TopiramateGluR5 receptor antagonist,anticonvulsant CAS# 97240-79-4 |
- Dorzolamide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2311
CAS No.:130693-82-2
- Brinzolamide
Catalog No.:BCC2313
CAS No.:138890-62-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 97240-79-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5284627 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H21NO8S | M.Wt | 339.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Topamax | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (294.67 mM) H2O : 4 mg/mL (11.79 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
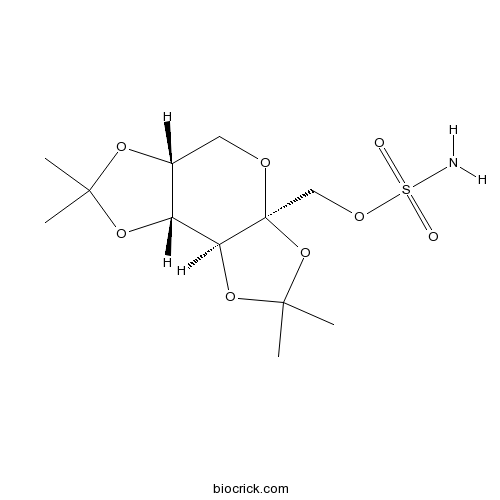
| Chemical Name | [(3aS,5aR,8aR,8bS)-2,2,7,7-tetramethyl-5,5a,8a,8b-tetrahydrodi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-a:5',3'-d]pyran-3a-yl]methyl sulfamate | ||
| SMILES | CC1(OC2COC3(C(C2O1)OC(O3)(C)C)COS(=O)(=O)N)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KJADKKWYZYXHBB-XBWDGYHZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H21NO8S/c1-10(2)18-7-5-16-12(6-17-22(13,14)15)9(8(7)19-10)20-11(3,4)21-12/h7-9H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H2,13,14,15)/t7-,8-,9+,12+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Anticonvulsant. Antagonizes GluR5 kainate receptors (IC50 = 0.46 μM), acts as a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptor-mediated currents, inhibits Nav channels (IC50 = 48.9 μM) and inhibits L-type Ca2+ channels. Also inhibits carbonic anhydrase (CA) (Ki values are 0.1 and 0.2 μM at rat CA II and CA IV respectively), which lowers intracellular neuronal pH. |

Topiramate Dilution Calculator

Topiramate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9467 mL | 14.7336 mL | 29.4672 mL | 58.9345 mL | 73.6681 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5893 mL | 2.9467 mL | 5.8934 mL | 11.7869 mL | 14.7336 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2947 mL | 1.4734 mL | 2.9467 mL | 5.8934 mL | 7.3668 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0589 mL | 0.2947 mL | 0.5893 mL | 1.1787 mL | 1.4734 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0295 mL | 0.1473 mL | 0.2947 mL | 0.5893 mL | 0.7367 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant compound.
- Picfeltarraenin IA
Catalog No.:BCN1041
CAS No.:97230-47-2
- Picfeltarraenin IB
Catalog No.:BCN2845
CAS No.:97230-46-1
- Eriobofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7436
CAS No.:97218-06-9
- Meisoindigo
Catalog No.:BCC5132
CAS No.:97207-47-1
- 3-Ethoxyandrosta-3,5-dien-17-one
Catalog No.:BCC8630
CAS No.:972-46-3
- 6-Epi-8-O-acetylharpagide
Catalog No.:BCN4550
CAS No.:97169-44-3
- 6-Geranylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN3001
CAS No.:97126-57-3
- AMN 082 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7344
CAS No.:97075-46-2
- Porfimer Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5353
CAS No.:97067-70-4
- (-)-Epigallocatechin(EGC)
Catalog No.:BCN4519
CAS No.:970-74-1
- (+)-Gallocatechin
Catalog No.:BCN5928
CAS No.:970-73-0
- Disulfiram
Catalog No.:BCC2098
CAS No.:97-77-8
- Troglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC2016
CAS No.:97322-87-7
- 8-Hydroxy-4-cadinen-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4520
CAS No.:97372-53-7
- 3alpha-Hydroxytanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN2496
CAS No.:97399-71-8
- Aristolactam AIa
Catalog No.:BCN4854
CAS No.:97399-90-1
- Aristolactam AIIIa
Catalog No.:BCN4521
CAS No.:97399-91-2
- Paniculidine A
Catalog No.:BCN4522
CAS No.:97399-93-4
- Paniculidine B
Catalog No.:BCN4523
CAS No.:97399-94-5
- Paniculidine C
Catalog No.:BCN4524
CAS No.:97399-95-6
- Cynatratoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7087
CAS No.:97399-96-7
- Tanshindiol A
Catalog No.:BCN3123
CAS No.:97411-46-6
- 2',3'-Dehydrosalannol
Catalog No.:BCN4549
CAS No.:97411-50-2
- (-)-Mandelic acid benzyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8374
CAS No.:97415-09-3
Levetiracetam and topiramate poisoning: Two overdoses on those drugs with no lasting effects.[Pubmed:28320983]
Drug Discov Ther. 2017 May 30;11(2):115-117.
Levetiracetam and Topiramate are newer anticonvulsants, which is why international data on overdoses of these drugs are lacking. Only a few mild adverse reactions have been noted. These anticonvulsants have been the drug of choice for neurologists. Despite their wide usage, there is a dearth of literature on symptoms and signs of their toxicity. Presented here is the case of a 21-year-old female who overdosed twice on levetiracetam and Topiramate. The woman was admitted and discharged after the first overdose. Ten days later, she took multiple tablets of both drugs and was seen again. Amazingly, the woman went home after the incident with no complications at all.
Topiramate modulates post-infarction inflammation primarily by targeting monocytes or macrophages.[Pubmed:28339742]
Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Apr 1;113(5):475-487.
Aims: Monocytes/macrophages response plays a key role in post-infarction inflammation that contributes greatly to post-infarction ventricular remodelling and cardiac rupture. Therapeutic targeting of the GABAA receptor, which is enriched in monocytes/macrophages but not expressed in the myocardium, may be possible after myocardial infarction (MI). Methods and results: After MI was induced by ligation of the coronary artery, C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally administered with one specific agonist or antagonist of the GABAA receptor (Topiramate or bicuculline), in the setting of presence or depletion of monocytes/macrophages. Our data showed that within the first 2 weeks after MI, when monocytes/macrophages dominated, in contrast with bicuculline, Topiramate treatment significantly reduced Ly-6Chigh monocyte numbers by regulating splenic monocytopoiesis and promoted foetal derived macrophages preservation and conversion of M1 to M2 or Ly-6Chigh to Ly-6Clow macrophage phenotype in the infarcted heart, though GABAAergic drugs failed to affect M1/M2 or Ly-6Chigh/Ly-6Clow macrophage polarization directly. Accordingly, pro-inflammatory activities mediated by M1 or Ly-6Chigh macrophages were decreased and reparative processes mediated by M2 or Ly-6Clow macrophages were augmented. As a result, post-infarction ventricular remodelling was attenuated, as reflected by reduced infarct size and increased collagen density within infarcts. Echocardiographic indices, mortality and rupture rates were reduced. After depletion of monocytes/macrophages by clodronate liposomes, GABAAergic drugs exhibited no effect on cardiac dysfunction and surrogate clinical outcomes. Conclusion: Control of the GABAA receptor activity in monocytes/macrophages can potently modulate post-infarction inflammation. Topiramate emerges as a promising drug, which may be feasible to translate for MI therapy in the future.
Effect of topiramate on choroidal thickness and anterior chamber parameters in the treatment of patients with migraine.[Pubmed:28351170]
Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017 Dec;36(4):381-386.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of Topiramate on choroidal thickness and anterior chamber parameters using optical coherence tomography in the treatment of patients with migraine. METHODS: A total of 22 eyes of 22 adults (12 females, 10 males) diagnosed with migraine and scheduled to Topiramate treatment for pain control were recruited in this prospective study. Choroidal thickness (CT), anterior chamber depth (ACD), anterior chamber angle (ACA), spherical refractive equivalent (SphEq) and intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements were recorded at baseline (prior the Topiramate therapy), first and second month visits for the statistical analysis. One-way ANOVA with repeated measures test was used for the statistical evaluation. RESULTS: Mean age of the patients was 40.2 +/- 6.5 years. Mean CT at central fovea was 324 +/- 47 mum initially, 341 +/- 45 mum in the first month and 344 +/- 46 mum in the second month, thus first and second month measures were significantly higher than base values (p < 0.001). There was also a slight increase in IOP values among baseline (15.5 +/- 2.4 mmHg) and follow-up visits (17.5 +/- 2.6 mmHg, 19.0 +/- 3.3 mmHg, respectively, ` p = 0.001). Baseline ACD (3.66 +/- 0.22 mm) measures significantly decreased at the first month (3.63 +/- 0.22 mm) and second month (3.62 +/- 0.22 mm, p = 0.009). Also, a significant reduction was detected in the first (36.2 +/- 4.9 degrees ) and second month (35.9 +/- 5.1 degrees ) ACA measures comparing with baseline (39.1 +/- 5.1 degrees , p = 0.05). A significant myopic shift was determined in the first and second month SphEq values (-0.08 +/- 0.6, -0.10 +/- 0.6, respectively, p = 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: The study revealed increased CT and altered anterior chamber parameters and IOP due to Topiramate therapy. Therefore, the patients using Topiramate should be carefully monitored by an ophthalmologist considering the possible side effects.
Topiramate selectively protects against seizures induced by ATPA, a GluR5 kainate receptor agonist.[Pubmed:15111016]
Neuropharmacology. 2004 Jun;46(8):1097-104.
Although the mechanism of action of Topiramate is not fully understood, its anticonvulsant properties may result, at least in part, from an interaction with AMPA/kainate receptors. We have recently shown that Topiramate selectively inhibits postsynaptic responses mediated by GluR5 kainate receptors. To determine if this action of Topiramate is relevant to the anticonvulsant effects of the drug in vivo, we determined the protective activity of Topiramate against seizures induced by intravenous infusion of various ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists in mice. Topiramate (25-100 mg/kg, i.p.) produced a dose-dependent elevation in the threshold for clonic seizures induced by infusion of ATPA, a selective agonist of GluR5 kainate receptors. Topiramate was less effective in protecting against clonic seizures induced by kainate, a mixed agonist of AMPA and kainate receptors. Topiramate did not affect clonic seizures induced by AMPA or NMDA. In contrast, the thresholds for tonic seizures induced by higher doses of these various glutamate receptor agonists were all elevated by Topiramate. Unlike Topiramate, carbamazepine elevated the threshold for AMPA- but not ATPA-induced clonic seizures. Our results are consistent with the possibility that the effects of Topiramate on clonic seizure activity are due to functional blockade of GluR5 kainate receptors. Protection from tonic seizures may be mediated by other actions of the drug. Together with our in vitro cellular electrophysiological results, the present observations strongly support a unique mechanism of action of Topiramate, which involves GluR5 kainate receptors.
Selective antagonism of GluR5 kainate-receptor-mediated synaptic currents by topiramate in rat basolateral amygdala neurons.[Pubmed:12904467]
J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 6;23(18):7069-74.
Topiramate is a widely used antiepileptic agent whose mechanism of action is poorly understood. The drug has been reported to interact with various ion channel types, including AMPA/kainate receptors. In whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from principal neurons of the rat basolateral amygdala, Topiramate at low concentrations (IC50, approximately 0.5 microm) selectively inhibited pharmacologically isolated excitatory synaptic currents mediated by kainate receptors containing the GluR5 subunit. Topiramate also partially depressed predominantly AMPA-receptor-mediated EPSCs, but with lower efficacy. Topiramate did not alter the degree of facilitation in paired-pulse experiments, and it reduced the amplitude of miniature EPSCs without affecting their frequency, demonstrating that the block of synaptic responses occurs postsynaptically. Inhibition of GluR5 kainate receptors could represent a key mechanism underlying the anticonvulsant activity of Topiramate. Moreover, these results support the concept that GluR5 kainate receptors represent a novel target for antiepileptic drug development.
Topiramate as an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes.[Pubmed:10768298]
Epilepsia. 2000;41 Suppl 1:S35-9.
PURPOSE: This study investigated the effectiveness of Topiramate (TPM) as an inhibitor of six isozymes of carbonic anhydrase (CA). METHODS: The inhibition constants (Ki) of TPM and acetazolamide (AZM) for CA I, CA II, CA III, CA IV, CA V, and CA VI were determined for human (HCA), rat (RCA), or mouse (MCA). The activity of CA was studied by using purified isozymes, erythrocytes, subcellular fractions of kidney or brain, and saliva, and was assayed at 37 degrees C or 25 degrees C by 18O mass spectrometry and/or by measuring the pH shift at 0 degrees C. RESULTS: Topiramate Ki values for HCA I, HCA II, HCA IV, and HCA VI were approximately 100, 7, 10, and >100 microM, respectively. TPM Ki values for RCA I, RCA II, RCA III, RCA IV, and RCA V were approximately 180, 0.1 to 1, >100, 0.2 to 10 and 18 microM, respectively. For RCA II and RCA IV, the Ki values were temperature dependent. TPM Ki values for MCA II and MCA IV ranged between 1 and 20 microM. CONCLUSIONS: These results indicate that TPM is more potent as an inhibitor of CA II and CA IV than of CA I, CA III, and CA VI. In all three species, AZM was usually 10 to 100 times more potent than TPM as an inhibitor of CA isozymes.
Topiramate attenuates voltage-gated sodium currents in rat cerebellar granule cells.[Pubmed:9300637]
Neurosci Lett. 1997 Aug 15;231(3):123-6.
Whole-cell, voltage-clamp recordings were made from rat cerebellar granule cells in culture under experimental conditions designed to study voltage-gated Na+ currents that were elicited by depolarizing commands from a holding potential of -60 mV up to +20 mV. These tetrodotoxin-sensitive inward currents were reduced in a dose-related manner by bath application of the structurally novel, anticonvulsant drug Topiramate (10-1000 microM; n = 16). Dose-response analysis of this effect revealed an IC50 of 48.9 microM. Topiramate also made the steady-state inactivation curve of this current shift toward more negative values (midpoint of the inactivation curve -46.9 mV under control conditions and -56.5 mV during Topiramate application; n = 5). We propose that these effects may contribute to control the sustained depolarizations with repetitive firing of action potentials that occur within neuronal networks during seizure activity. Therefore they may represent a mechanism of action for this novel anticonvulsant drug.


