-48,51-54H,11-12H2,(H,55,56)(H,57,58)/t23-,24-,25-,26-,31-,32-,35+,36+,37-,38-,41-,42-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sennoside A, a kind of irritant laxative isolated from rhei rhizome, causes purgative actions in the intestine, it and Sennoside B have protective effects on gastric lesion. Sennoside A also is a new dual HIV-1 inhibitor effective on HIV-1 replication. |
| Targets | HIV | PGE | Potassium Channel |
| In vitro | Sennoside A, derived from the traditional chinese medicine plant Rheum L., is a new dual HIV-1 inhibitor effective on HIV-1 replication.[Pubmed: 27765358 ]Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1383-1391.Despite the availability of effective antiretroviral therapies, drugs for HIV-1 treatment with new mode of action are still needed. An innovative approach is aimed to identify dual HIV-1 inhibitors, small molecules that can inhibit two viral functions at the same time. Rhubarb, originated from Rheum palmatum L. and Rheum officinale Baill., is one of the earliest and most commonly used medicinal plants in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practice. We wanted to explore TCM for the identification of new chemical scaffolds with dual action abilities against HIV-1.
|
| In vivo | The influence of glycyrrhiza and antibiotics on the purgative action of sennoside a from Daiokanzoto in mice.[Pubmed: 21881230]Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(9):1438-42.Daiokanzoto (DKT), a Kampo medicine that includes the combination of two crude drugs (rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), is clinically effective for constipation.
The aim of this study is to clarify the influence of glycyrrhiza, three glycyrrhiza constituents (glycyrrhizin, liquiritin, and liquiritin apioside), and eight antibiotics on the purgative action of DKT, rhubarb, or Sennoside A, a constituent of rhubarb, in mice.
Protective mechanism on gastric lesion of Sennoside A and Sennoside B[Reference: WebLink]The FASEB Journal, 2015, 29(1): 716.10.Sennoside A and sennoside B is evacuant to increase the sensitivity of the colon.
|
| Animal Research | Rheinanthrone, a metabolite of sennoside A, triggers macrophage activation to decrease aquaporin-3 expression in the colon, causing the laxative effect of rhubarb extract.[Pubmed: 24412547]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 27;152(1):190-200.Aquaporin-3 (AQP3) is expressed in mucosal epithelial cells in the colon and is important for regulating fecal water content. We examined the role of AQP3 in the laxative effect of rhubarb extract.
|
| Structure Identification | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(9):1106-9.High-performance liquid chromatographic determination and metabolic study of sennoside a in daiokanzoto by mouse intestinal bacteria.[Pubmed: 21881253]Daiokanzoto (DKT, combination of rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), a Kampo medicine, is clinically effective for constipation. Sennoside A is well known to induce diarrhea. Sennoside A is a prodrug that is transformed into an active metabolite, rheinanthrone, by intestinal bacteria.
|

Sennoside A Dilution Calculator

Sennoside A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1591 mL | 5.7955 mL | 11.591 mL | 23.182 mL | 28.9774 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2318 mL | 1.1591 mL | 2.3182 mL | 4.6364 mL | 5.7955 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1159 mL | 0.5795 mL | 1.1591 mL | 2.3182 mL | 2.8977 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0232 mL | 0.1159 mL | 0.2318 mL | 0.4636 mL | 0.5795 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0116 mL | 0.058 mL | 0.1159 mL | 0.2318 mL | 0.2898 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1286
CAS No.:81-25-4
- Taurocholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6954
CAS No.:81-24-3
- 2-Amino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8519
CAS No.:81-16-3
- Musk ketone
Catalog No.:BCN8357
CAS No.:81-14-1
- 6-Amino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8758
CAS No.:81-05-0
- 20R-Ginsenoside Rg2
Catalog No.:BCN2554
CAS No.:80952-72-3
- (20R)-Ginsenoside Rh1
Catalog No.:BCN3700
CAS No.:80952-71-2
- Zingibroside R1
Catalog No.:BCN3433
CAS No.:80930-74-1
- Gnetumontanin B
Catalog No.:BCN3756
CAS No.:809237-87-4
- Concanamycin A
Catalog No.:BCC3919
CAS No.:80890-47-7
- 3,22-Dihydroxyolean-12-en-29-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1347
CAS No.:808769-54-2
- Pyracrenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7455
CAS No.:80832-44-6
- Purpurin
Catalog No.:BCN3477
CAS No.:81-54-9
- Warfarin
Catalog No.:BCC5221
CAS No.:81-81-2
- Rhodamine B
Catalog No.:BCN7215
CAS No.:81-88-9
- 4-Hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)cyclohexanone
Catalog No.:BCN1346
CAS No.:81053-14-7
- Methyl 4-prenyloxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN7520
CAS No.:81053-49-8
- EUK 134
Catalog No.:BCC4317
CAS No.:81065-76-1
- Kauniolide
Catalog No.:BCC5313
CAS No.:81066-45-7
- Pravastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4141
CAS No.:81093-37-0
- Cisapride
Catalog No.:BCC4207
CAS No.:81098-60-4
- Clarithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC9219
CAS No.:81103-11-9
- Racecadotril
Catalog No.:BCC4614
CAS No.:81110-73-8
- N-Nonyldeoxynojirimycin
Catalog No.:BCC7752
CAS No.:81117-35-3
Sennoside A, derived from the traditional chinese medicine plant Rheum L., is a new dual HIV-1 inhibitor effective on HIV-1 replication.[Pubmed:27765358]
Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1383-1391.
BACKGROUND: Despite the availability of effective antiretroviral therapies, drugs for HIV-1 treatment with new mode of action are still needed. An innovative approach is aimed to identify dual HIV-1 inhibitors, small molecules that can inhibit two viral functions at the same time. Rhubarb, originated from Rheum palmatum L. and Rheum officinale Baill., is one of the earliest and most commonly used medicinal plants in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practice. We wanted to explore TCM for the identification of new chemical scaffolds with dual action abilities against HIV-1. METHODS: R. palmatum L. and R. officinale Baill. extracts along with their main single isolated constituents anthraquinone derivatives were tested on both HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase (RT)-associated DNA Polymerase (RDDP) and Ribonuclease H (RNase H) activities in biochemical assays. Active compounds were then assayed for their effects on HIV-1 mutated RTs, integrase (IN) and viral replication. RESULTS: Both R. palmatum L. and R. officinale Baill. extracts inhibited the HIV-1 RT-associated RNase H activity. Among the isolated constituents, Sennoside A and B were effective on both RDDP and RNase H RT-associated functions in biochemical assays. Sennoside A was less potent when tested on K103N, Y181C, Y188L, N474A and Q475A mutated RTs, suggesting the involvement of two RT binding sites for its antiviral activity. Sennoside A affected also HIV-1 IN activity in vitro and HIV-1 replication in cell-based assays. Viral DNA production and time of addition studies showed that Sennoside A targets the HIV-1 reverse transcription process. CONCLUSION: Sennoside A is a new scaffold for the development of HIV-1 dual RT inhibitors.
The influence of glycyrrhiza and antibiotics on the purgative action of sennoside a from Daiokanzoto in mice.[Pubmed:21881230]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(9):1438-42.
Daiokanzoto (DKT), a Kampo medicine that includes the combination of two crude drugs (rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), is clinically effective for constipation. The aim of this study is to clarify the influence of glycyrrhiza, three glycyrrhiza constituents (glycyrrhizin, liquiritin, and liquiritin apioside), and eight antibiotics on the purgative action of DKT, rhubarb, or Sennoside A, a constituent of rhubarb, in mice. The purgative actions of rhubarb and Sennoside A were significantly intensified when glycyrrhiza was co-administered orally to mice. Liquiritin and liquiritin apioside but not glycyrrhizin showed significant amplification of the purgative action in a dose-dependent manner. The purgative actions of DKT and Sennoside A were significantly reduced by the pre-administration of ampicillin, cefcapene pivoxil, faropenem, fosfomycin, or kanamycin, but were not affected by the pre-administration of clarithromycin or levofloxacin. On the other hand, the purgative action of Sennoside A was significantly reduced by the pre-administration of minocycline, whereas that of DKT was not affected. The effect of minocycline on the purgative action of Sennoside A was lost when glycyrrhiza was co-administered. These results suggest that liquiritin and liquiritin apioside contribute as active substances for the purgative action of DKT, and some antibiotics reduce the purgative action of DKT and Sennoside A. Furthermore, glycyrrhiza has the ability to recover the purgative action of Sennoside A suppressed by minocycline via an unknown mechanism.
Rheinanthrone, a metabolite of sennoside A, triggers macrophage activation to decrease aquaporin-3 expression in the colon, causing the laxative effect of rhubarb extract.[Pubmed:24412547]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 27;152(1):190-200.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Aquaporin-3 (AQP3) is expressed in mucosal epithelial cells in the colon and is important for regulating fecal water content. We examined the role of AQP3 in the laxative effect of rhubarb extract. METHODS: After orally administering rhubarb extract or its major component (Sennoside A) to rats, the fecal water content, AQP3 expression and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) concentrations in the colon were examined. The mechanism by which Sennoside A decreases the expression of AQP3 was examined using the human colon cancer HT-29 cells and macrophage-derived Raw264.7 cells. RESULTS: During diarrhea by rhubarb extract administration, the PGE2 levels in the colon increased while the AQP3 expression significantly decreased. Similar changes were also observed when Sennoside A was administered. When Sennoside A or its metabolites, rheinanthrone and rhein were added to Raw264.7 cells, a significant increase in the PGE2 concentration was observed only in cells treated with rheinanthrone. Fifteen minutes after adding PGE2 to the HT-29 cells, the AQP3 expression decreased to approximately 40% of the control. When pretreated with indomethacin, Sennoside A neither decreased the AQP3 expression nor induced diarrhea. CONCLUSIONS: Sennoside A may decrease AQP3 expression in the colon to inhibit water transport from the luminal to the vascular side, leading to a laxative effect. The decreases in the levels of AQP3 are caused by rheinanthrone, which is a metabolite of Sennoside A, this metabolite activates the macrophages in the colon and increases the secretion of PGE2; PGE2 acts as a paracrine factor and decreases AQP3 expression in colon mucosal epithelial cells.
High-performance liquid chromatographic determination and metabolic study of sennoside a in daiokanzoto by mouse intestinal bacteria.[Pubmed:21881253]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(9):1106-9.
Daiokanzoto (DKT, combination of rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), a Kampo medicine, is clinically effective for constipation. Sennoside A is well known to induce diarrhea. Sennoside A is a prodrug that is transformed into an active metabolite, rheinanthrone, by intestinal bacteria. In this study, we investigated the effects of glycyrrhiza on the activity of Sennoside A metabolism in intestinal bacteria using mouse feces. A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for the determination of Sennoside A in incubation mixture of DKT with mouse feces was established. The retention time of Sennoside A was 9.26+/-0.02 min with a TSKgel ODS-80TsQA column by linear gradient elution using a mobile phase containing aqueous phosphoric acid and acetonitrile and detection at 265 nm. We found that the activity of Sennoside A metabolism in intestinal bacteria was significantly accelerated when glycyrrhiza, liquiritin or liquiritin apioside coexisted with Sennoside A, whereas that of glycyrrhizin was not altered. This method is applicable for determination of the activity of Sennoside A metabolism by anaerobic incubation of DKT with mouse feces.


