Tagitinin CCAS# 59979-56-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 59979-56-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 167995869.0 | Appearance | Powder |
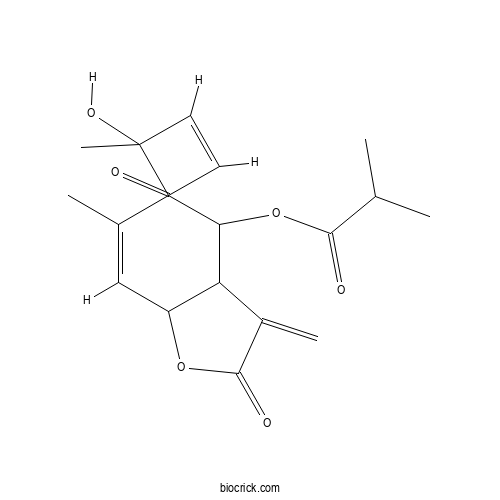
| Formula | C19H24O6 | M.Wt | 348.39 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(7Z,10Z)-6-hydroxy-6,10-dimethyl-3-methylidene-2,9-dioxo-3a,4,5,11a-tetrahydrocyclodeca[b]furan-4-yl] 2-methylpropanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2C(C(CC(C=CC1=O)(C)O)OC(=O)C(C)C)C(=C)C(=O)O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DUQSSEQKLJQACA-NJMVCRMVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H24O6/c1-10(2)17(21)25-15-9-19(5,23)7-6-13(20)11(3)8-14-16(15)12(4)18(22)24-14/h6-8,10,14-16,23H,4,9H2,1-3,5H3/b7-6-,11-8- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Tagitinin C Dilution Calculator

Tagitinin C Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8703 mL | 14.3517 mL | 28.7035 mL | 57.4069 mL | 71.7587 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5741 mL | 2.8703 mL | 5.7407 mL | 11.4814 mL | 14.3517 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.287 mL | 1.4352 mL | 2.8703 mL | 5.7407 mL | 7.1759 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.287 mL | 0.5741 mL | 1.1481 mL | 1.4352 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0287 mL | 0.1435 mL | 0.287 mL | 0.5741 mL | 0.7176 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3'-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCX1440
CAS No.:92496-65-6
- D-mannuronic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1439
CAS No.:921-56-2
- D-dimannuronic acid disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1438
CAS No.:34044-53-6
- D-trimannuronic acid trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1437
CAS No.:66754-13-0
- D-tetramannuronic acid tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1436
CAS No.:149511-34-2
- D-pentamannuronic acid pentasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1435
CAS No.:183668-50-0
- D-hexamannuronic acid hexasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1434
CAS No.:183668-52-2
- D-heptamannuronic acid heptasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1433
CAS No.:862694-97-1
- D-octamannuronic acid octasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1432
CAS No.:862694-98-2
- D-nonamannuronic acid nonasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1431
CAS No.:862694-99-3
- L-diguluronic acid disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1430
CAS No.:34044-54-7
- L-triguluronic acid trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1429
CAS No.:66754-14-1
- Rubrofusarin triglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1442
CAS No.:245724-07-6
- Vernoflexuoside
Catalog No.:BCX1443
CAS No.:57576-33-7
- Nicotinamide riboside
Catalog No.:BCX1444
CAS No.:1341-23-7
- 1β-Methoxydiversifolin
Catalog No.:BCX1445
CAS No.:110382-36-0
- 6-Carboxyl-7-hydroxy-2,3-dimethylchromone
Catalog No.:BCX1446
CAS No.:108170-57-6
- Neotame
Catalog No.:BCX1447
CAS No.:165450-17-9
- 4-Deoxyphorbol
Catalog No.:BCX1448
CAS No.:79083-67-3
- 16,17-Didehydroganoderic acid D
Catalog No.:BCX1449
CAS No.:1427189-02-3
- Stigmastanol
Catalog No.:BCX1450
CAS No.:83-45-4
- Methyl cis-11-eicosenoate
Catalog No.:BCX1451
CAS No.:2390-09-2
- 2'-Acetyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCX1452
CAS No.:92950-40-8
- Liraglutide
Catalog No.:BCX1453
CAS No.:204656-20-2
Sesquiterpenoids from Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) A. Gray induce apoptosis and inhibit the cell cycle progression of acute myeloid leukemia cells.[Pubmed:36321958]
Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2022 Nov 3;78(1-2):65-72.
Three sesquiterpene lactones (1-3) were isolated from the aerial part of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) A. Gray grown in the Hoa Binh province in Viet Nam. The structures of these three sesquiterpene lactones were identified as tagitinin A (1), 1beta-hydroxytirotundin 3-O-methyl ether (2), and Tagitinin C (3) by analyzing spectroscopic data. For the first time, compound 2 was isolated from T. diversifolia growing in Viet Nam. Furthermore, contrary to existing literature, we determined that compound 1 was the major isolate. Compounds 1 and 3 significantly decreased numbers of acute myeloid leukemia OCI-AML3 cells by promoting apoptosis and causing cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase at concentrations as low as 2.5 mug/mL (compound 1) and 0.25 mug/mL (compound 3). Additionally, all three compounds showed cytotoxic activity against five human cancer cell lines (A549, T24, Huh-7, 8505, and SNU-1), with IC(50) values ranging from 1.32 +/- 0.14 to 46.34 +/- 2.74 muM. Overall, our findings suggest that compounds 1 and 3 may be potential anti-cancer therapeutics and thus warrant further study.
Standardised Ethanol Extract of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) A Gray Leaves Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Increase Mitochondrial DNA Copy Numbers in Skeletal Muscles of Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Rats.[Pubmed:35846491]
Malays J Med Sci. 2022 Jun;29(3):43-53.
BACKGROUND: In this study, we examined the anti-diabetic activity of standardised extracts of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) A Gray (T. diversifolia) leaves for their effects on insulin resistance and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number. METHODS: T. diversifolia leaves were extracted using an ultrasound-assisted method and standardised using Tagitinin C. There were six groups: i) normal control; ii) diabetic group; iii) metformin group (300 mg/kg) and iv) groups treated with three different doses of extract (50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg and 150 mg/kg). Blood samples were taken before and after 28 days of treatment for fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and insulin analysis, which were used for a Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) calculation. The soleus and gastrocnemius muscles were harvested after 28 days of treatment for the measurement of mtDNA copy number. RESULTS: The results showed an improvement in blood glucose levels and HOMA-IR scores in all treatment groups. The results of mtDNA copy number analysis also revealed significant improvement with the highest number observed at an extract dose of 100 mg/kg in which the mtDNA copy number increased up to 3 times in the soleus muscles (P < 0.001). CONCLUSION: T. diversifolia extract has the potential to be used as an anti-diabetic agent that improves insulin resistance, possibly by increasing mtDNA content.
Identification of 1beta,2alpha-epoxytagitinin C as a Notch inhibitor, oxidative stress mechanism and its anti-leukemia activity.[Pubmed:34779991]
J Nat Med. 2022 Jan;76(1):234-243.
Notch signaling plays crucial roles in cell differentiation and proliferation, but aberrant activation of this signaling results in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Notch signaling is thus a promising drug target for oncotherapy, and the development of Notch signaling inhibitors is eagerly awaited. Notch inhibitory activity-guided fractionation of a Spilanthes acmella extract led to the identification of five sesquiterpene lactones: tagitinin A (1), 1beta,2alpha-epoxyTagitinin C (2), Tagitinin C (3), orizabin (4), and 2alpha-hydroxytirotundin (5). 1beta,2alpha-EpoxyTagitinin C (2) exhibited Notch signaling inhibition, with an IC(50) of 25.6 muM, and was further evaluated for its activity against HPB-ALL, a Notch-activated leukemia cell line. Compound 2 showed potent cytotoxicity against HPB-ALL (IC(50) 1.7 muM) and arrested the cell cycle at the G2/M phase, but did not induce apoptotic cell death. Notch inhibitory mechanism analysis suggested that compound 2 transcriptionally suppresses Notch1 mRNA. In addition, we found that oxidative stress induction is critical for Notch signaling inhibition and the cytotoxicity of compound 2. This is the first mechanism of small molecule Notch inhibition. Our results demonstrate that 1beta,2alpha-epoxyTagitinin C (2) is a potential anti-leukemia agent and further investigation of this compound is warranted.
Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells.[Pubmed:34345202]
Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jun 26;17(11):2703-2717.
Rationale: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common malignant tumor of the digestive system. However, the efficacy of surgery and chemotherapy is limited. Ferroptosis is an iron- and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent form of regulated cell death (RCD) and plays a vital role in tumor suppression. Ferroptosis inducing agents have been studied extensively as a novel promising way to fight against therapy resistant cancers. The aim of this study is to investigate the mechanism of action of Tagitinin C (TC), a natural product, as a novel ferroptosis inducer in tumor suppression. Methods: The response of CRC cells to Tagitinin C was assessed by cell viability assay, clonogenic assay, transwell migration assay, cell cycle assay and apoptosis assay. Molecular approaches including Western blot, RNA sequencing, quantitative real-time PCR and immunofluorescence were employed as well. Results: Tagitinin C, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Tithonia diversifolia, inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells including HCT116 cells, and induced an oxidative cellular microenvironment resulting in ferroptosis of HCT116 cells. Tagitinin C-induced ferroptosis was accompanied with the attenuation of glutathione (GSH) levels and increased in lipid peroxidation. Mechanistically, Tagitinin C induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and oxidative stress, thus activating nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). As a downstream gene (effector) of Nrf2, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression increased significantly with the treatment of Tagitinin C. Upregulated HO-1 led to the increase in the labile iron pool, which promoted lipid peroxidation, meanwhile Tagitinin C showed synergistic anti-tumor effect together with erastin. Conclusion: In summary, we provided the evidence that Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells and has synergistic effect together with erastin. Mechanistically, Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through ER stress-mediated activation of PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway. Tagitinin C, identified as a novel ferroptosis inducer, may be effective chemosensitizer that can expand the efficacy and range of chemotherapeutic agents.
Evaluation of Naturally Occurring HIF-1 Inhibitors for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.[Pubmed:34216084]
Chembiochem. 2021 Sep 14;22(18):2799-2804.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare and severe progressive disorder characterized by high pulmonary artery pressure. Chronic hypoxia causes a metabolic disorder and the Warburg effect in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) is a key enzyme in Warburg effect increased by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1). We constructed a cell-based luciferase assay system for HIF-1 inhibitors. Using this system, six HIF-1 inhibitors were identified. Among these inhibitors, the effect of Tagitinin C (1) on PASMC was investigated. Tagitinin C (1) clearly decreased the amount of HIF-1beta and the HIF-1 target PDK1. This result indicates that HIF-1 inhibitors effectively decrease PDK1 activity, which is a cause of the metabolic disorder and Warburg effect observed in PASMCs. Identifying naturally occurring HIF-1 inhibitors could provide novel insights into the development of PAH medications.
Sesquiterpene lactone potentiates the immunomodulatory, antiparasitic and cardioprotective effects on anti-Trypanosoma cruzi specific chemotherapy.[Pubmed:31685438]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105961.
We investigated the immunomodulatory, antiparasitic and cardioprotective effects of a sesquiterpene lactone (SL) administered alone or combined with benznidazole (Bz), in a murine model of Chagas' disease by in vitro and in vivo assays. Antiparasitic and cytotoxic potential of Tagitinin C (SL) and Bz were tested in vitro against T. cruzi epimastigotes and cardiomyocytes. Swiss mice challenged with T. cruzi were also treated for 20 days with Tagitinin C (10 mg/kg) alone and combined with Bz (100 mg/kg). Tagitinin C exhibited a higher antiparasitic (IC(50): 1.15 microM) and cytotoxic (CC(50) at 6.54 microM) potential than Bz (IC(50): 35.81 microM and CC(50:) 713.5 microM, respectively). When combined, these drugs presented an addictive interaction, determining complete suppression of parasitemia and parasitological cure in all infected mice (100%) compared to those receiving Bz alone (70%). Anti-T. cruzi immunoglobulin G, and pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha levels were reduced in animals treated with Tagitinin C combined with Bz, while IL-10 production was unaffected. Heart inflammation was undetectable in 90% of the animals receiving this combination, while only 50% of the animals receiving Bz alone showed no evidence of myocarditis. Together, our findings indicated that the combination of Tagitinin C and Bz exerts potent antiparasitic, immunomodulatory and cardioprotective effects. Due to the remarkable suppression of parasitemia and high parasitological cure, this combination was superior to Bz monotherapy, indicating a high potential for the treatment of Chagas's disease.
Fast and Efficient Method to Obtain Tagitinin F by Photocyclization of Tagitinin C.[Pubmed:31400235]
Photochem Photobiol. 2020 Jan;96(1):14-20.
There is some evidence in the literature of the photocyclization reaction of Tagitinin C (1) to Tagitinin F (2). Compound 2 has high pharmacological potential, but it is not easy to obtain, while compound 1 is easily obtained from a widespread plant, Tithonia diversifolia. Among different reaction conditions monitored, one was found that allowed the cyclization of 1 into 2 in <15 min in a photo-dependent reaction. Scaling-up the photocyclization of the pure compound 1 into 2 demonstrated 100% yield, and the isolation of 2 from a UV-irradiated extract was eight-fold higher than the quantity isolated from the non-UV-irradiated extract. We were also able to better understand the process of photoconversion and determine methods to isolate and quantify these compounds, which are known for their important antitumoral activities among other important pharmacological properties.
Encapsulation of tagitinin C in liposomes coated by Tithonia diversifolia pectin.[Pubmed:30784339]
J Microencapsul. 2019 Jan;36(1):53-61.
Tagitinin C, a sesquiterpene lactone compound from Tithonia diversifolia, is known to have various bioactivities including anticancer effects. The disadvantages of Tagitinin C which make its therapeutic application limited are low water solubility and poor stability. In this work, we encapsulated Tagitinin C in the form of liposomal nanoparticles to overcome its limitations and evaluated its anticancer activity. Liposomes were prepared using phosphatidylcholine, tween 80 and with/without T. diversifolia pectin. Tagitinin C liposomes exhibited small sizes, a range of 252-311 nm, and negative surface charges. Liposomes coated by T. diversifolia pectin resulted in a slightly slower release rate than pectin-uncoated liposomes. The cytotoxicity of Tagitinin C in pectin-coated liposomes was more pronounced than that in liposomes without pectin. Tagitinin C in liposomes showed significantly increased toxicity against human lung cancer cells LU-1 in comparison with DMSO-Tagitinin C. Therefore, Tagitinin C liposomes demonstrate significant potential as delivery systems for cancer therapy.
The antifibrotic effect of isolate tagitinin C from tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) A. Gray on keloid fibroblast cell.[Pubmed:30637049]
Pan Afr Med J. 2018 Aug 8;30:264.
INTRODUCTION: Keloids characterized by fibroblast hyperproliferation and depositions of collagen which similar to cancer cells. Tagitinin C is a class of sesquiterpene lactones (SLS) was isolated from the leaves of the moon flower Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) A. Gray. The study aim is to evaluate the effects of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia to keloid fibroblasts (KF). METHODS: Monolayer cultures of keloid fibroblast (three passages) were treated with 8 serial concentration of Tagitinin C (0.015 to 2) mug/mL during 72 and 120 hours. A positive control using mitomycin C. Cellular viabilities were measured by MTT assay. Collagen depositions were measured by Sirius Red assay for nonsoluble collagen. RESULTS: The reading of the result was conducted by ELISA reader. Data were analyzed by probit regression with SPSS 19 for Windows. The result showed that Tagitinin C can inhibit keloid fibroblasts (KF) viability with IC(50) 0.122 mug/mL (incubation 72h) and 0.039 mug/mL (120h), whereas mitomycin C IC(50) 0.120 mug/mL (72h) and IC(50) of 0.100 mug/mL (120h). At IC(50) concentration of Tagitinin C on keloid collagen deposition 53.1% (72h) and 44.3% (120h), whereas the IC(50) concentration of mitomycin C on keloid collagen deposition 60.4% (72h) and 52.1% (120h). Selectivity index Tagitinin C on normal fibroblasts (NF) is 287 for 72h incubation and 791 for 120h incubation. CONCLUSION: It can be concluded that the ability of Tagitinin C inhibits KF viability and decreasing keloid collagen deposition is consistent with the concentration (concentration-dependent) and incubation time (time-dependent). Tagitinin C has a low toxicity level on NF with high selectivity index.
Identification of tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia as antitrypanosomal compound using bioactivity-guided fractionation.[Pubmed:29146170]
Fitoterapia. 2018 Jan;124:145-151.
Tithonia diversifolia (Asteraceae), is used as traditional medicine in tropical countries for the treatment of various diseases, including malaria. Although numerous studies have assessed the antimalarial properties, nothing is known about the effect of T. diversifolia extracts on trypanosomiasis. In this study extracts of T. diversifolia aerial parts were evaluated for their bioactivity against Trypanosoma brucei. The activity was studied against bloodstream forms of T. brucei (TC221), as well as against mammalian cells (BALB/3T3 mouse fibroblasts), as a counter-screen for toxicity. Both methanolic and aqueous extracts showed significant effects with IC(50) values of 1.1 and 2.2mug/mL against T. brucei (TC221) and 5.2 and 3.7mug/mL against BALB/3T3 cells, respectively. A bioassay-guided fractionation on the methanolic extract yielded in identification of active fractions (F8 and F9) with IC(50) values of 0.41 and 0.43mug/mL, respectively, against T. brucei (TC221) and 1.4 and 1.5mug/mL, respectively, against BALB/3T3 cells,. The phytochemical composition of the extracts and the purified fractions were investigated using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and 1D and 2D NMR spectra showing the presence of sesquiterpene lactones that in turn were subjected to the isolation procedure. Tagitinin A and C were rather active but the latter presented a very strong inhibition on T. brucei (TC221) with an IC(50) value of 0.0042mug/mL. This activity was 4.5 times better than that of the reference drug suramin. The results of this study shed light on the antitrypanosomal effects of T. diversifolia extracts and highlighted Tagitinin C as one of the possible responsible for this effect. Further structure activity relationships studies on tagitinins are needed to consider this sesquiterpenes as lead compounds for the development of new antitrypanosomal drugs.
Anti-TMV activity and functional mechanisms of two sesquiterpenoids isolated from Tithonia diversifolia.[Pubmed:28755690]
Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2017 Aug;140:24-29.
Unlike chemical pesticides, antiviral plants are biodegradable, replenishable and safe. In this study, 14 sesquiterpene compounds from Tithonia diversifolia were tested for their activities against Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) using the half-leaf method. Tagitinin C (Ses-2) and 1beta-methoxydiversifolin-3-0-methyl ether (Ses-5) were found to have in vivo curative activities of 62.86% and 60.27% respectively, at concentrations of 100mug/mL, respectively. In contrast, the in vivo curative inhibition rate of control agent ningnanmycin was 52.48%. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ID-ELISA) also verified Ses-2 and Ses-5 had higher inhibition activities than the control agent ningnanmycin. Additionally, qRT-PCR showed that both Ses-2 and Ses-5 can partly inhibit the expression of CP and RdRp, two genes that play key roles in TMV infection. When TMV started to systemically spread, Ses-2 inhibited CP expression while Ses-5 inhibited RdRp expression. These results suggest that the two bio-agents have anti-TMV activities and may be used as bio-pesticides to control the plant virus.


