TetrahydropalmatineCAS# 2934-97-6 |
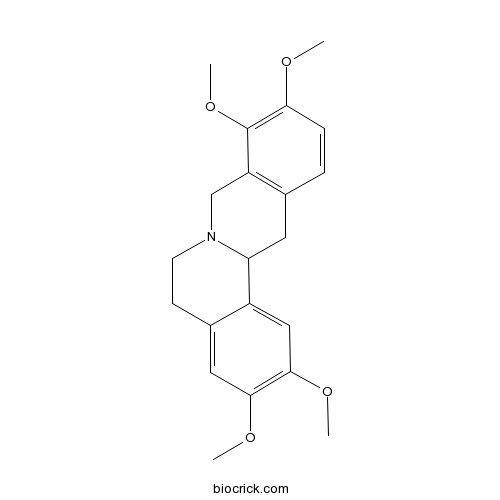
- Rotundine
Catalog No.:BCN5983
CAS No.:10097-84-4
- D-Tetrahydropalmatine
Catalog No.:BCN2334
CAS No.:3520-14-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2934-97-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5417 | Appearance | Light yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H25NO4 | M.Wt | 355.42 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | DL-Tetrahydropalmatine;Corydalis B | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 6.67 mg/mL (18.77 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5H-isoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinoline | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C2=C(CC3C4=CC(=C(C=C4CCN3C2)OC)OC)C=C1)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AEQDJSLRWYMAQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25NO4/c1-23-18-6-5-13-9-17-15-11-20(25-3)19(24-2)10-14(15)7-8-22(17)12-16(13)21(18)26-4/h5-6,10-11,17H,7-9,12H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tetrahydropalmatine, a plant alkaloid used as an ingredient in dietary supplement products, is a potent and selective D1 receptor antagonist. Tetrahydropalmatine shows a promyogenic effect by upregulation of p38MAPK, Akt resulting in enhanced MyoD activation, it can effectively protect endothelial cells against γ-irradiation injury. Tetrahydropalmatine has a potential as a therapeutic candidate to prevent fibrosis and improve muscle regeneration and repair and applied to the prevention of endothelial cell dysfunctions associated with ionizing irradiation-induced lung injury. |
| Targets | GABA receptor | p38MAPK | Akt | 5-HT Receptor | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase |
| In vitro | Protective effects of tetrahydropalmatine against gamma-radiation induced damage to human endothelial cells.[Pubmed: 20562023 ]Life Sci. 2010 Jul 3;87(1-2):55-63.Irradiation-induced damage to pulmonary endothelial cells is thought to be an important mediator of the pathogenesis of radiation pneumonopathy. Tetrahydropalmatine (THP) has been shown to have a protective effect against oxidative stress. This study was designed to investigate the potential radioprotective effect of THP against irradiation-induced endothelial cellular damage and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
|
| In vivo | L-tetrahydropalmatine inhibits methamphetamine-induced locomotor activity via regulation of 5-HT neuronal activity and dopamine D3 receptor expression.[Pubmed: 25172791]Phytomedicine. 2014 Sep 25;21(11):1287-91.Methamphetamine (METH) is a psychomotor stimulant that produces hyperlocomotion in rodents. l-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP) is an active ingredient found in Corydalis ternata which has been used as a traditional herbal preparation in Asian countries for centuries, however, the effect of l-THP on METH-induced phenotypes largely unknown.
Levo-tetrahydropalmatine inhibits cocaine's rewarding effects: experiments with self-administration and brain-stimulation reward in rats[Pubmed: 17888459 ]Neuropharmacology. 2007 Nov;53(6):771-82.It was recently reported that levo-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP), a dopamine (DA) D1 and D2 receptor antagonist purified from the Chinese herb Stephanie, appears to be effective in attenuating cocaine self-administration, cocaine-triggered reinstatement and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in preclinical animal models.
|
| Cell Research | Tetrahydropalmatine promotes myoblast differentiation through activation of p38MAPK and MyoD.[Pubmed: 25450677]Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Dec 12;455(3-4):147-52.Myoblast differentiation is fundamental to the development and regeneration of skeletal muscle after injury or disease. MyoD family transcription factors play a key role to promote myoblast differentiation.
|
| Animal Research | Antihypertensive effects of DL-tetrahydropalmatine: an active principle isolated from Corydalis.[Pubmed: 8886500]Anxiolytic-like action of orally administered dl-tetrahydropalmatine in elevated plus-maze.[Pubmed: 12921909]Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Aug;27(5):775-9.dl-Tetrahydropalmatine (dl-THP), a naturally occurring alkaloid, has been intensively studied for its sedative and hypnotic effects. Putative explanation for its mechanism and target of action involves the dopaminergic neurotransmission system.
In view of the close interactions between the dopaminergic and the GABAergic neurons in the amygdala, pharmacological effects of dl-THP were tested for activity at the GABAA receptor benzodiazepine site (BDS).
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996 Aug;23(8):738-42.1. The effects of DL-Tetrahydropalmatine (DL-THP) on cardio-vascular function and hypothalamic release of monoamines were assessed in rats under urethane anaesthesia.
|

Tetrahydropalmatine Dilution Calculator

Tetrahydropalmatine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8136 mL | 14.0679 mL | 28.1357 mL | 56.2715 mL | 70.3393 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5627 mL | 2.8136 mL | 5.6271 mL | 11.2543 mL | 14.0679 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2814 mL | 1.4068 mL | 2.8136 mL | 5.6271 mL | 7.0339 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0563 mL | 0.2814 mL | 0.5627 mL | 1.1254 mL | 1.4068 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1407 mL | 0.2814 mL | 0.5627 mL | 0.7034 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Tetrahydropalmatine, an active component isolated from corydalis, acts through inhibition of amygdaloid release of dopamine to inhibit an epileptic attack in rats.
In Vivo:Tetrahydropalmatine (THP), an active component isolated from corydalis (a Chinese herbal medicine), possesses analgesic effects. Picrotoxin treatment alone has a significant effect on the following activity measure: there is an increase in horizontal motion time (HMT), vertical motion time (VMT), clockwise turnings (CT), anticlockwise turning (ACT) and a decrease in freezing time (FT). Tetrahydropalmatine treatment alone causes a decrease in HMT, VMT and total distance traveled (TDT), but an increase in FT. Pretreatment of rats with an i.p. dose of 10 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg of Tetrahydropalmatine significantly attenuates the Picrotoxin-induced enhancement in HMT, VMT, CT, ACT and TDT, as well as reduction in FT. Another 48 rats under urethane anesthesia are randomly divided into six groups, each of eight rats. The s.c. injection of Picrotoxin causes an increase in amygdaloid release of dopamine (DA), while i.p. injection of Tetrahydropalmatine at 10 mg/kg has an insignificant effect on amygdaloid release of DA. Again, the Picrotoxin-induced increase in amygdaloid release of DA is significantly attenuated by pretreatment with Tetrahydropalmatine. The Picrotoxin-induced augmented amygdaloid release of DA is almost completely abolished by pretreatment with Tetrahydropalmatine 30 min before s.c. injection of Picrotoxin[1].
References:
[1]. Chang CK, et al. DL-Tetrahydropalmatine may act through inhibition of amygdaloid release of dopamine to inhibit an epileptic attack in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2001 Jul 20;307(3):163-6.
- Licarbazepine
Catalog No.:BCC7794
CAS No.:29331-92-8
- Genipin-1-O-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN5349
CAS No.:29307-60-6
- Deoxyelephantopin
Catalog No.:BCN4655
CAS No.:29307-03-7
- L-685,458
Catalog No.:BCC2344
CAS No.:292632-98-5
- 25,26-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
Catalog No.:BCC4201
CAS No.:29261-12-9
- SB-3CT
Catalog No.:BCC5486
CAS No.:292605-14-2
- Dehydrotrametenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2718
CAS No.:29220-16-4
- L-Kynurenine
Catalog No.:BCC3899
CAS No.:2922-83-0
- H-DL-Phe(4-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3279
CAS No.:2922-40-9
- Adenine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4453
CAS No.:2922-28-3
- Methylprednisolone hemisuccinate
Catalog No.:BCC9044
CAS No.:2921-57-5
- 3',6'-Bis(diethylamino)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)spiro[isoindole-1,9'-xanthene]-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8597
CAS No.:29199-09-5
- Ciclopirox
Catalog No.:BCC4899
CAS No.:29342-05-0
- Olean-12-ene-3,11-dione
Catalog No.:BCN5195
CAS No.:2935-32-2
- H-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3310
CAS No.:2935-35-5
- SR3335
Catalog No.:BCC1964
CAS No.:293753-05-6
- T0901317
Catalog No.:BCC1178
CAS No.:293754-55-9
- Thevetiaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4024
CAS No.:29376-68-9
- Ro 90-7501
Catalog No.:BCC7351
CAS No.:293762-45-5
- Anhydrosecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7521
CAS No.:29388-33-8
- Secoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5196
CAS No.:29388-59-8
- Cyclen
Catalog No.:BCN8441
CAS No.:294-90-6
- 7-Nitroindazole
Catalog No.:BCC6713
CAS No.:2942-42-9
- 4',7-Di-O-methylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN5197
CAS No.:29424-96-2
L-tetrahydropalmatine inhibits methamphetamine-induced locomotor activity via regulation of 5-HT neuronal activity and dopamine D3 receptor expression.[Pubmed:25172791]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Sep 25;21(11):1287-91.
Methamphetamine (METH) is a psychomotor stimulant that produces hyperlocomotion in rodents. l-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP) is an active ingredient found in Corydalis ternata which has been used as a traditional herbal preparation in Asian countries for centuries, however, the effect of l-THP on METH-induced phenotypes largely unknown. In this study, to evaluate the effect of l-THP on METH-induced psychotropic effects, rats were pretreated with l-THP (10 and 15 mg/kg) before acute METH injection, following which the total distance the rats moved in an hour was measured. To clarify a possible mechanism underlying the effect of l-THP on METH-induced behavioral changes, dopamine receptor mRNA expression levels in the striatum of the rats was measured following the locomotor activity study. In addition, the effect of l-THP (10 and 15 mg/kg) on serotonergic (5-HTergic) neuronal pathway activation was studied by measurement of 5-HT (80 mug/10mul/mouse)-induced head twitch response (HTR) in mice. l-THP administration significantly inhibited both hyperlocomotion in rats and HTR in mice. l-THP inhibited climbing behavior-induced by dopaminergic (DAergic) neuronal activation in mice. Furthermore, l-THP attenuated the decrease in dopamine D3 receptor mRNA expression levels in the striatum of the rats induced by METH. These results suggest that l-THP can ameliorate behavioral phenotype induced by METH through regulation of 5-HT neuronal activity and dopamine D3 receptor expression.
Anxiolytic-like action of orally administered dl-tetrahydropalmatine in elevated plus-maze.[Pubmed:12921909]
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Aug;27(5):775-9.
dl-Tetrahydropalmatine (dl-THP), a naturally occurring alkaloid, has been intensively studied for its sedative and hypnotic effects. Putative explanation for its mechanism and target of action involves the dopaminergic neurotransmission system. In view of the close interactions between the dopaminergic and the GABAergic neurons in the amygdala, pharmacological effects of dl-THP were tested for activity at the GABAA receptor benzodiazepine site (BDS). Effects of dl-THP were examined in mice employing the elevated plus-maze, the holeboard and the horizontal-wire tests. In the elevated plus-maze, mice treated with low doses of dl-THP (0.5-10 mg/kg) exhibited significant increase in the percentage of entries and time spent in open arms without altering the number of closed-arm entries when compared to the control group, indicative of its selective anxiolytic effect. In the holeboard and horizontal wire tests, where exploratory behavior and potential muscle relaxant effect were assessed, respectively, only mice treated with as much as 50 mg/kg dl-THP manifested sedation and myorelaxation, as observed in the significant decrease in the number of head dips and the decrease in the percentage of mice grasping wire in comparison to control. Notably, coadministration of the BDS antagonist flumazenil abolished the dl-THP-induced anxiolysis as seen in the reversal of the increase of both the number of entries and time spent in open arms back to basal levels in the elevated plus-maze test. The results suggest that dl-THP at defined low dosages acts as anxiolytics in mice, and the BDS mediates, at least in part, such anxiolytic effect of dl-THP.
Antihypertensive effects of DL-tetrahydropalmatine: an active principle isolated from Corydalis.[Pubmed:8886500]
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996 Aug;23(8):738-42.
1. The effects of DL-Tetrahydropalmatine (DL-THP) on cardio-vascular function and hypothalamic release of monoamines were assessed in rats under urethane anaesthesia. 2. Intravenous administration of DL-THP (1-10 mg/kg) produced hypotension, bradycardia, a decrease in hypothalamic serotonin and noradrenaline release and an increase in hypothalamic dopamine release in rats. 3. Intrahypothalamic administration of DOI (a serotonergic 5-HT2 receptor antagonist) or apomorphine (a dopamine D2-receptor agonist) produced the opposite effects and reversed DL-THP-induced hypotension and bradycardia. 4. The data suggest that DL-THP acts through the 5-HT2 and/or D2-receptor antagonism in the hypothalamus to induce hypotension and bradycardia in rats.
Levo-tetrahydropalmatine inhibits cocaine's rewarding effects: experiments with self-administration and brain-stimulation reward in rats.[Pubmed:17888459]
Neuropharmacology. 2007 Nov;53(6):771-82.
It was recently reported that levo-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP), a dopamine (DA) D1 and D2 receptor antagonist purified from the Chinese herb Stephanie, appears to be effective in attenuating cocaine self-administration, cocaine-triggered reinstatement and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in preclinical animal models. The present study was designed to contrast l-THP's effects on cocaine self-administration under fixed-ratio (FR) and progressive-ratio (PR) reinforcement, and to study l-THP's effects on cocaine-enhanced brain stimulation reward (BSR). Systemic administration of l-THP produced dose-dependent, biphasic effects, i.e., low-to-moderate doses (1, 3, 10 mg/kg) increased, while a high dose (20 mg/kg) inhibited cocaine self-administration behavior under FR2 reinforcement. The increased cocaine self-administration is likely a compensatory response to a reduction in cocaine's rewarding effects, because the same low doses of l-THP dose-dependently attenuated cocaine self-administration under PR reinforcement and also attenuated cocaine-enhanced BSR. These attenuations of PR cocaine self-administration and cocaine-enhanced BSR are unlikely due to l-THP-induced sedation or locomotor inhibition, because only 10 mg/kg, but not 1-3 mg/kg, of l-THP inhibited locomotion, sucrose self-administration and asymptotic operant performance in the BSR paradigm. In vivo microdialysis demonstrated that l-THP slightly elevates extracellular nucleus accumbens DA by itself, but dose-dependently potentiates cocaine-augmented DA, suggesting that a postsynaptic, rather than presynaptic, DA receptor antagonism underlies l-THP's actions on cocaine reward. Together, the present data, combined with previous findings, support the potential use of l-THP for treatment of cocaine addiction.
Tetrahydropalmatine promotes myoblast differentiation through activation of p38MAPK and MyoD.[Pubmed:25450677]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Dec 12;455(3-4):147-52.
Myoblast differentiation is fundamental to the development and regeneration of skeletal muscle after injury or disease. MyoD family transcription factors play a key role to promote myoblast differentiation. In a screen for MyoD activators, we identified Tetrahydropalmatine (THP), a natural compound isolated from Corydalis turtschaninovii. The treatment of C2C12 myoblasts with THP enhanced the level of MyoD, Myogenin and myosin heavy chain (MHC) proteins and the formation of larger multinucleated myotubes, compared to the control treatment. The THP treatment dramatically enhanced the activities of p38MAPK and Akt, the key promyogenic kinases which activate MyoD. The enhanced myoblast differentiation by THP treatment can be blocked by inhibition of p38MAPK or Akt by SB203580 or LY294002, respectively. In addition, THP treatment restored myotube formation of Cdo-depleted C2C12 cells through activation of p38MAPK. Moreover, THP enhanced the efficiency of trans-differentiation of 10T1/2 fibroblasts into myoblasts mediated by MyoD. These results indicate that THP has a promyogenic effect by upregulation of p38MAPK and Akt resulting in enhanced MyoD activation. Our findings suggest that THP has a potential as a therapeutic candidate to prevent fibrosis and improve muscle regeneration and repair.
Protective effects of tetrahydropalmatine against gamma-radiation induced damage to human endothelial cells.[Pubmed:20562023]
Life Sci. 2010 Jul 3;87(1-2):55-63.
AIMS: Irradiation-induced damage to pulmonary endothelial cells is thought to be an important mediator of the pathogenesis of radiation pneumonopathy. Tetrahydropalmatine (THP) has been shown to have a protective effect against oxidative stress. This study was designed to investigate the potential radioprotective effect of THP against irradiation-induced endothelial cellular damage and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. MAIN METHODS: Human EA.hy926 cells were treated with THP and irradiation. Cell viability was measured using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For the detection of apoptosis, morphological observation, flow cytometry and a caspase-3 activity assay were employed. The expression of cytochrome-c and Bax/Bcl-2 protein were detected by western blot analysis. Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was measured by flow cytometry. Malondialdehyde (MDA), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured to assess cellular oxidative stress induced injury. KEY FINDINGS: Preincubation of EA.hy926 cells with THP before gamma-radiation resulted in significant inhibition of apoptosis and enhancement of cell viability, as revealed by morphological observation, flow cytometry and MTT assay. THP significantly reduced intracellular ROS formation, levels of intracellular MDA and LDH, and enhanced the production of intracellular antioxidants (GSH and SOD) in EA.hy926 cells. Meanwhile, THP also inhibited the decrease of intracellular mitochondrial membrane potential (psim), caspase-3 activation, cytochrome-c release and reduced Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in THP pretreated, irradiated cells. SIGNIFICANCE: Our findings demonstrated THP could effectively protect endothelial cells against gamma-irradiation injury, which could potentially be applied to the prevention of endothelial cell dysfunctions associated with ionizing irradiation-induced lung injury.


